Principality of Transylvania (1711–1867)
Topic: Place
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
(Grand) Principality of Transylvania | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1711–1867 | |||||||||
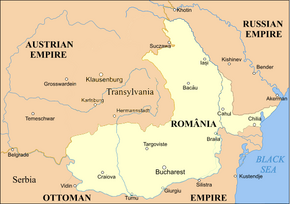 Grand Principality of Transylvania, 1859 | |||||||||
| Capital | Hermannstadt (Nagyszeben, Sibiu) 1711–1791, 1848–1861 Klausenburg (Kolozsvár, Cluj) 1791–1848, 1861–1867 | ||||||||
| Common languages | German, Hungarian, Romanian | ||||||||
| Religion |
| ||||||||
| Monarch | |||||||||
• 1711–1740 | Charles III (first) | ||||||||
• 1848-1867 | Franz Joseph I (last) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Rákóczi's Revolt crushed | 1711 | ||||||||
• Immigration of Transylvanian Landler | 1734–1756 | ||||||||
• Revolt of Horea | 1784 | ||||||||
• Hungarian Revolution | 1848 | ||||||||
• Incorporated into Hungary | 1867 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Principality of Transylvania, from 1765 Grand Principality of Transylvania, was an Austrian crownland[1] and realm of the Hungarian Crown[2][3] ruled by the Habsburg and Habsburg-Lorraine monarchs of the Habsburg Monarchy (later Austrian Empire).[4][5][6] During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848[7] (after the Transylvanian Diet's confirmation on 30 May and the king's approval on 10 June[8][9] that Transylvania again become an integral part of Hungary, an initiative rejected by the Romanians and Saxons who formed the majority population of Transylvania[1][6][10]). After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary.[11] In 1867, as a result of the Austro-Hungarian Compromise, the principality was reunited with Hungary proper.
History
In the Great Turkish War the Habsburg Emperor Leopold I had occupied the vassal Ottoman Principality of Transylvania and forced Prince Michael I Apafi to acknowledge his overlordship in his capacity as King of Hungary. Upon Apafi's death in 1690, Emperor Leopoeld decreed the Diploma Leopoldinum, which affiliated the Transylvanian territory with the Habsburg Monarchy. In 1697 Michael's son and heir Prince Michael II Apafi finally renounced Transylvania in favour of Leopold; the transfer to the Habsburg lands was confirmed by the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz between the Holy League and the Ottoman Empire.
After Rákóczi's War of Independence had failed, the Peace of Szatmár was concluded in 1711: Habsburg control over Transylvania was consolidated, and the Princes of Transylvania were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors (Gubernatoren). In 1765 Maria Theresa and her son Emperor Joseph II proclaimed the Grand Principality of Transylvania, consolidating the special separate status of Transylvania within the Habsburg Monarchy, established by the Diploma Leopoldinum in 1691.
From about 1734 onwards, southern Transylvania became the settlement area of German-speaking Transylvanian Landler expellees, Crypto-Protestants from the Habsburg hereditary lands of Upper Austria, Styria and Carinthia, who were exiled to the easternmost outpost of the Habsburg Monarchy. The area around Sibiu (Hermannstadt) had been colonized by Transylvanian Saxons since medieval times; here the Landler had to settle in regions devastated during the Great Turkish War.
The majority of the Transylvanian population was Romanian, many of them peasants working for Hungarian magnates under the precarious conditions of serfdom. The 1784 Revolt of Horea, Cloșca and Crișan, however, and all demands of political equality were of no avail.
During the 1848 Revolutions, the Hungarian insurgents called for the re-unification of Transylvania with Hungary — opposed by Romanian (Wallachian) revolutionaries led by Avram Iancu — , but also for the abolition of serfdom. The April Laws of 1848 proclaimed the re-unification, but after the Hungarian revolt was crushed, Transylvania remained under military administration for several years, and the March Constitution of Austria defined the Principality of Transylvania as being a separate crown land that is entirely independent of Hungary.[12]
In 1853, the Transylvanian Military Frontier, which existed from 1762, was abolished and again incorporated into Transylvania.
On 19 November 1865, the Transylvanian Diet voted for the affiliation with Hungary, which was codified on 6 December 1868[13]. With the subsequent Austro-Hungarian Compromise (Ausgleich), the centuries-long autonomous status of Hungarian nobility, Székelys and Transylvanian Saxons ended and the Grand Principality of Transylvania was incorporated into Hungary proper within the Dual Monarchy.
Borders
Before its abolition in 1867, the Principality of Transylvania bordered the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary to the northwest and west, the Habsburg Bukovina to the northeast, the Habsburg Military Frontier to the southwest, and the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia to the south and east.
Demographics
| Year | Total | Romanians | Hungarians and Székelys | Germans | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 | ~500,000 | ~50% | ~30% | ~20% | Estimation by Benedek Jancsó[14] |
| 1700 | ~800,000–865,000 | Recent estimates[15] | |||
| 1712-1713 | 34% | 47% | 19% | Official estimate[14] | |
| 1720 | 806,221 | 49.6% | 37.2% | 12.2% | Estimation by Károly Kocsis & Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi[16] |
| 1721 | - | 48,28% | 36.09% | 15.62% | Estimation by Ignác Acsády[17] |
| 1730 | ~725,000 | 57.9% | 26.2% | 15.1% | Austrian statistics |
| 1765 | ~1,000,000 | 55.9% | 26% | 12% | Estimation by Bálint Hóman and Gyula Szekfü |
| 1773[18] | 1,066,017 | 63.5% | 24.2% | 12.3% | |
| 1784 | 1,440,986 | - | - | - | Official census |
| 1790[19] | 1,465,000 | 50.8% | 30.4% | - | |
| 1835 | - | 62.3% | 23.3% | 14.3% | |
| 1850 | 2,073,372 | 59.1% | 25.9% | 9.3% |
Governors
See also
- Transylvania
- List of rulers of Transylvania
- Transylvanian Saxons
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Chambers's Encyclopaedia Vol. IX, 1860, Chambers's Encyclopaedia based on Brockhaus Enzyklopädie, 10th Edition
- ↑ Trócsányi, Zsolt (2002), TRANSYLVANIA IN THE HABSBURG EMPIRE, Akadémiai Kiadó, http://mek.oszk.hu/03400/03407/html/278.html, retrieved 10 March 2016
- ↑ Trócsányi, Zsolt (2002), FROM THE ENLIGHTENMENT TO REACTION UNDER EMPEROR FRANCIS (1771–1830): The Diet of 1790–91;The 'Supplex Libellus Valachorum', Akadémiai Kiadó, http://mek.oszk.hu/03400/03407/html/329.html, retrieved 10 March 2016
- ↑ Penny Cyclopaedia of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge. C. Knight. 1843. pp. 162–. https://books.google.com/books?id=muBPAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA162.
- ↑ Francis Lieber; Edward Wigglesworth (1836). Encyclopædia Americana: A Popular Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, Literature, History, Politics, and Biography, Brought Down to the Present Time ; Including a Copious Collection of Original Articles in American Biography ; on the Basis of the Seventh Edition of the German Conversations-Lexicon. Desilver, Thomas, & Company. pp. 320–. https://books.google.com/books?id=09IuAQAAIAAJ&pg=PA320.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lucy Mallows; Rudolf Abraham (26 November 2012). Transylvania. Bradt Travel Guides. pp. 22–. ISBN 978-1-84162-419-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=Yt1M3egMbWMC&pg=PA22.
- ↑ Laszlo Péter, Hungary's Long Nineteenth Century: Constitutional and Democratic Traditions in a European Perspective, BRILL, 2012, p. 56
- ↑ "Unió Erdéllyel". Múlt-Kor. 29 May 2003. http://mult-kor.hu/cikk.php?id=467.
- ↑ "unió Erdélylyel". Magyar Katolikus Lexikon. http://lexikon.katolikus.hu/U/uni%C3%B3%20Erd%C3%A9lylyel.html.
- ↑ Keith Hitchins (1979). Rumanian studies. An international annual of the humanities and social sciences. Vol. 4. 1976-1979. (Ed. Keith Hitchins). Brill Archive. pp. 32–. ISBN 90-04-06003-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=7rwUAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA32.
- ↑ Austrian Constitution of 4 March 1849. (Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV)
- ↑ Austrian Constitution of 4 March 1849. (Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV)
- ↑ Prof. dr. PÁL Judit - Unió vagy autonómia? Erdély uniójának törvényi szabályozása. Magyar Kisebbség. Nemzetpolitikai szemle. Új sorozat. XIV. évf. 2009. 1-2. (51-52.) sz. 64-80. - Prof. dr. PÁL Judit - Union or autonomy? The legal reagulation of the union of Transylvania. Magyar Kisebbség. Nemzetpolitikai szemle. Új sorozat. XIV. évf. 2009. 1-2. (51-52.) sz. 64-80.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Trócsányi, Zsolt (2002). A NEW REGIME AND AN ALTERED ETHNIC PATTERN (1711–1770) (Demographics), In: Béla Köpeczi, HISTORY OF TRANSYLVANIA Volume II. From 1606 to 1830, Columbia University Press, New York, 2002, p. 2-527, ISBN 0-88033-491-6
- ↑ Trócsányi, Zsolt (2002). A NEW REGIME AND AN ALTERED ETHNIC PATTERN (1711–1770) (Demographics), In: Béla Köpeczi, HISTORY OF TRANSYLVANIA Volume II. From 1606 to 1830, Columbia University Press, New York, 2002, p. 2 - 522/531, ISBN 0-88033-491-6
- ↑ Károly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi, Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin, Simon Publications LLC, 1998, p. 102 (Table 19) [1]
- ↑ Acsády Ignác: Magyarország népessége a Pragamtica Sanctio korában, Magyar statisztikai közlemények 12. kötet - Ignác Acsády: The population of Hungary in the ages of the Pragmatica Sanction, Magyar statisztikai közlemények vol. 12.
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ Peter Rokai – Zoltan Đere – Tibor Pal – Aleksandar Kasaš, Istorija Mađara, Beograd, 2002, pages 376–377.
 KSF
KSF
