Chiral inversion
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (April 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Chiral inversion is the process of conversion of one enantiomer of a chiral molecule to its mirror-image version with no other change in the molecule.[1][2][3][4]
Chiral inversion happens depending on various factors (viz. biological-, solvent-, light-, temperature- induced, etc.) and the energy barrier associated with the stereogenic element present in the chiral molecule. 2-Arylpropionic acid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) provide one of the best pharmaceutical examples of chiral inversion. Chirality is attributed to a molecule due to the presence of a stereogenic element (viz. center, planar, helical, or axis). Many pharmaceutical drugs are chiral and have a labile (configurationally unstable) stereogenic element. Chiral compounds with stereogenic center are found to have high energy barriers for inversion and generally undergo biologically mediated chiral inversion. While compounds with helical or planar chirality have low energy barriers and chiral inversions are often caused by solvent, light, temperature.[5] When this happens, the configuration of the chiral molecule may rapidly change reversibly or irreversibly depending on the conditions. The chiral inversion has been intensively studied in the context of the pharmacological and toxicological consequences.[6] Other than NSAIDs, chiral drugs with different chemical structures can also show this effect.
Chiral drugs have different effects on the body depending on whether one enantiomer or both enantiomers act on different biological targets. As a result, chiral inversion can change how a pharmaceutical drug works in the body. From a pharmacological and toxicological point of view, it is very important to learn more about chiral inversion, the things that make it happen, and the tools used to figure out chiral inversion.
Types
Essentially there are two types of chiral inversion, unidirectional and bidirectional.[7] Inversion process is dependent on species and substrate.
- Unidirectional
- chiral inversion (enzyme mediated) was described only with 2-arylpropionate nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), namely ibuprofen, ketoprofen, fenoprofen, benoxaprophen, etc.[8] For this group, only S-enantiomer (eutomer) is active i.e. has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. In the body, only inactive R-enantiomer can undergo chiral inversion by hepatic enzymes into the active S-enantiomer and not vice versa. The “inactive” R-isomer (distomer) may be responsible for the gastrointestinal irritation and related side-effects associated with NSAIDs.[9] In certain situations, carbenicillin, ethiazide, etoposide, zopiclone, pantoprazole, clopidogrel, ketorolac, albendazole-sulfoxide, lifibrol, and 5-aryl-thiazolidinedione also go through unidirectional chiral inversion.[10] Chiral inversions were found to happen in a group of important compounds called α-amino acids. Amino acids exist in two mirror-image versions (D- and L- configurations). Several D-amino acids, like D-methionine, D-proline, D-serine, D-alanine, D-aspartate, D-leucine, and D-phenylalanine, have been shown to go through unidirectional chiral inversion in mammals.[11][12]
- Bidirectional
- chiral inversion or racemization type of inversion is shown by pharmaceutical drugs including 3-hydroxy-benzodiazapine class of drugs (oxazepam, lorazepam, temazepam), thalidomide, and tiaprofenic acid.[7] A brief list of select pharmaceutical drugs that go through chiral inversion are presented in Table below..
| Pharmaceutical drug | Therapeutic category | Species | Model system | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | NSAID | Man, rat, mouse, guinea pig | In vivo | Aso, Yoshioka, & Yasushi, 1990[13][14] |
| Ketoprofen | NSAID | Rabbit, rat, human | In vivo | Jamali, Mehvar, & Psutto, 1989[15] |
| Benoxaprophen | NSAID | Human | In vivo | Caldwell, Hutt, & Fournel-Gifleu, 1988[8] |
| Fenoprofen | NSAID | Human, rabbit | In vivo | Jamali, Mehvar, & Psutto, 1989 [15] |
| Ketorolac | NSAID | Man/Rat | In vitro | Vakily, Corrigan, & Jamali, 1995[16] |
| Carbenicillin | Antimicrobial | Man | In vitro | Aso, Yoshioka, & Yasushi, 1990[13] |
| Thalidomide | Immunomodulatory agent | Man | In vitro | Eriksson, Björkman, & Höglund, 2001[17] |
| Ketamine | General anaesthetic | Rat | In vivo | Edwards, & Mather, 2001[18] |
| Ethiazide | Diuretic | Man | In vitro | Aso, Yoshioka, & Yasushi, 1990[13] |
| Zopiclone | Hypnotics and sedatives | Rat | In vitro | Fernandez, et al.., 2002[19] |
| Clopidogrel | Antiplatlet medication | Rat | In vitro | Reist, et al., 2000[20] |
| Albendazol-sulfoxide | Anthelmintic agent | Sheep/Cattle | In vitro | Virkel, Lifschitz, Pis, & Lanusee, 2002[21] |
| Lifibrol | Lipid lowering agent | Dog | In vitro | Walter, & Hsu, 1994[22] |
| 5-Aryl-Thiazolidinedione | Antidiabetic agent | Man/Dog | In vitro | Welch, Kress, Beconi, & Mathre, 2003[23] |
| Pantoprazole | Proton-pump inhibitor | Rat | In vitro | Masubuchi, Yamazaki, & Tanaka, 1998[24] |
| Etoposide | Antineoplastic agent | Rat | In vivo | Aso, Yoshioka, & Yasushi, 1990[13] |
Mechanism
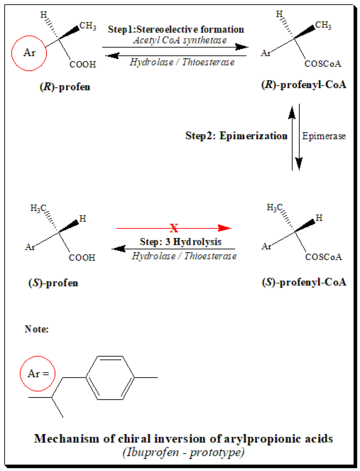
It is well documented that (R)-enantiomers of profens in the presence of coenzyme A (CoA), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and Mg+2 are converted to active (S)-forms. The pathways of chiral inversion is illustrated taking ibuprofen as the prototype, in the scheme below.[14][25]
The pathway consists mainly of three steps:
- Stereoselective activation: Stereoselective activation of (R)-profen by the formation of the thioester, in the presence of CoA, ATP and Mg+2. (S)-profen does not form the thioester.
- Epimerization (Racemization): The enzyme epimerase 2-arylpropionic-CoA changes the (R)-thioester to the (S)-thioester. This process is called "racemization" or "epimerization."
- Hydrolysis: With the help of hydrolase/thioesterase, thioesters are broken down into their (R)- and (S)-forms
Because the acyl-CoA thioester (profenyl-CoA) changes the structure of triglycerides and phospholipids, metabolic chiral inversion may cause toxic effects.[10]
Factors influencing inversion
Chiral drugs with stereo-labile configuration are likely to undergo interconversion of the enantiomers that may be enzymatic (biological) or non-enzymatic. Enzyme-mediated conversion is the process of chiral inversion that happens in a living organism. Non-enzymatic inversion of drugs is important and relevant in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process. This may have impact on the shelf-life of a drug and the economic feasibility of the resolution. Inversion can also happen without enzymes when precolumn derivatization is used in enantioselective chromatographic separation techniques. Racemization can also happen in the acidic environment of the stomach and other bodily fluids.
Enzyme-mediated (biological)
Enzyme-mediated (biological) chiral inversion of organic compounds is caused by highly chiral endogenous molecules found in receptors, enzymes, and other structures.[8] While enzyme inhibitors suppress enzyme activity, enzyme inducers boost enzyme concentration and activity. The primary determinants of inter-individual variability in drug metabolism in humans are thought to include genetic polymorphism and a variety of other variables, including age, gender, biological conditions, pregnancy, illnesses, stress, nutrition, and drugs. For instance, Reichel et al.[26] reported that a 2-arylpropionyl-coenzyme-A epimerase was molecularly cloned and expressed as a crucial enzyme in the inversion metabolism of ibuprofen. Ibuprofen's chiral inversion by enzymes has been documented in humans.[27]
Species differences
Tissue variations
The liver, gastrointestinal tract (GIT), lungs, kidney, and brain are among the tissues that participate in the chiral inversion of medicines. The liver has been shown to be the most crucial organ in the development of this mechanism.[28] Although some studies contend that rat liver homogenates lack the enzymatic mechanisms necessary to invert the R-enantiomers of flurbiprofen, naproxen, suprofen, and ibuprofen, the liver may also be involved in the inversion of R-ibuprofen in rats.[15] On the other hand, it was noted that certain medicines underwent chiral inversion without the involvement of the liver (hepatocytes). Although liver did not play a substantial role in the inversion of benoxaprofen, studies using benoxaprofen and ketoprofen show that one of the primary sites of inversion in rats is the GI tract.[15]
Route of administration
Inter-individual variability
Non-enzymatic
Sample handling and manufacturing process
Temperature and pH
Analytical methods
Chiral inversion is a very important part of designing and making drugs. Because this process can change how chiral drugs work in the body and can cause side effects that can be serious or even fatal. Traditionally, chiral inversions have been studied with NMR spectroscopy at different temperatures and chiroptical methods like polarimetry. But strong, complementary methods based on dynamic chromatography (GC, HPLC, SFC, CEC, and MEKC) and electrophoresis have been made and used to figure out how the enantiomeric composition of stereo-labile chiral compounds changes over time.[29] Most of the time, liquid chromatographic methods are used to do enantioselective analysis of chiral drugs. When an analyte with one stereogenic center or axis is separated well, the chromatogram will show two peaks. But if the analyte is stereo-labile, the peaks tend to merge.[30] How much coalescence there is will depend on how fast chiral inversion and enantioresolution happen. Over time, the peaks will merge into a flat area. Dynamic chromatography shows how the elution profile changes over time. This makes it useful for figuring out how pH, temperature, and solvents affect chiral inversion, which can happen on the stationary phase, in the injector, or in the detector.[29]
Multidimensional approaches have been used to improve separation and detection. Table below shows a list of common methods and experiments used to figure out chiral inversion. Any of these methods can then be used to determine chiral inversion. Which instrument is used to analyze a chiral compound depends on its physical and chemical properties (i.e., the solubility, vapor pressure, thermal and solvent stability, and detection).[29]
| Instrument | Experimental operational approaches |
| Dynamic NMR | Combining classical kinetic studies with chiral separation |
| Dynamic gas chromatography | Continuous flow models |
| Dynamic supercritical fluid chromatography | Peak form analysis - involves comparison of real chromatograms with simulated peaks |
| Dynamic liquid chromatography | Stopped-flow method |
| Dynamic capillary electrophoresis | Stochastic methods |
| Dynamic micellar electrokinetic chromatography | Deconvolution methods |
| Dynamic capillary electrochromatography | Approximation function methods |
For example, capillary electrophoresis or liquid chromatography could be used if the analyte can be ionized and has a high vapor pressure, but it is also soluble in polar solvents.[31] On the other hand, gas chromatography is the best way to test a substance that is stable at high temperatures but has a low vapor pressure. When compared to gas or liquid chromatography, supercritical fluid chromatography is a better way to measure chiral inversion because it uses mass spectrometers and a green method.[32]
Significance in drug development

Enantiomers of a chiral drug often interact in an enantioselective way in a chiral environment. This may be offered by different biotic substances (viz. proteins, nucleic acids, phospholipids and oligosaccharides). They are made up of chiral building blocks that are put together in space in handed conformations. These biological targets function as receptors for the drug enantiomers. So, at the binding sites of these receptors, enantiomers will be seen as different chemical species. The three point attachment model (Easson & Stedman model)[33] can be used to see how chiral discrimination works. Figure depicts how the enantiomers of a drug interact with receptors in a way that depends on the drug's shape. This model was made for chiral drugs with a single stereogenic center. It says that there are three binding sites in the receptor (B', C' and D') that match the drug's pharmacophoric groups (B, C, D). A three-point fit (good fit) is possible for the eutomer at BB', CC' and DD'(Fig. A). Even though the distomer is the wrong enantiomer, it can fit either a one-point interaction (bad fit), or a two-point attachment (CC' and DD') with the same receptor site as shown in (Fig. B).
Eutomer is the version that works the way you want it to, and distomer is the version that doesn't work or works in a way you don't want it to.[34][35] Most of the time, the mirror-image versions have different binding affinities. In the eutomer, the ligands or moiety around a stereogenic element have more binding energy than in the distomer. When the eutomer goes through chiral inversion, it loses its ability to bind to a biological receptor. Because of these enantiospecific interactions, therapeutic and toxicological properties are enantioselective[27][6] So, the stereo-stability of chiral drugs may have big effects on the process of making new drugs, especially when it comes to how pharmaceutical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic information is read and understood. At every stage of designing, making, and testing a drug for safety, chiral inversion must be taken into account.
See also
References
- ↑ The impact of stereochemistry on drug development and use. New York: Wiley. 1997. pp. 85–105. ISBN 978-0-471-59644-8. OCLC 35262289.
- ↑ "Chiral Inversions" (in en). Chirality in Drug Design and Development. CRC Press. 2004-03-15. doi:10.1201/9780203021811. ISBN 978-0-8247-5062-6. http://www.crcnetbase.com/doi/10.1201/9780203021811.ch8.
- ↑ Stereochemical aspects of drug action and disposition. Springer. 2003. ISBN 978-3-540-41593-0. OCLC 52515592.
- ↑ "Drug racemization and its significance in pharmaceutical research". Stereochemical aspects of drug action and disposition. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 153. Berlin: Springer. 2003. pp. 104–112. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-55842-9_4. ISBN 978-3-540-41593-0. OCLC 52515592.
- ↑ "Chiral Inversion of Organic Pollutants" (in en). Chiral Organic Pollutants (1st ed.). CRC Press. 2020-12-30. pp. 27–40. doi:10.1201/9781003000167-3. ISBN 978-1-003-00016-7. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781000298888/chapters/10.1201/9781003000167-3. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Chiral toxicology: it's the same thing...only different". Toxicological Sciences 110 (1): 4–30. July 2009. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp097. PMID 19414517.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Chiral drugs: an overview". International Journal of Biomedical Science 2 (2): 85–100. June 2006. doi:10.59566/IJBS.2006.2085. PMID 23674971.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "The metabolic chiral inversion and dispositional enantioselectivity of the 2-arylpropionic acids and their biological consequences". Biochemical Pharmacology 37 (1): 105–114. January 1988. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(88)90762-9. PMID 3276314.
- ↑ "Clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs". Pharmacology & Therapeutics 33 (2–3): 383–433. 1987. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(87)90072-6. PMID 3310039.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Chiral inversion of drugs: coincidence or principle?". Current Drug Metabolism 5 (6): 517–533. December 2004. doi:10.2174/1389200043335360. PMID 15578945.
- ↑ "Biological implications of oxidation and unidirectional chiral inversion of D-amino acids". Current Drug Metabolism 13 (3): 321–331. March 2012. doi:10.2174/138920012799320392. PMID 22304623.
- ↑ "Stereospecificity of phenylalanine plasma kinetics and hydroxylation in man following oral application of a stable isotope-labelled pseudo-racemic mixture of L- and D-phenylalanine". Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 128 (2–3): 181–198. March 1983. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(83)90319-4. PMID 6851137.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 "Epimerization and racemization of some chiral drugs in the presence of human serum albumin". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 38 (1): 180–184. January 1990. doi:10.1248/cpb.38.180. PMID 2337941.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Metabolic chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionic acid derivatives (profens)". Medical Research Journal 2 (1): 1–5. 2017-09-21. doi:10.5603/MRJ.2017.0001. ISSN 2451-4101. https://journals.viamedica.pl/medical_research_journal/article/view/54856.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 "Enantioselective aspects of drug action and disposition: therapeutic pitfalls". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 78 (9): 695–715. September 1989. doi:10.1002/jps.2600780902. PMID 2685226.
- ↑ "The problem of racemization in the stereospecific assay and pharmacokinetic evaluation of ketorolac in human and rats". Pharmaceutical Research 12 (11): 1652–1657. November 1995. doi:10.1023/A:1016245101389. PMID 8592665.
- ↑ "Clinical pharmacology of thalidomide". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 57 (5): 365–376. August 2001. doi:10.1007/s002280100320. PMID 11599654.
- ↑ "Tissue uptake of ketamine and norketamine enantiomers in the rat: indirect evidence for extrahepatic metabolic inversion". Life Sciences 69 (17): 2051–2066. September 2001. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01287-5. PMID 11589520.
- ↑ "Stereoselective distribution and stereoconversion of zopiclone enantiomers in plasma and brain tissues in rats". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 54 (3): 335–340. March 2002. doi:10.1211/0022357021778574. PMID 11902799.
- ↑ "Racemization, enantiomerization, diastereomerization, and epimerization: Their meaning and pharmacological significance" (in en). Chirality 7 (6): 396–400. 1995. doi:10.1002/chir.530070603. ISSN 0899-0042. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chir.530070603.
- ↑ "In vitro ruminal biotransformation of benzimidazole sulphoxide anthelmintics: enantioselective sulphoreduction in sheep and cattle". Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 25 (1): 15–23. February 2002. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2885.2002.00373.x. PMID 11874522.
- ↑ "Chiral assay methods for lifibrol and metabolites in plasma and the observation of unidirectional chiral inversion following administration of the enantiomers to dogs". Chirality 6 (2): 105–115. 1994. doi:10.1002/chir.530060211. PMID 8204414.
- ↑ "Studies on the racemization of a stereolabile 5-aryl-thiazolidinedione". Chirality 15 (2): 143–147. February 2003. doi:10.1002/chir.10180. PMID 12520506.
- ↑ "Unusual reversal of enantioselectivity in the asymmetric autocatalysis of pyrimidyl alkanol triggered by chiral aromatic alkanols and amines". Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 15 (3): 555–558. January 2017. doi:10.1039/C6OB02415G. PMID 27942665.
- ↑ Smith and Williams' Introduction to the Principles of Drug Design and Action (3rd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. 1998. pp. 117–183. ISBN 978-1-315-27379-2. OCLC 1100515958.
- ↑ "Molecular cloning and expression of a 2-arylpropionyl-coenzyme A epimerase: a key enzyme in the inversion metabolism of ibuprofen". Mol Pharmacol 51 (4): 576–82. April 1997. doi:10.1124/mol.51.4.576. PMID 9106621.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Role of racemization in optically active drugs development". Chirality 19 (6): 453–463. June 2007. doi:10.1002/chir.20397. PMID 17393472.
- ↑ Berry, B. W.; Jamali, F. (1991). "Presystemic and systemic chiral inversion of R-(-)-fenoprofen in the rat". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 258 (2): 695–701. doi:10.1016/S0022-3565(25)20451-7. ISSN 0022-3565. PMID 1865366.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 "Stereolabile chiral compounds: analysis by dynamic chromatography and stopped-flow methods". Chemical Society Reviews 34 (7): 595–608. July 2005. doi:10.1039/b502508g. PMID 15965541.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Determination of the interconversion energy barrier of enantiomers by separation methods". Journal of Chromatography A 1000 (1–2): 779–800. June 2003. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00238-3. PMID 12877200.
- ↑ "Chiral pharmaceuticals: A review on their environmental occurrence and fate processes". Water Research 124: 527–542. November 2017. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.003. PMID 28806704. Bibcode: 2017WatRe.124..527S. https://www.dora.lib4ri.ch/eawag/islandora/object/eawag%3A15611.
- ↑ "Stereoselective supercritical fluidic chromatography –mass spectrometry (SFC-MS) as a fast bioanalytical tool to assess chiral inversion in vivo and in vitro" (in en). International Journal of Mass Spectrometry 444. 2019. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2019.06.008. Bibcode: 2019IJMSp.44416172C.
- ↑ "Studies on the relationship between chemical constitution and physiological action: Molecular dissymmetry and physiological activity". The Biochemical Journal 27 (4): 1257–1266. 1933-01-01. doi:10.1042/bj0271257. PMID 16745220.
- ↑ "Stereochemistry, a basis for sophisticated nonsense in pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26 (6): 663–668. 1984. doi:10.1007/BF00541922. PMID 6092093.
- ↑ "Stereoselectivity of bioactive xenobiotics. A pre-Pasteur attitude in medicinal chemistry, pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology". Biochemical Pharmacology 37 (1): 9–18. January 1988. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(88)90749-6. PMID 3276322.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF