September 1859 geomagnetic storm
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 14 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 14 min
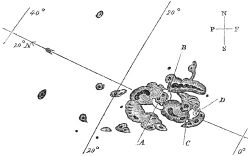
The September 1859 geomagnetic storm (also known as the Carrington Event)[1] was a powerful geomagnetic storm during solar cycle 10 (1855–1867). A solar coronal mass ejection (CME) hit Earth's magnetosphere and induced the largest geomagnetic storm on record on September 1–2, 1859. The associated "white light flare" in the solar photosphere was observed and recorded by British astronomers Richard C. Carrington and Richard Hodgson. The storm caused strong auroral displays and wrought havoc with telegraph systems. The now-standard unique IAU identifier for this flare is SOL1859-09-01.
A solar storm of this magnitude occurring today would cause widespread electrical disruptions, blackouts and damage due to extended outages of the electrical grid.[2][3] The solar storm of 2012 was of similar magnitude, but it passed Earth's orbit without striking the planet, missing by nine days.[4]
Carrington flare

Just a few months before the solar maximum on 1860.1, during the 10th solar cycle,[5] many sunspots appeared on the Sun from August 28 to September 2, 1859. On August 29, southern auroras were observed as far north as Queensland, Australia.[6] Just before noon on September 1, the English amateur astronomers Richard Carrington and Richard Hodgson independently recorded the earliest observations of a solar flare.[7] Carrington and Hodgson compiled independent reports which were published side-by-side in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, and exhibited their drawings of the event at the November 1859 meeting of the Royal Astronomical Society.[8][9]
The flare was associated with a major coronal mass ejection (CME) that travelled directly toward Earth, taking 17.6 hours to make the 150 million kilometer (93 million mile) journey. Typical CMEs take several days to arrive at Earth, but it is believed that the relatively high speed of this CME was made possible by a prior CME, perhaps the cause of the large aurora event on August 29 that "cleared the way" of ambient solar wind plasma for the Carrington event.[7]
Because of a geomagnetic solar flare effect ("magnetic crochet")[10] observed in the Kew Observatory magnetometer record by Scottish physicist Balfour Stewart, and a geomagnetic storm observed the following day, Carrington suspected a solar-terrestrial connection.[11] Worldwide reports on the effects of the geomagnetic storm of 1859 were compiled and published by American mathematician Elias Loomis, which support the observations of Carrington and Stewart.[12]

On September 1–2, 1859, one of the largest geomagnetic storms (as recorded by ground-based magnetometers) occurred. Auroras were seen around the world, those in the northern hemisphere as far south as the Caribbean; those over the Rocky Mountains in the U.S. were so bright that the glow woke gold miners, who began preparing breakfast because they thought it was morning.[7] People in the northeastern United States could read a newspaper by the aurora's light.[13] The aurora was visible from the poles to low latitude areas such as south-central Mexico,[14][15] Queensland, Cuba, Hawaii,[16] southern Japan and China,[17] and even at lower latitudes very close to the equator, such as in Colombia.[18] Estimates of the storm strength range from −800 nT to −1750 nT.[19]
Telegraph systems all over Europe and North America failed, in some cases giving telegraph operators electric shocks.[20] Telegraph pylons threw sparks.[21] Some telegraph operators could continue to send and receive messages despite having disconnected their power supplies.[22]
On Saturday, September 3, 1859, the Baltimore American and Commercial Advertiser reported:
Those who happened to be out late on Thursday night had an opportunity of witnessing another magnificent display of the auroral lights. The phenomenon was very similar to the display on Sunday night, though at times the light was, if possible, more brilliant, and the prismatic hues more varied and gorgeous. The light appeared to cover the whole firmament, apparently like a luminous cloud, through which the stars of the larger magnitude indistinctly shone. The light was greater than that of the moon at its full, but had an indescribable softness and delicacy that seemed to envelop everything upon which it rested. Between 12 and 1 o'clock, when the display was at its full brilliancy, the quiet streets of the city resting under this strange light, presented a beautiful as well as singular appearance.[23]
In 1909, an Australian gold miner C.F. Herbert retold his observations in a letter to The Daily News in Perth:
I was gold-digging at Rokewood, about four miles from Rokewood township (Victoria). Myself and two mates looking out of the tent saw a great reflection in the southern heavens at about 7 o'clock p.m., and in about half an hour, a scene of almost unspeakable beauty presented itself, lights of every imaginable color were issuing from the southern heavens, one color fading away only to give place to another if possible more beautiful than the last, the streams mounting to the zenith, but always becoming a rich purple when reaching there, and always curling round, leaving a clear strip of sky, which may be described as four fingers held at arm's length. The northern side from the zenith was also illuminated with beautiful colors, always curling round at the zenith, but were considered to be merely a reproduction of the southern display, as all colors south and north always corresponded. It was a sight never to be forgotten, and was considered at the time to be the greatest aurora recorded... The rationalist and pantheist saw nature in her most exquisite robes, recognising, the divine immanence, immutable law, cause, and effect. The superstitious and the fanatical had dire forebodings, and thought it a foreshadowing of Armageddon and final dissolution.[24]
In June 2013, a joint venture from researchers at Lloyd's of London and Atmospheric and Environmental Research (AER) in the United States used data from the Carrington Event to estimate the current cost of a similar event to the U.S. alone at $0.6–2.6 trillion.[2]
Other evidence and similar events
Ice cores containing thin nitrate-rich layers have been analysed to reconstruct a history of past solar storms predating reliable observations. Some researchers claim that data from Greenland ice cores show evidence of individual solar-proton events, including the Carrington event.[25] More ice core work casts significant doubt on this interpretation, and shows that nitrate spikes are not a result of solar energetic particle events. Indeed, no consistency is found in cores from Greenland and Antarctica, and nitrate events can be due to terrestrial events such as burnings, so use of this technique is now in doubt.[26][27][28] Other research has looked for signatures of large solar flares and CMEs in carbon-14 in tree rings and beryllium-10 in ice cores, finding such a signature of a large solar storm in 774 CE but finding that such events occur on average only once every several millennia.[29]
Less severe storms occurred in 1921 and 1960, when widespread radio disruption was reported. The March 1989 geomagnetic storm knocked out power across large sections of Quebec. On July 23, 2012 a "Carrington-class" solar superstorm (solar flare, coronal mass ejection, solar EMP) was observed; its trajectory narrowly missed Earth.[4][30]
See also
References
- ↑ Philips, Tony (January 21, 2009). "Severe Space Weather—Social and Economic Impacts". NASA Science: Science News (science.nasa.gov). https://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2009/21jan_severespaceweather.htm?list5029. Retrieved February 16, 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lloyd's and Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc. (2013). Solar storm risk to the north American electric grid. With input from Homeier, Nicole; Horne, Richard; Maran, Michael; Wade, David. Lloyd's. http://www.lloyds.com/~/media/lloyds/reports/emerging%20risk%20reports/solar%20storm%20risk%20to%20the%20north%20american%20electric%20grid.pdf. Retrieved 2019-07-31.
- ↑ Baker, D. N. (2008). Severe Space Weather Events—Understanding Societal and Economic Impacts. The National Academy Press, Washington, DC. doi:10.17226/12507. ISBN 978-0-309-12769-1.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Phillips, Dr. Tony (July 23, 2014). "Near Miss: The Solar Superstorm of July 2012". NASA. https://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2014/23jul_superstorm/. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
- ↑ Mursula, K.; Ulich, Th. (1998). "A new method to determine the solar cycle length". Geophysical Research Letters 25 (11): 1837–1840. doi:10.1029/98GL51317. Bibcode: 1998GeoRL..25.1837M.
- ↑ "SOUTHERN AURORA.". The Moreton Bay Courier (Brisbane: National Library of Australia): p. 2. September 7, 1859. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article3722206. Retrieved May 17, 2013.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Odenwald, Sten F.; Green, James L. (July 28, 2008). "Bracing the Satellite Infrastructure for a Solar Superstorm". Scientific American 299 (2): 80–7. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0808-80. PMID 18666683. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=bracing-for-a-solar-superstorm. Retrieved February 16, 2011.
- ↑ Carrington, R. C. (1859). "Description of a Singular Appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 20: 13–15. doi:10.1093/mnras/20.1.13. Bibcode: 1859MNRAS..20...13C. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=njp.32101081655332&view=1up&seq=351.
- ↑ Hodgson, R. (1859). "On a curious Appearance seen in the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 20: 15–16. doi:10.1093/mnras/20.1.15. Bibcode: 1859MNRAS..20...15H. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=njp.32101081655332&view=1up&seq=353.
- ↑ Thompson, Richard. "A Solar Flare Effect". Australian Government: Space Weather Services. http://www.ips.gov.au/Educational/3/1/1. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ↑ Clark, Stuart (2007). The Sun Kings: The Unexpected Tragedy of Richard Carrington and the Tale of How Modern Astronomy Began. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-12660-9. https://archive.org/details/sunkingsunexpect00clar.
- ↑ See:
- Loomis, Elias (November 1859). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September, 1859". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 28: 385–408. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679510&view=1up&seq=403.
- Loomis, Elias (January 1860). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859—2nd article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 29: 92–97. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679511&view=1up&seq=112.
- Loomis, Elias (February 1860). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859—3rd article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 29: 249–266. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679511&view=1up&seq=269.
- Loomis, Elias (May 1860). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859—4th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 29: 386–399. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679511&view=1up&seq=406.
- Loomis, Elias (July 1860). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859, and the geographical distribution of auroras and thunder storms—5th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 30: 79–100. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679512&view=1up&seq=93.
- Loomis, Elias (November 1860). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859—6th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 30: 339–361. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679512&view=1up&seq=363.
- Loomis, Elias (July 1861). "The great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859—7th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 32: 71–84. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679513&view=1up&seq=85.
- Loomis, Elias (September 1861). "On the great auroral exhibition of August 28 to September 4, 1859, and auroras generally—8th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 32: 318–335. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679513&view=1up&seq=334.
- Loomis, Elias (July 1862). "On electrical currents circulating near the earth's surface and their connection with the phenomena of the aurora polaris—9th article". The American Journal of Science. 2nd series 34: 34–45. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x001679515&view=1up&seq=62.
- ↑ Richard A. Lovett (March 2, 2011). "What If the Biggest Solar Storm on Record Happened Today?". National Geographic News. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2011/03/110302-solar-flares-sun-storms-earth-danger-carrington-event-science/. Retrieved September 5, 2011.
- ↑ Hayakawa, H. (2018). "Low-latitude Aurorae during the Extreme Space Weather Events in 1859". The Astrophysical Journal 869 (1): 57. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aae47c. Bibcode: 2018ApJ...869...57H.
- ↑ González‐Esparza, J. A.; M. C. Cuevas‐Cardona (2018). "Observations of Low Latitude Red Aurora in Mexico During the 1859 Carrington Geomagnetic Storm". Space Weather 16 (6): 593. doi:10.1029/2017SW001789. Bibcode: 2018SpWea..16..593G.
- ↑ Green, J. (2006). "Duration and extent of the great auroral storm of 1859". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 130–135. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.054. PMID 28066122. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..130G.
- ↑ Hayakawa, H. (2016). "East Asian observations of low-latitude aurora during the Carrington magnetic storm". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 68 (6): pp. 99. doi:10.1093/pasj/psw097. Bibcode: 2016PASJ...68...99H.
- ↑ Moreno Cárdenas, Freddy; Cristancho Sánchez, Sergio; Vargas Domínguez, Santiago; Hayakawa, Satoshi; Kumar, Sandeep; Mukherjee, Shyamoli; Veenadhari, B. (2016). "The grand aurorae borealis seen in Colombia in 1859". Advances in Space Research 57 (1): 257–267. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2015.08.026. Bibcode: 2016AdSpR..57..257M.
- ↑ "Near Miss: The Solar Superstorm of July 2012 – NASA Science". https://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2014/23jul_superstorm/.
- ↑ Committee on the Societal and Economic Impacts of Severe Space Weather Events: A Workshop, National Research Council (2008). Severe Space Weather Events—Understanding Societal and Economic Impacts: A Workshop Report. National Academies Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-309-12769-1.
- ↑ Odenwald, Sten F. (2002). The 23rd Cycle. Columbia University Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-231-12079-1. https://archive.org/details/23rdcyclelearnin00oden.
- ↑ Carlowicz, Michael J.; Lopez, Ramon E. (2002). Storms from the Sun: The Emerging Science of Space Weather. National Academies Press. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-309-07642-5.
- ↑ "The Aurora Borealis". Baltimore American and Commercial Advertiser: p. 2; Column 2. September 3, 1859. https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=tCoNjB6AT50C&dat=18590903&printsec=frontpage. Retrieved February 16, 2011.
- ↑ Herbert, Count Frank (8 October 1909). "The Great Aurora of 1859". The Daily News (Perth, WA): p. 9. https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/77351480. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ↑ McCracken, K. G.; Dreschhoff, G. A. M.; Zeller, E. J.; Smart, D. F.; Shea, M. A. (2001). "Solar cosmic ray events for the period 1561–1994 1. Identification in polar ice, 1561–1950". Journal of Geophysical Research 106 (A10): 21,585–21,598. doi:10.1029/2000JA000237. Bibcode: 2001JGR...10621585M.

- ↑ Wolff, E. W.; Bigler, M.; Curran, M. A. J.; Dibb, J.; Frey, M. M.; Legrand, M. (2012). "The Carrington event not observed in most ice core nitrate records". Geophysical Research Letters 39 (8): 21,585–21,598. doi:10.1029/2012GL051603. Bibcode: 2012GeoRL..39.8503W. https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1218&context=earthsci_facpub.

- ↑ Duderstadt, K. A. (2014). "Nitrate deposition to surface snow at Summit, Greenland, following the 9 November 2000 solar proton event". J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 119 (11): 6938–6957. doi:10.1002/2013JD021389. Bibcode: 2014JGRD..119.6938D. https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1019&context=earthsci_facpub.
- ↑ Mekhaldi, F. et al. (November 2017), "No Coincident Nitrate Enhancement Events in Polar Ice Cores Following the Largest Known Solar Storms", Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 122 (21): 11,900–11,913, doi:10.1002/2017JD027325, Bibcode: 2017JGRD..12211900M, https://eprints.utas.edu.au/26149/1/122198%20final.pdf
- ↑ Battersby, Stephen (2019-11-19). "Core Concept: What are the chances of a hazardous solar superflare?" (in en). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 116 (47): 23368–23370. doi:10.1073/pnas.1917356116. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 31744927.
- ↑ "Video (04:03) – Carrington-class coronal mass ejection narrowly misses Earth". NASA. April 28, 2014. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7ukQhycKOFw. Retrieved July 26, 2014.
Further reading
- Bell, Trudy E.; Phillips, Tony (May 6, 2008). "A Super Solar Flare". Science@NASA (science.nasa.gov). https://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2008/06may_carringtonflare.htm.
- Boteler, D. (2006). "The super storms of August/September 1859 and their effects on the telegraph system". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 159–172. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.01.013. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..159B.
- Boteler, D. (2006). "Comment on time conventions in the recordings of 1859". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 301–303. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.07.006. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..301B.
- "The Largest Magnetic Storm on Record...or Is It? The 'Carrington Event' of August 27 to September 7, 1859: Recorded at Greenwich Observatory, London". British Geological Survey. 2011. http://www.geomag.bgs.ac.uk/carrington.html. Retrieved March 28, 2009.
- Brooks, Michael (March 23, 2009). "Space storm alert: 90 seconds from catastrophe". New Scientist. Archived from the original on March 22, 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090322055348/http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg20127001.300-space-storm-alert-90-seconds-from-catastrophe.html?full=true. Retrieved March 28, 2009.
- Burke, W.; Huang, C.; Rich, F. (2006). "Energetics of the April 2000 magnetic superstorm observed by DMSP". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 239–252. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.07.085. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..239B.
- Calvin, Robert Clauer; Siscoe, George L., eds (2006). "The Great Historical Geomagnetic Storm of 1859: A Modern Look". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 115–388. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.09.002.
- Carrington, R. C. (1859). "Description of a Singular Appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 20: 13–5. doi:10.1093/mnras/20.1.13. Bibcode: 1859MNRAS..20...13C. http://adsbit.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-iarticle_query?bibcode=1859MNRAS..20...13C.
- Clark, Stuart (2007). The Sun Kings: The Unexpected Tragedy of Richard Carrington and the Tale of How Modern Astronomy Began. ISBN 978-0-691-12660-9. https://archive.org/details/sunkingsunexpect00clar.
- Cliver, E. W.; Svalgaard, L. (2004). "The 1859 Solar–Terrestrial Disturbance and the Current Limits of Extreme Space Weather Activity". Solar Physics 224 (1–2): 407. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-4980-z. Bibcode: 2004SoPh..224..407C. http://www.leif.org/research/1859%20Storm%20-%20Extreme%20Space%20Weather.pdf.
- Cliver, E. (2006). "The 1859 space weather event: Then and now". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 119–129. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.07.077. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..119C. http://www.dtic.mil/get-tr-doc/pdf?AD=ADA471584.
- Green, J.; Boardsen, S. (2006). "Duration and extent of the great auroral storm of 1859". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 130–135. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.054. PMID 28066122. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..130G.
- Green, J.; Boardsen, S.; Odenwald, S.; Humble, J.; Pazamickas, K. (2006). "Eyewitness reports of the great auroral storm of 1859". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 145–154. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.12.021. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..145G.
- Hayakawa, H. (2016). "East Asian observations of low-latitude aurora during the Carrington magnetic storm". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 68 (6): 99. doi:10.1093/pasj/psw097. Bibcode: 2016PASJ...68...99H.
- Humble, J. (2006). "The solar events of August/September 1859 – Surviving Australian observations". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 155–158. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.053. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..155H.
- Kappenman, J. (2006). "Great geomagnetic storms and extreme impulsive geomagnetic field disturbance events – An analysis of observational evidence including the great storm of May 1921". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 188–199. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.055. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..188K.
- Kemp, Bill (July 31, 2016). "PFOP: Solar Superstorm Awed Locals in 1859". The Pantagraph (Bloomington, Ill.). https://www.pantagraph.com/news/local/pfop-solar-superstorm-awed-locals-in/article_b7b6a777-c2a6-5e54-90e5-173a5cadabae.html.
- Li, X.; Temerin, M.; Tsurutani, B.; Alex, S. (2006). "Modeling of 1–2 September 1859 super magnetic storm". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 273–279. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.06.070. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..273L.
- Manchester IV, W. B.; Ridley, A. J.; Gombosi, T. I.; De Zeeuw, D. L. (2006). "Modeling the Sun-to-Earth propagation of a very fast CME". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 253–262. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.09.044. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..253M.
- Nevanlinna, H. (2006). "A study on the great geomagnetic storm of 1859: Comparisons with other storms in the 19th century". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 180–187. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.07.076. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..180N.
- Odenwald, S.; Green, J.; Taylor, W. (2006). "Forecasting the impact of an 1859-calibre superstorm on satellite resources". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 280–297. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.10.046. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..280O.
- Ridley, A. J.; De Zeeuw, D. L.; Manchester, W. B.; Hansen, K. C. (2006). "The magnetospheric and ionospheric response to a very strong interplanetary shock and coronal mass ejection". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 263–272. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.06.010. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..263R.
- Robertclauer, C.; Siscoe, G. (2006). "The great historical geomagnetic storm of 1859: A modern look". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 117–118. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.09.001. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..117R.
- Shea, M.; Smart, D. (2006). "Geomagnetic cutoff rigidities and geomagnetic coordinates appropriate for the Carrington flare Epoch". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 209–214. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.156. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..209S. https://zenodo.org/record/1258752.
- Shea, M.; Smart, D.; McCracken, K.; Dreschhoff, G.; Spence, H. (2006). "Solar proton events for 450 years: The Carrington event in perspective". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 232–238. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.02.100. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..232S. https://zenodo.org/record/1258750.
- Shea, M.; Smart, D. (2006). "Compendium of the eight articles on the "Carrington Event" attributed to or written by Elias Loomis in the American Journal of Science, 1859–1861". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 313–385. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.07.005. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..313S. https://zenodo.org/record/1258762.
- Silverman, S. (2006). "Comparison of the aurora of September 1/2, 1859 with other great auroras". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 136–144. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.157. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..136S.
- Silverman, S. (2006). "Low latitude auroras prior to 1200 C.E. and Ezekiel's vision". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 200–208. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.03.158. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..200S.
- Siscoe, G.; Crooker, N.; Clauer, C. (2006). "Dst of the Carrington storm of 1859". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 173–179. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.02.102. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..173S.
- Smart, D.; Shea, M.; McCracken, K. (2006). "The Carrington event: Possible solar proton intensity–time profile". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 215–225. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.04.116. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..215S.
- Solar Storm 1859 at Solar Storms—Excerpts of Articles from Newspapers concerning the Carrington Event
- Townsend, L. W.; Stephens, D. L.; Hoff, J. L.; Zapp, E. N.; Moussa, H. M.; Miller, T. M.; Campbell, C. E.; Nichols, T. F. (2006). "The Carrington event: Possible doses to crews in space from a comparable event". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 226–231. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.01.111. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..226T.
- Tsurutani, B. T.; Gonzalez, W. D.; Lakhina, G. S.; Alex, S. (2003). "The extreme magnetic storm of 1–2 September 1859". Journal of Geophysical Research 108 (A7): 1268. doi:10.1029/2002JA009504. Bibcode: 2003JGRA..108.1268T. https://zenodo.org/record/1000695.
- Wilson, L. (2006). "Excerpts from and Comments on the Wochenschrift für Astronomie, Meteorologie und Geographie, Neue Folge, zweiter Jahrgang (new series 2)". Advances in Space Research 38 (2): 304–312. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2006.07.004. Bibcode: 2006AdSpR..38..304W.
 KSF
KSF