Synchronous condenser
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min

In electrical engineering, a synchronous condenser (sometimes called a syncon, synchronous capacitor or synchronous compensator) is a DC-excited synchronous motor, whose shaft is not connected to anything but spins freely.[1] Its purpose is not to convert electric power to mechanical power or vice versa, but to adjust conditions on the electric power transmission grid. Its field is controlled by a voltage regulator to either generate or absorb reactive power as needed to adjust the grid's voltage, or to improve power factor. The condenser’s installation and operation are identical to large electric motors and generators (some generators are actually designed to be able to operate as synchronous condensers with the prime mover disconnected[2]).
Increasing the device's field excitation results in its furnishing reactive power (measured in units of var) to the system. Its principal advantage is the ease with which the amount of correction can be adjusted.
Synchronous condensers are an alternative to capacitor banks and static VAR compensators for power-factor correction in power grids.[3] One advantage is that the amount of reactive power from a synchronous condenser can be continuously adjusted. Reactive power from a capacitor bank decreases when grid voltage decreases while the reactive power from a synchronous condenser inherently increases as voltage decreases.[1] Additionally, synchronous condensers are more tolerant of power fluctuations and severe drops in voltage.[3] However, synchronous machines have higher energy losses than static capacitor banks.[1]
Most synchronous condensers connected to electrical grids are rated between 20 MVAR (megavar) and 200 MVAR and many are hydrogen cooled. There is no explosion hazard as long as the hydrogen concentration is maintained above 70%, typically above 91%.[4] A syncon can be 8 metres long and 5 meters tall, weighing 170 tonnes.[5]
Synchronous condensers also help stabilize grids. The inertial response of the machine and its inductance can help stabilize a power system during rapid fluctuations of loads such as those created by short circuits or electric arc furnaces. For this reason, large installations of synchronous condensers are sometimes used in association with high-voltage direct current converter stations to supply reactive power to the alternating current grid. Synchronous condensers are also finding use in facilitating the switchover between power grids[6] and providing power grid stabilization as turbine-based power generators are replaced with solar and wind energy.[7][3]
Theory
A rotating coil [8] in a magnetic field tends to produce a sine-wave voltage. When connected to a circuit some current will flow depending on how the voltage on the system is different from this open-circuit voltage. Note that mechanical torque (produced by a motor, required by a generator) corresponds only to the real power. Reactive power does not result in any torque.
As the mechanical load on a synchronous motor increases, the stator current increases regardless of the field excitation. For both under- and over-excited motors, the power factor (p.f.) tends to approach unity with increase in mechanical load. This change in power factor is larger than the change in with increase in load.
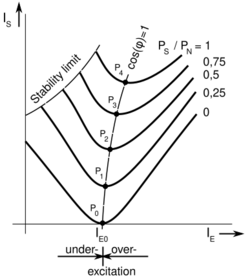
The phase of armature current varies with field excitation. The current has larger values for lower and higher values of excitation. In between, the current has minimum value corresponding to a particular excitation (see graph on right). The variations of with excitation are known as curves because of their shape.
For the same mechanical load, the armature current varies with field excitation over a wide range and so causes the power factor also to vary accordingly. When over-excited, the motor runs with leading power factor (and supplies vars to the grid) and when under-excited with lagging power factor (and absorbs vars from the grid). In between, the power factor is unity. The minimum armature current corresponds to the point of unity power factor (voltage and current in phase).
As in a synchronous motor, the stator of the machine is connected to a three-phase supply of voltage (assumed to be constant), and this creates a rotating magnetic field within the machine. Likewise, the rotor is excited with a DC current to act as an electromagnet. In normal operation the rotor magnet follows the stator field at synchronous speed. The rotating electromagnet induces a three-phase voltage in the stator windings as if the machine were a synchronous generator. If the machine is considered to be ideal, with no mechanical, magnetic, or electrical losses, its equivalent circuit will be an AC generator in series with the winding inductance of the stator. The magnitude of depends on the excitation current and the speed of rotation, and as the latter is fixed, depends only on . If is critically adjusted to a value , will be equal and opposite to , and the current in the stator will be zero. This corresponds to the minimum in the curve shown above. If, however, is increased above , will exceed , and the difference is accounted for by a voltage appearing across the stator inductance : where is the stator reactance. Now the stator current is no longer zero. Since the machine is ideal, , and will all be in phase, and will be entirely reactive (i.e. in phase quadrature). Viewed from the supply side of the machine's terminals, a negative reactive current will flow out of the terminals, and the machine will therefore appear as a capacitor, the magnitude of whose reactance will fall as increases above . If is adjusted to be less than , will exceed , and a positive reactive current will flow into the machine. The machine will then appear as an inductor whose reactance falls as is reduced further. These conditions correspond to the two rising arms of the V-curves (above). In a practical machine with losses, the equivalent circuit will contain a resistor in parallel with the terminals to represent mechanical and magnetic losses, and another resistor in series with the generator and L, representing copper losses in the stator. Thus in a practical machine will contain a small in-phase component, and will not fall to zero.
Application
An over-excited synchronous motor has a leading power factor. This makes it useful for power-factor correction of industrial loads. Both transformers and induction motors draw lagging (magnetising) currents from the line. On light loads, the power drawn by induction motors has a large reactive component and the power factor has a low value. The added current flowing to supply reactive power creates additional losses in the power system. In an industrial plant, synchronous motors can be used to supply some of the reactive power required by induction motors. This improves the plant power factor and reduces the reactive current required from the grid.
A synchronous condenser provides stepless automatic power-factor correction with the ability to produce up to 150% additional vars. The system produces no switching transients and is not affected by system electrical harmonics (some harmonics can even be absorbed by synchronous condensers). They will not produce excessive voltage levels and are not susceptible to electrical resonances. Because of the rotating inertia of the synchronous condenser, it can provide limited voltage support during very short power drops.
Rotating synchronous condensers were introduced in 1930s[2] and were common in 1950s, but due to high costs were eventually displaced in new installations by the static var compensators (SVCs).[2] They remain an alternative (or a supplement) to capacitors for power-factor correction because of problems that have been experienced with harmonics causing capacitor overheating and catastrophic failures. Synchronous condensers are also useful for supporting voltage levels. The reactive power produced by a capacitor bank is in direct proportion to the square of its terminal voltage, and if the system voltage decreases, the capacitors produce less reactive power, when it is most needed,[2] while if the system voltage increases the capacitors produce more reactive power, which exacerbates the problem. In contrast, with a constant field, a synchronous condenser naturally supplies more reactive power to a low voltage and absorbs more reactive power from a high voltage, plus the field can be controlled. This reactive power improves voltage regulation in situations such as when starting large motors, or where power must travel long distances from where it is generated to where it is used, as is the case with power wheeling, the transmission of electric power from one geographic region to another within a set of interconnected electric power systems.
When compared to an SVC, the synchronous condenser has a few advantages:[2]
- the rotational inertia allows it to ride-through the short circuit condition;
- reactive power delivery does not depend on the line voltage;
- it is relatively insensitive to overloads and typically can operate for half an hour at 110-120% of capacity and can briefly deliver up to 200% of rated reactive power.
Synchronous condensers may also be referred to as Dynamic Power Factor Correction systems. These machines can prove very effective when advanced controls are utilized. A PLC based controller with PF controller and regulator will allow the system to be set to meet a given power factor or can be set to produce a specified amount of reactive power.
On electric power systems, synchronous condensers can be used to control the voltage on long transmission lines, especially for lines with a relatively high ratio of inductive reactance to resistance.[9]
In addition to purpose-built units, existing steam or combustion turbines can be retrofit for use as a syncon. In this situation, the turbine can be retrofit with either an auxiliary starting motor, use the existing generator as an electric means of startup, or a synchronous self-shifting (SSS) clutch with the existing turbine/fuel source.[10] Using a separate starter motor is usually recommended instead of the existing generator for startup, as the generator shaft/coupling generally can't withstand the torques imposed on them during startup. Using purely electric startup methods, the syncon relies on the starter motor to provide an initial startup, and the generator or auxiliary motor provide the system with the necessary rotational inertia to produce reactive power. With the SSS clutch retrofit, the existing turbine setup is largely reused. Here, the turbine uses its existing fuel source to start and sync to the grid, which is when the SSS clutch disconnects the turbine and generator. The generator thus uses grid energy to keep spinning, to provide leading or lagging reactive power as needed. Each setup has its own advantages and disadvantages: the electric drive only systems do not require combustion from the old turbines, where an old generation system would generally produce more emissions than a newer one of the same fuel type while the combustion driven system would have the ability to alternate between generating real and reactive power as needed.[11]
Gallery
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 B. M. Weedy, Electric Power Systems Second Edition, John Wiley and Sons, London, 1972, ISBN 0-471-92445-8 page 149
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Kundur 1994, p. 638.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Fairley, Peter (2015-07-24). "Zombie Coal Plants Reanimated to Stabilize the Grid". IEEE. https://spectrum.ieee.org/zombie-coal-plants-reanimated-to-stabilize-the-grid.
- ↑ "All About Circuits". http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_2/chpt_13/3.html.
- ↑ Parkinson, Giles (25 October 2021). "Wind and solar limits relaxed after four big spinning machines installed" (in en-AU). https://reneweconomy.com.au/wind-and-solar-limits-relaxed-after-four-big-spinning-machines-installed/.
- ↑ Fairley, Peter (2023-11-13). "To Free The Baltic Grid, Old Technology Is New Again". IEEE. https://spectrum.ieee.org/baltic-power-grid.
- ↑ "GE synchronous condensers – 100 years on". 2020-02-12. https://www.modernpowersystems.com/features/featurege-synchronous-condensers-100-years-on-7769875/.
- ↑ http://www.pscpower.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Power-Factor.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ↑ Donald Fink, Wayne Beaty (ed) Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers Eleventh Edition, Mc Graw Hill, 1978, ISBN 0-07-020974-X, page 14-33
- ↑ POWER (2020-09-01). "Putting Idle Turbine Generators to Work" (in en-US). https://www.powermag.com/putting-idle-turbine-generators-to-work/.
- ↑ Directors, Clarion Energy Content (2011-10-01). "Converting Existing Synchronous Generators into Synchronous Condensers" (in en-US). https://www.power-eng.com/coal/converting-existing-synchronous-generators-into-synchronous-condensers/.
Sources
- Kundur, Prabha (22 January 1994). "Reactive Power and Voltage Control". Power System Stability and Control. McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 627–687. ISBN 978-0-07-035958-1. OCLC 1054007373. https://www.rgpv.ac.in/campus/EX/Reactive%20power%20and%20voltage%20control.pdf.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF



