Bio-inspired photonics
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min

Bio-inspired photonics or bio-inspired optical materials are the application of biomimicry (the use of natural models, systems, and elements for human innovations[1]) to the field of photonics (the science and application of light generation, detection, and manipulation[2]). This differs slightly from biophotonics which is the study and manipulation of light to observe its interactions with biology.[3] One area that inspiration may be drawn from is structural color, which allows color to appear as a result of the detailed material structure.[4] Other inspiration can be drawn from both static and dynamic camouflage in animals like the chameleon[5] or some cephalopods.[6] Scientists have also been looking to recreate the ability to absorb light using molecules from various plants and microorganisms.[7] Pulling from these heavily evolved constructs allows engineers to improve and optimize existing photonic technologies, whilst also solving existing problems within this field.
History

One of the earliest encounters with biological photonics was as early as the 6th century B.C.E (before common era). The Greek philosopher Anaximander, widely regarded as the first scientist, had a student named Anaximenes, who had the first documented mention of bioluminescence.[8][9] He described seeing a glow in the water when striking it with an oar.[10] Similarly, Aristotle also experienced the same phenomena, which he documented in works like Meteorologica[11] and De Coloribus.[12] He mentions seeing "things which are neither fire nor forms of fire seem to produce light by nature.[12]"
Although it was experienced that early, there was still no explanation to why it was occurring. It was not until the early microscopes, utilized by Robert Hooke in the mid-1600s,[13] that allowed humans to observe nature in greater detail. Hooke himself published what he had seen in the text Micrographia in 1665.[14] Here he describes various biological structures such as the feathers of colorful birds, wing and eyes of flies, and pearlescent scales of silverfish. This ability to look at the microstructures of nature, gave scientists information on the mechanisms behind the interactions between biology and light. The Theorie of Imperfection, published by the Russian biophysicist Zhuralev and American biochemist Seliger, is the first working hypothesis about the ultra-weak emission of photons by biological systems.[15] Further developments in microscopy, like scanning electron microscopy (SEM),[16] only increased this and would allow scientists to mimic these observed structures.
In addition, the concept of biomimicry was spurred by many scientists, including Leonardo da Vinci. He spent a great deal of time studying the anatomy of birds and their flight capabilities. As demonstrated by various sketches and notes he left behind, he even attempted to create a "flying machine".[17] Although unsuccessful, it was one of the earliest examples of biomimicry.

Molecular biomimetics
Molecular biomimetics involves the design of optical materials based on specific molecules and/or macromolecules to induce coloration.[18] Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) are specifically aimed at sensing macromolecules.[19] They can also form them into specific structures that change color.[20] Pigment-inspired materials aiming for specific molecular light absorption have been developed as for example melanin-inspired films prepared by polymerization of melanin precursors such as dopamine and 5,6-dihydroxyindole to provoke color saturation.[21][22][23] Polydopamine is a synthetic polymer with color properties similar to melanin.[24] It can also act to enhance the vibrancy and stability of structural colors.[20] Materials based on the multi-layer stacking of guanine molecular crystals found in living organisms (e.g. fish[25] and chameleons[26]) have been proposed as potential reflective coatings and solar reflectors. Protein-based optical materials, for instance self-assembling reflectin proteins found in cephalopods [27][28] and silk,[29] have incited interest in artificial materials for camouflage systems,[30] electronic paper (e-paper)[31] and biomedical applications.[32] Non-protein biological macromolecules such as DNA have also been utilized for bio-inspired optics.[33] The most abundant biopolymer on earth, cellulose, has been also utilized as a principal component for bio-optics.[34][18] Modification of wood or other cellulose sources can mitigate scattering and absorption of light leading to optically interesting materials such as transparent wood and paper.[35][36] Pressure and solvent polarity affect the color of a manufactured cellulose membrane, to the point of detection by the naked eye. Cellulose can also be used as nanofibrils or nanocrystals after treatments. One such treatment involves a nitrating agent to form nitrocellulose.[20] Cellulose nanocrystals can polarize light.[37]
Bioinspired periodic/aperiodic structures
Structural color is a type of coloration that arises from the interaction of light with nano-sized structures.[38] This interaction is possible because these photonic structures are of the same size as the wavelength of light. Through a mechanism of constructive and destructive interference, certain colors get amplified, while others diminish.
Photonic structures are abundant in nature, existing in a wide range of organisms. Different organisms use different structures, each with a different morphology designed to obtain the desired effect. Examples of this are the photonic crystal underlying the bright colors in peacock feathers[39] or the tree-like structures responsible for the bright blue in some Morpho butterflies.[40]
An example of bio-inspired photonics using structures is the so-called moth eye. Moths have a structure of ordered cylinders in their eyes that do not produce color, but instead reduce reflectivity.[41] This concept has led to creation of antireflective coatings.[42]
A combination of chemical structure and how it interacts with visible light creates color within organisms' nature.[4] The creation of specific biological photonics requires identifying the chemical components of the structure, the optical response created by the physics and the structure's function.[20] The complex structures created by nature can range from simple, quasi-ordered structures to hierarchical complex formations.[4]
2-D Structures
Simple Array Structure (Peacock Feathers)
Nature sometimes manipulates the nanostructure, such as its crystal lattice parameters in order to create its patterns and colors.[20][43][44][45][46] The Barbule (the individual strands of a feather that hold its color) of the peacock is made of an outer layer of keratin and an inner layer containing an array of melanin rods connected by keratin with holes separating them. When the melanin rods are parallel to the lattice arrangement of the structure of the keratin outer layer it creates the brown color. The rest of the colors of the feather are created by changing the spacing of the melanin layers.[20][47][48][49]
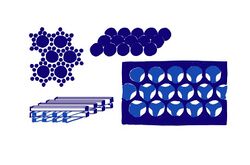
Aperiodic Photonic Structures
Aperiodic Photonic Structures do not have a unit cell and are capable of creating band gaps without the requirement of a high index of refraction difference. Also known as quasi-ordered crystal structure creates blue and green coloring.[20]
3-D Structures
Helicoidal Multilayers
These are twisted multilayers where fibers are aligned in the same direction and each layer they are slightly rotated.[50][51] This structure allows nature to reflect polarized light and creates an intense value due to Bragg reflection.[4][20][51]
Application Examples
Bioinspired antibacterial structural color hydrogel
As a form of application, biophotonics are used in order to indicate antibacterial and self-healing properties. Since the existence of silver nanoparticles prevent bacterial adhesion (there is already bacteria existing in the hydrogel) it causes hydrogel degradation and color fading. This allows for the engineered hydrogel to display with color its integrity after self-healing.[4][52]
Photonic nanoarchitectures in butterflies and beetles
Nanoarchitectures contribute to the iridescence of butterflies and beetles. Multilayers are common, typically in a 1-D or 3-D structure, 2-D structures are more rare.[53] Disorder and irregularity in the structure are “intentional” and adapted to the habitat. The structure has been successfully recreated and can be used as a coating.[54] It is also used in some applications where stable, vibrant color is required. It is flexible enough that it can be designed to have a pattern.[55]
Mimicking fireflies to improve LED efficiency
When observing fireflies (Photuris sp.) using SEM, it was observed that their light emitting cuticle had a specific 2D periodic structure. It is structured following a “factory roof” like pattern with scales oriented at a tilted slope and a sharp edge on the protruding side of the scales.[56][57] When modeling a similar structure using a photoresist layer on light emitting diodes (LEDs), it resulted in a 68% power increase and 55% increase in light extraction efficiency (LEE). This technology reduces the amount of energy consumed to produce the same amount of light.[58]
Responsive materials
Responsive materials are materials or devices that can respond to external stimuli as they occur. A little bit of time is taken to adjust to the new surroundings, but the idea remains consistent with what is seen in nature. The most commonly used examples are the chameleon or octopus, as their responsive skin allows them to change the color or even the texture of their skin.[59] The mechanisms behind these tactics are called chromatophores, which are pigment-filled sacs that uses muscles and nerves to change the animal's external appearance. These chromatophores are activated by neuronal activity, so an animal can change its color just by thinking about it.[60] The animal uses another mechanism to be able to know what color or shape to take; a photo-sensitive cell within their skin called opsin is able to detect light (and possibly color). The animal can use these opsins to their advantage to quickly assess their surroundings, before turning on their chromatophores to accurately camouflage to their circumstances.
A lot of creatures have camouflage incorporated into their bodies — take the fish in the figure on the right for example. In this hypothetical, the animal can appear in two different ways depending on their surroundings: in the middle of the ocean away from all solid objects, it can appear near-translucent; near the sea floor where potential predators will only sense it from above, it can turn darker to naturally blend in with the rocky bottom. Many fish, such as the marine hatchetfish, use a combination of camouflage techniques to achieve these appearances.[61] Silvering, a common tactic, utilizes highly reflective scales to reflect the surrounding light effectively enough to make the scales appear invisible from the side. Counterillumination, a tactic used more by deep-sea dwellers, uses a luminous organ located in the bottom of the body to emit light in order to appear brighter from underneath. At this angle, the light emitted is at an intensity meant to replicate the sunlight as it appears on the surface of the water. Thus, from below the creature is essentially invisible to many predators.
Within the luminous organ is a laminar structure of photocytes and nerve branches, with relatively small gap junctions between them.[62] It is thought that the vast interconnectivity and the layered structure of these neuro-photocyte units is what allows a deep-sea fish to rapidly respond to a situation with spontaneous luminescence. Because all of the nerves are directly connected to the spinal cord (and by extension, the brain), researchers believe that electronic signals can trigger these photocytes to react.[63] With this line of thinking, scientists are working to develop technology using this type of neuro-photocyte unit.
These biologically inspired materials can be applied in many different circumstances.[64] This technology can be used to camouflage objects, create a device that can mold its shape yet still retain its desired properties, or even help people in relation to biomedical applications. A coating of this technology can help incorporate a foreign body into a living ecosystem, i.e. a human body. The technology of this device allows a person's antibodies to detect the new object as a non-threat, thus permitting easier acceptance of manmade tools into the body, such as a cardiac pacing device to the chest.
References
- ↑ (in English) The brain, the nervous system, and their diseases. Bloomsbury Academic. 2015. ISBN 978-1-61069-337-0. OCLC 880809097. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/880809097.
- ↑ (in en) Photonics and Lasers: An Introduction. John Wiley & Sons. 2006-04-14. ISBN 978-0-471-79158-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=82f-gIvtC7wC.
- ↑ Handbook of biophotonics. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2011. ISBN 978-3-527-41047-7. OCLC 748773038. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/748773038.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Bioinspired Photonics : Optical Structures and Systems Inspired by Nature.. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 2015. ISBN 978-1-4665-0403-5. OCLC 963587905. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/963587905.
- ↑ "A Camouflaged Film Imitating the Chameleon Skin with Color-Changing Microfluidic Systems Based on the Color Information Identification of Background" (in en). Journal of Bionic Engineering 18 (5): 1137–1146. 2021-09-01. doi:10.1007/s42235-021-00091-y. ISSN 2543-2141.
- ↑ "Cephalopod dynamic camouflage: bridging the continuum between background matching and disruptive coloration". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 364 (1516): 429–437. February 2009. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0270. PMID 19008200.
- ↑ "Molecular factors controlling photosynthetic light harvesting by carotenoids". Accounts of Chemical Research 43 (8): 1125–1134. August 2010. doi:10.1021/ar100030m. PMID 20446691.
- ↑ Bioluminescence in focus : a collection of illuminating essays. Kerala, India: Research Signpost. 2009. ISBN 978-81-308-0357-9. OCLC 497860307. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/497860307.
- ↑ "Bioluminescence: the First 3000 Years (Review)". Journal of Siberian Federal University. Biology 1 (3): 194–205. September 2008. doi:10.17516/1997-1389-0264. http://journal.sfu-kras.ru/en/article/935.
- ↑ (in English) The cyclopedia, or, Universal dictionary of arts, sciences, and literature. Cole Collection of Chemistry. Philadelphia: Published by Samuel F. Bradford and Murray, Fairman and Co.. 1805. OCLC 18853022. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/18853022.
- ↑ On Aristotle Meteorology 1.4-9, 12. London: Bristol Classical Press. 2012. ISBN 978-1-4725-0174-5. OCLC 875239302. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/875239302.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Aristotle. "De Coloribus". https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Aristotle/de_Coloribus*.html.
- ↑ "Crafting the Microworld: How Robert Hooke Constructed Knowledge About Small Things". Notes and Records of the Royal Society of London 70 (1): 23–44. March 2016. doi:10.1098/rsnr.2015.0057. PMID 27017680.
- ↑ Micrographia: or, Some physiological descriptions of minute bodies made by magnifying glasses: With observations and inquiries thereupon. London: Printed by Jo. Martyn, and Ja. Allestry, Printers to the Royal Society, and are to be sold at their Shop at the Bell, in S. Paul's Church-yard. 1665. https://catalog.loc.gov/vwebv/search?searchCode=LCCN&searchArg=11004270&searchType=1&permalink=y.
- ↑ "Origins of biophotonics". https://q-mag.org/origins-of-biophotonics.html.
- ↑ "Optical and digital microscopic imaging techniques and applications in pathology". Analytical Cellular Pathology 34 (1–2): 5–18. 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/150563. PMID 21483100.
- ↑ Leonardo da Vinci. Minneapolis, MN: Oliver Press. 2008. ISBN 978-1-934545-00-3. OCLC 213812382. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/213812382.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "Bio-Optics and Bio-Inspired Optical Materials". Chemical Reviews 117 (20): 12705–12763. October 2017. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00153. PMID 28937748.
- ↑ "Microcontact-BSA imprinted capacitive biosensor for real-time, sensitive and selective detection of BSA". Biotechnology Reports 3: 65–72. September 2014. doi:10.1016/j.btre.2014.06.006. PMID 28626651.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 20.7 "Photonics in nature and bioinspired designs: sustainable approaches for a colourful world" (in en). Nanoscale Advances 2 (11): 5106–5129. 2020-11-11. doi:10.1039/D0NA00445F. ISSN 2516-0230. PMID 36132040. Bibcode: 2020NanoA...2.5106V.
- ↑ "Bio-Inspired Structural Colors Produced via Self-Assembly of Synthetic Melanin Nanoparticles". ACS Nano 9 (5): 5454–5460. May 2015. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b01298. PMID 25938924.
- ↑ "Artificial biomelanin: highly light-absorbing nano-sized eumelanin by biomimetic synthesis in chicken egg white". Biomacromolecules 15 (10): 3811–3816. October 2014. doi:10.1021/bm501139h. PMID 25224565.
- ↑ "Antibacterial performance of polydopamine-modified polymer surfaces containing passive and active components". ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 3 (12): 4602–4610. December 2011. doi:10.1021/am200978h. PMID 22044029.
- ↑ "Polydopamine--a nature-inspired polymer coating for biomedical science". Nanoscale 3 (12): 4916–4928. December 2011. doi:10.1039/c1nr10969c. PMID 22024699. Bibcode: 2011Nanos...3.4916L.
- ↑ "Biogenic Guanine Crystals from the Skin of Fish May Be Designed to Enhance Light Reflectance". Crystal Growth & Design 8 (2): 507–511. 2008. doi:10.1021/cg0704753. ISSN 1528-7483.
- ↑ "Photonic crystals cause active colour change in chameleons". Nature Communications 6 (1): 6368. March 2015. doi:10.1038/ncomms7368. PMID 25757068. Bibcode: 2015NatCo...6.6368T.
- ↑ "Reflectins: the unusual proteins of squid reflective tissues". Science 303 (5655): 235–238. January 2004. doi:10.1126/science.1091288. PMID 14716016. Bibcode: 2004Sci...303..235C.
- ↑ "The self-organizing properties of squid reflectin protein". Nature Materials 6 (7): 533–538. July 2007. doi:10.1038/nmat1930. PMID 17546036. Bibcode: 2007NatMa...6..533K. https://zenodo.org/record/1233463.
- ↑ "Biopatterning of Silk Proteins for Soft Micro-optics". ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 7 (16): 8809–8816. April 2015. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01380. PMID 25853731.
- ↑ "Reconfigurable infrared camouflage coatings from a cephalopod protein". Advanced Materials 25 (39): 5621–5625. October 2013. doi:10.1002/adma.201301472. PMID 23897625. Bibcode: 2013AdM....25.5621P.
- ↑ "Biological versus electronic adaptive coloration: how can one inform the other?". Journal of the Royal Society, Interface 10 (78): 20120601. January 2013. doi:10.1098/rsif.2012.0601. PMID 23015522.
- ↑ "Biocompatible Silk Printed Optical Waveguides". Advanced Materials 21 (23): 2411–2415. 2009. doi:10.1002/adma.200801580. ISSN 0935-9648. Bibcode: 2009AdM....21.2411P.
- ↑ "DNA – a new material for photonics?". Nature Photonics 1 (1): 3–5. 2007. doi:10.1038/nphoton.2006.56. ISSN 1749-4885. Bibcode: 2007NaPho...1....3S.
- ↑ "Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material". Angewandte Chemie 44 (22): 3358–3393. May 2005. doi:10.1002/anie.200460587. PMID 15861454.
- ↑ "Transparent wood for functional and structural applications". Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences 376 (2112): 20170182. February 2018. doi:10.1098/rsta.2017.0182. PMID 29277747.
- ↑ "Optically Transparent Nanofiber Paper". Advanced Materials 21 (16): 1595–1598. 2009. doi:10.1002/adma.200803174. ISSN 0935-9648. Bibcode: 2009AdM....21.1595N.
- ↑ "Recent advances in the manipulation of circularly polarised light with cellulose nanocrystal films" (in en). Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 23 (2): 63–73. April 2019. doi:10.1016/j.cossms.2018.11.004. ISSN 1359-0286. Bibcode: 2019COSSM..23...63F.
- ↑ "Physics of structural colors". Reports on Progress in Physics 71 (7): 076401. 2008. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/71/7/076401. ISSN 0034-4885. Bibcode: 2008RPPh...71g6401K.
- ↑ "Coloration strategies in peacock feathers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100 (22): 12576–12578. October 2003. doi:10.1073/pnas.2133313100. PMID 14557541. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..10012576Z.
- ↑ "Structural color of Morpho butterflies". American Journal of Physics 77 (11): 1010–1019. 2009. doi:10.1119/1.3192768. ISSN 0002-9505. Bibcode: 2009AmJPh..77.1010S.
- ↑ "Reduction of Lens Reflexion by the "Moth Eye" Principle". Nature 244 (5414): 281–282. 1973. doi:10.1038/244281a0. ISSN 0028-0836. Bibcode: 1973Natur.244..281C.
- ↑ "Anti-reflecting and photonic nanostructures". Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 69 (1–3): 1–35. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2010.04.001. ISSN 0927-796X.
- ↑ "Diffraction gratings: aberrations and applications". Optics & Laser Technology 31 (3): 195–218. April 1999. doi:10.1016/s0030-3992(99)00019-5. ISSN 0030-3992. Bibcode: 1999OptLT..31..195S.
- ↑ "Nanoimprinted Tio2 sol-gel passivating diffraction gratings for solar cell applications". Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications 20 (2): 143–148. 2011-07-21. doi:10.1002/pip.1131. ISSN 1062-7995.
- ↑ Navarro, Ramón; Cunningham, Colin R; Prieto, Eric, eds (2012-09-13). "High-performance dielectric diffraction gratings for space applications \\". SPIE Proceedings. Modern Technologies in Space- and Ground-based Telescopes and Instrumentation II (SPIE) 8450: 84502Z. doi:10.1117/12.928286. Bibcode: 2012SPIE.8450E..2ZZ.
- ↑ Jiao, Jianzhong, ed (2013-09-30). "Diffraction gratings for lighting applications". SPIE Proceedings. LED-based Illumination Systems (SPIE) 8835: 88350I. doi:10.1117/12.2024026. Bibcode: 2013SPIE.8835E..0IC.
- ↑ "Interferometric study on birds' feathers". Journal of Biomedical Optics 18 (5): 56011. May 2013. doi:10.1117/1.jbo.18.5.056011. PMID 23698284. Bibcode: 2013JBO....18e6011D.
- ↑ "Iridescent structurally based coloration of eyespots correlates with mating success in the peacock". Behavioral Ecology 18 (6): 1123–1131. 2007-09-20. doi:10.1093/beheco/arm088. ISSN 1465-7279.
- ↑ "Structural origin of the brown color of barbules in male peacock tail feathers". Physical Review E 72 (1 Pt 1): 010902. July 2005. doi:10.1103/physreve.72.010902. PMID 16089929. Bibcode: 2005PhRvE..72a0902L.
- ↑ "Biomimetic optical materials: Integration of nature's design for manipulation of light". Progress in Materials Science 58 (6): 825–873. July 2013. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.03.003. ISSN 0079-6425.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 "Pointillist structural color in Pollia fruit". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109 (39): 15712–15715. September 2012. doi:10.1073/pnas.1210105109. PMID 23019355. Bibcode: 2012PNAS..10915712V.
- ↑ "Antibacterial Structural Color Hydrogels". ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 9 (44): 38901–38907. November 2017. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b11258. PMID 29027783.
- ↑ "Biological growth and synthetic fabrication of structurally colored materials". Journal of Optics 21 (7): 073001. 2019-06-11. doi:10.1088/2040-8986/aaff39. ISSN 2040-8978. Bibcode: 2019JOpt...21g3001M.
- ↑ "Photonic nanoarchitectures in butterflies and beetles: valuable sources for bioinspiration". Laser & Photonics Reviews 5 (1): 27–51. 2010-12-27. doi:10.1002/lpor.200900018. ISSN 1863-8880.
- ↑ "Artificial Structural Colors and Applications". Innovation 2 (1): 100081. February 2021. doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100081. PMID 34557736. Bibcode: 2021Innov...200081X.
- ↑ "Light extraction from the bioluminescent organs of fireflies". Biomimetics and Bioinspiration (San Diego, CA: International Society for Optics and Photonics.) 7401: 740108. August 2009. doi:10.1117/12.825473. Bibcode: 2009SPIE.7401E..08B.
- ↑ "Light extraction: what we can learn from fireflies". The Nature of Light: Light in Nature IV. 8480. San Diego, California, USA: International Society for Optics and Photonics.. October 2012. pp. 84800G. doi:10.1117/12.928696.
- ↑ "Optimal overlayer inspired by Photuris firefly improves light-extraction efficiency of existing light-emitting diodes". Optics Express 21 (S1): A179–A189. January 2013. doi:10.1364/OE.21.00A179. PMID 23389270. Bibcode: 2013OExpr..21A.179B.
- ↑ "Squid adjust their body color according to substrate". Scientific Reports 12 (1): 5227. March 2022. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09209-6. PMID 35347207. Bibcode: 2022NatSR..12.5227N.
- ↑ Courage, Katherine Harmon (August 21, 2014). "Octopus-Inspired Camouflage Flashes To Life In Smart Material" (in en). https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/octopus-chronicles/octopus-inspired-camouflage-flashes-to-life-in-smart-material/.
- ↑ "Bio-inspired photonics - marine hatchetfish camouflage strategies for RF steganography" (in EN). Optics Express 29 (2): 2587–2596. January 2021. doi:10.1364/OE.414091. PMID 33726451. Bibcode: 2021OExpr..29.2587L.
- ↑ "The caudal luminous organs of lanternfishes: general innervation and ultrastructure". The American Journal of Anatomy 149 (1): 1–22. May 1977. doi:10.1002/aja.1001490102. PMID 857636.
- ↑ "Structural and ultrastructural comparison of photophores of two species of deep-sea fishes: Argyropelecus hemigymnus and Maurolicus muelleri: comparison of photophores in two species of fishes" (in en). Journal of Fish Biology 64 (6): 1552–1567. June 2004. doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2004.00410.x.
- ↑ "Biomimetic design of photonic materials for biomedical applications". Acta Biomaterialia 121: 143–179. February 2021. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.008. PMID 33301982.
 |
 KSF
KSF