Resolution (chromatography)
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
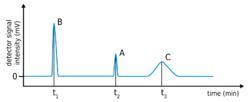
In chromatography, resolution is a measure of the separation of two peaks of different retention time t in a chromatogram.[1][2][3][4]
Expression
Chromatographic peak resolution is given by
where tR is the retention time and wb is the peak width at baseline. Here compound 1 elutes before compound 2.
If the peaks have the same width
- .
Plate number
The theoretical plate height is given by
where L is the column length and N the number of theoretical plates.[5] The relation between plate number and peak width at the base is given by
- .
See also
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Peak Resolution Rs in chromatography". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04465
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Peak Resolution in gas chromatography". doi:10.1351/goldbook.R05317
- ↑ Maryutina, Tatiana A.; Savonina, Elena Yu.; Fedotov, Petr S.; Smith, Roger M.; Siren, Heli; Hibbert, D. Brynn (2018). "Terminology of separation methods (IUPAC Recommendations 2017)". Pure and Applied Chemistry 90 (1): 181–231. doi:10.1515/pac-2017-0111. ISSN 0033-4545.
- ↑ Ettre, L. S. (1993). "Nomenclature for chromatography (IUPAC Recommendations 1993)". Pure and Applied Chemistry 65 (4): 819–872. doi:10.1351/pac199365040819. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "plate number, N". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04694
External links
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Resolution_(chromatography)48 views | Status: cached on February 13 2026 06:31:06↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF