Outline of Thailand
Topic: Place
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
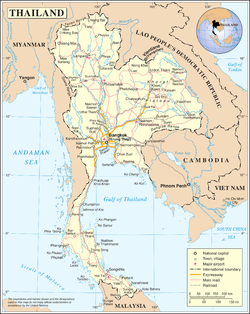
The following outline is an overview of and topical guide to Thailand.
Thailand is a country at the centre of the Indochina peninsula in Southeast Asia, known as Siam until 1939. As of 2023[update] Thailand is a monarchy governed by a military junta that took power in May 2014. Although a constitutional system was established in 1932, the monarchy and military have continued to intervene periodically in politics. Thailand experienced rapid economic growth between 1985 and 1996, becoming a newly industrialized country and a major exporter. Manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy. Among the ten ASEAN countries, Thailand ranks second in quality of life and the country's HDI had been rated as "high". Its large population and growing economic influence have made it a middle power in the region and around the world.
Tai groups and people who speak Tai are the majority population in Thailand, with Tai-Lao speakers making up 25% of the population. The heartland of Thailand is the Chao Phraya River Valley, where the original inhabitants were Mon-speaking people. The Mon people are now a minority, and the Mon language is endangered. The valley later gained control over Eastern Thailand as well, known as the Korat Plateau. This area is not mountainous, as its name would suggest. Although the people of this area have largely adopted Thai culture, there is still a mixture of many Tai-Kadai, Khmer, and Cambodian speakers. Northern Thailand is mountainous and holds many minority groups: "hill tribes." Another mountainous region is the Malay Peninsula, where the 3rd largest population of Malay people live. Many in this area speak Mon-related languages.
General reference
- Common English country names: Thailand, archaic Siam
- Official English country name: The Kingdom of Thailand
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): Thai
- Demonym(s): Thai
- Etymology: Name of Thailand
- International rankings of Thailand
- ISO country codes: TH, THA, 764
- ISO region codes: See TH
- Internet country code top-level domain: .th
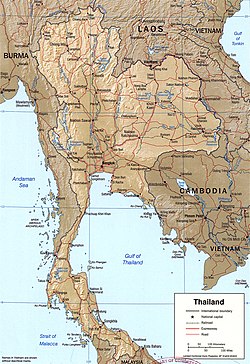
Geography of Thailand
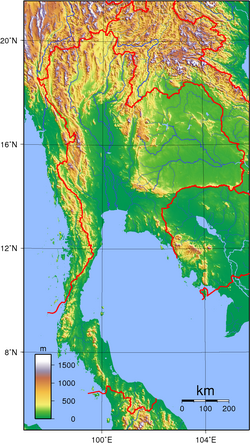
Geography of Thailand
- Thailand is: a country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia
- Time zone: Indochina Time ICT
- Extreme points of Thailand
- High: Doi Inthanon 2,565 m (8,415 ft)
- Low: Gulf of Thailand and Andaman Sea 0 m
- Land boundaries: 4,863 km
 Burma 1,800 km
Burma 1,800 km Laos 1,754 km
Laos 1,754 km Cambodia 803 km
Cambodia 803 km Malaysia 506 km
Malaysia 506 km
- Coastline: 3,219 km
- Population of Thailand: 63,038,247 people (December 2007 estimate) - 20th most populous country
- Area of Thailand: 513,115 km2 (198,115 sq mi) - 49th largest country
- Time in Thailand
- Thai lunar calendar
- Thai solar calendar
- Atlas of Thailand
Environment of Thailand

- Climate of Thailand
- Effect of the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake on Thailand
- Environmental issues in Thailand
- Deforestation in Thailand
- Renewable energy in Thailand
- Protected areas of Thailand
- Biosphere reserves in Thailand
- Forest Parks of Thailand
- Historical parks of Thailand
- National parks of Thailand
- Wildlife of Thailand
- Birds of Thailand
- Mammals of Thailand
Natural geographic features of Thailand

- Islands of Thailand
- Mountains of Thailand
- Thai highlands
- Volcanoes in Thailand
- Rivers of Thailand
- River Systems of Thailand
- World Heritage Sites in Thailand
Regions of Thailand
Regions of Thailand
- Directional regions
- Central Thailand
- Northern Thailand
- Northeast Thailand (Isan)
- Southern Thailand
- Patani (See also South Thailand insurgency)
- Economic regions
- Eastern Seaboard of Thailand
Ecoregions of Thailand
Ecoregions in Thailand
Administrative divisions of Thailand
Administrative divisions of Thailand
- Provinces of Thailand
- Districts of Thailand
- Tambon ("commune" or "subdistrict")
- Cities
- Muban ("village")
- Tambon ("commune" or "subdistrict")
- Districts of Thailand
Provinces of Thailand
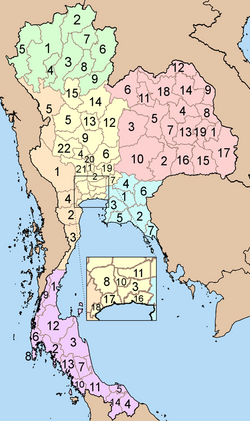
Thailand is divided into 76 provinces (จังหวัด, changwat) and the metropolitan municipality Bangkok (กรุงเทพมหานคร, Krung Thep Maha Nakhon).

Northern
West
|
Isan
|
|
Central
|
East
South
|
Districts of Thailand

Altogether Thailand has 877 districts (อำเภอ; Amphoe), not including the 50 districts of Bangkok which are called khet (เขต) since the Bangkok administration reform in 1972.
Cities in Thailand
List of cities in Thailand
- Capital of Thailand: Bangkok
Demography of Thailand
Demographics of Thailand
Government and politics of Thailand

Politics of Thailand
- Form of government: Constitutional monarchy
- Capital of Thailand: Bangkok (Krung Thep Maha Nakhon)
- Conflicts in Thailand
- 2014 Thai coup d'état
- South Thailand insurgency
- 2020–2021 Thai protests
- Elections in Thailand
- 1933
- 1937
- 1946
- 1948
- February 1957
- December 1957
- 1969
- 1975
- 1976
- 1983
- 1986
- 1988
- March 1992
- September 1992
- 1995
- 1996
- 2001
- 2005
- 2006
- 2007
- 2011
- 2014
- 2019
- Political parties in Thailand
Branches of the government of Thailand
Government of Thailand
Executive branch of the government of Thailand

- Head of state: King of Thailand, Vajiralongkorn
- Head of government: Prime Minister of Thailand, Prayut Chan-o-cha
- Cabinet of Thailand
- Ministries of Thailand
Legislative branch of the government of Thailand
- National Assembly of Thailand (bicameral)
- Upper house: Senate of Thailand
- Lower house: House of Representatives of Thailand
Judicial branch of the government of Thailand
Court system of Thailand
- Constitution Tribunal
- Rulings of the Constitutional Court of Thailand
- Administrative Court of Thailand
- Criminal Court of Thailand
- No juries
Foreign relations of Thailand
Foreign relations of Thailand
- Diplomatic missions in Thailand
- Diplomatic missions of Thailand
- Foreign aid to Thailand
- Thailand Customs
International organization membership
International organization membership of Thailand The Kingdom of Thailand is a member of, or participates in:[1]
|
|
Law and order in Thailand

Law of Thailand
- Constitution of Thailand
- Crime in Thailand
- Human trafficking in Thailand
- Human rights in Thailand
- Censorship in Thailand
- Internet censorship in Thailand
- LGBT rights in Thailand
- Freedom of religion in Thailand
- Censorship in Thailand
- Law enforcement in Thailand
- South Thailand insurgency
Military of Thailand
Military of Thailand
- Command
- Commander-in-chief:
- Ministry of Defence of Thailand
- Commander-in-chief:
- Forces
- Army of Thailand (more pictures)
- Navy of Thailand
- Marine Corps of Thailand
- Royal Thai Navy SEALs
- Air Force of Thailand
- Special forces of Thailand
- Military history of Thailand
- Military ranks of Thailand
History of Thailand


History of Thailand
- Peopling of Thailand
By period
- Prehistoric Thailand
- Early history of Thailand
- Initial states of Thailand (3 BCE-1238)
- Suvarnabhumi
- Dvaravati
- Lavo
- Hariphunchai
- Singhanavati
- Pan Pan
- Raktamaritika
- Langkasuka
- Srivijaya
- Tambralinga
- Sukhothai Kingdom (1238–1448 )
- Ayutthaya Kingdom (1351-1767)
- Thonburi Kingdom (1768–1782)
- Rattanakosin Kingdom (1782–2008)
- Kingdom of Thailand
- History of Thailand (1932–1973)
- History of Thailand (1973–2001)
By region

- Hariphunchai
- Isan
- Lanna
- Nakhon Si Thammarat
- Phitsanulok
By field
- Economic history of Thailand
- Military history of Thailand
- Japanese Invasion of Thailand
- United States Air Force in Thailand
Culture of Thailand

Culture of Thailand
- Architecture of Thailand
- Tallest buildings in Thailand
- Thai stilt house
- Cuisine of Thailand
- Diving in Thailand
- Diving sites in Ko Tao
- Etiquette in Thailand
- Festivals in Thailand
- Languages of Thailand
- Thai alphabet
- Media in Thailand
- Museums in Thailand
- National symbols of Thailand
- Coat of arms of Thailand
- Flag of Thailand
- National anthem of Thailand
- People of Thailand
- Ethnic groups in Thailand
- Indians in Thailand
- Thai names
- Ethnic groups in Thailand
- Prostitution in Thailand
- Public holidays in Thailand
- Women in Thailand
- World Heritage Sites in Thailand
Art in Thailand

- Art in Thailand
- Thai temple art and architecture
- Buddha images in Thailand
- Thai Buddha
- Cinema of Thailand
- List of cinemas in Thailand
- List of films shot in Thailand
- Dance of Thailand
- Literature of Thailand
- Music of Thailand
- Traditional Thai musical instruments
- Television in Thailand
- Theatre in Thailand
- List of theatres in Bangkok
- Video gaming in Thailand
Religion in Thailand
Religion in Thailand
- Buddhism in Thailand
- Dhammayuttika Nikaya
- Maha Nikaya
- List of Buddhist temples in Thailand
- Sangha Supreme Council
- Supreme Patriarch of Thailand
- Christianity in Thailand
- Protestantism in Thailand
- Hinduism in Thailand
- Islam in Thailand
- Sikhism in Thailand
Sports in Thailand
Sport in Thailand
- Badminton in Thailand
- Thailand Open
- Baseball in Thailand
- Boxing in Thailand
- Cricket in Thailand
- Thailand national cricket team
- Thailand national women's cricket team
- Cycling in Thailand
- Football in Thailand
- Football Association of Thailand
- List of football clubs in Thailand
- Thai football league system
- Thailand national football team
- Golf in Thailand
- Ice hockey in Thailand
- Muay Thai
- Rugby union in Thailand
- Thailand women's national rugby union team
- Thailand at the Olympics
- Volleyball in Thailand
Economy and infrastructure of Thailand


Economy of Thailand
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 33rd (thirty-third)
- Economic consequences of the 2006 Thai coup d'état
- Agriculture in Thailand
- Banking in Thailand
- National Bank of Thailand
- List of banks in Thailand
- Communications in Thailand
- Internet in Thailand
- Internet censorship in Thailand
- Telephone numbers in Thailand
- Internet in Thailand
- Companies of Thailand
- Currency of Thailand: Baht
- Economic history of Thailand
- Energy in Thailand
- Energy policy of Thailand
- Energy Industry Liberalization and Privatization (Thailand)
- Mining in Thailand
- Oil industry in Thailand
- Energy Industry Liberalization and Privatization (Thailand)
- Stock Exchange of Thailand
- Thai lottery
- Tourism in Thailand
- 32.6 million international visitors in 2016
- 9th most visited country (2016, World Tourism rankings)[2]
- Transport in Thailand (more pictures)
- Airports in Thailand
- Airports of Thailand
- Rail transport in Thailand
- MRT (Bangkok)
- BTS skytrain
- State Railway of Thailand
- Roads in Thailand
- Thai motorway network
- Airports in Thailand
- Sufficiency economy
Education in Thailand

Education in Thailand
- List of schools in Thailand
- List of schools in Bangkok
- List of international schools in Thailand
- List of universities in Thailand
- List of medical schools in Thailand
- Sanam Luang Dhamma Studies
Health in Thailand

Health in Thailand
- Hospitals in Thailand
- List of hospitals in Thailand
- Thai traditional medicine
See also
Thailand
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Asia
- Outline of geography
References
- ↑ "Thailand". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/thailand/.
- ↑ (in en) UNWTO Tourism Highlights: 2017 Edition | World Tourism Organization. 2017. doi:10.18111/9789284419029. ISBN 9789284419029.
External links
- Google Map of Thailand
- Thaigov.go.th Royal Government of Thailand
- Tourism Authority of Thailand Official tourism website
- Thai National Assembly Official Thai Parliament website
- Mfa.go.th Thailand Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- Thailand Internet Information National Electronics and Computer Technology Center
- CIA - The World Factbook - Thailand
- Birdwatching in Thailand
- Learn Thai Culture.com
- Thailand Country Fact Sheet from the Common Language Project
- Search Thailand
- THAILEX Travel Encyclopedia
- Longdo Map Thailand On-line Thailand map
- Thailand.org Travel Guide
 KSF
KSF

