Electromagnetic interactions
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
Interactions between electriccharges, the carrier of the electromagnetic interaction being the photon.
In classical physics, electromagnetism is described using electric and magnetic fields. The basic relations between these fields and matter are expressed by Maxwell's equations. In quantum theory, electromagnetic interactions are described by quantum electrodynamics (QED) and can be calculated using perturbation theory (Feynman diagrams). Typical electromagnetic interactions in high-energy physics are:
- - Coulomb scattering (e.g. electron-nucleon scattering),
- - Bhabha scattering (electron-positron scattering),
- - Möller scattering (electron-electron scattering),
- - Compton scattering (photon-electron scattering),
- - Bremsstrahlung (photon emission in deacceleration or acceleration),
- - Annihilation (e.g.
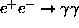 ),
), - - Pair creation (
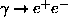 ),
), - - Decay of
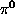 .
.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Electromagnetic_interactions23 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF