Surface energy transfer
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
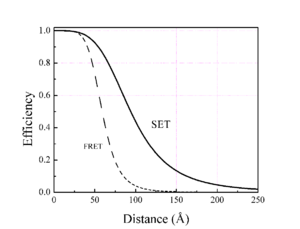
Surface energy transfer (SET) is a dipole-surface energy transfer process involving a metallic surface and a molecular dipole.[1]
Formula
The SET rate follows the inverse of the fourth power of the distance[2]
where
- is the donor emission lifetime;
- is the distance between donor-acceptor;
- is the distance at which SET efficiency decreases to 50% (i.e., equal probability of energy transfer and spontaneous emission).
Efficiency
The energy transfer efficiency also follows a similar form
Due to the fourth power dependence SET can cover a distance more than 15 nm, which is almost twice the efficiency of FRET.[3] Theoretically predicted in 1978 by Chance et al. it was proved experimentally in 2000s by different workers.[4]
Applications
The efficiency of SET as nanoruler has been used in live cells.[5]
Gold nano particles are frequently used in these studies as the nanoparticle surface.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ↑ Christopher J. Breshike; Ryan A. Riskowski; Geoffrey F. Strouse (2013). "Leaving Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Behind: Nanometal Surface Energy Transfer Predicts the Size-Enhanced Energy Coupling between a Metal Nanoparticle and an Emitting Dipole". J. Phys. Chem. C 117 (45): 23942–23949. doi:10.1021/jp407259r.
- ↑ C. S. Yun (2005). "Nanometal Surface Energy Transfer in Optical Rulers, Breaking the FRET Barrier". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (9): 3115–3119. doi:10.1021/ja043940i. PMID 15740151.
- ↑ T. L. Jennings; M. P. Singh; G. F. Strouse (2006). "Fluorescent Lifetime Quenching near d = 1.5 nm Gold Nanoparticles: Probing NSET Validity". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (16): 5462–5467. doi:10.1021/ja0583665. PMID 16620118.
- ↑ R. Chance; A. Prock; R. Silbey (1978). "Molecular Fluorescence and Energy Transfer Near Interfaces". Adv. Chem. Phys.. Advances in Chemical Physics 60: 1. doi:10.1002/9780470142561.ch1. ISBN 978-0-471-03459-9.
- ↑ Yan Chen (2010). "A Surface Energy Transfer Nanoruler for Measuring Binding Site Distances on Live Cell Surfaces". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132 (46): 16559–16570. doi:10.1021/ja106360v. PMID 21038856.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Surface_energy_transfer14 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 09:30:43↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF