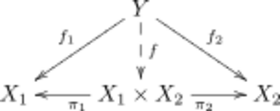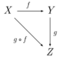Product (category theory)
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
In category theory, the product of two (or more) objects in a category is a notion designed to capture the essence behind constructions in other areas of mathematics such as the Cartesian product of sets, the direct product of groups or rings, and the product of topological spaces. Essentially, the product of a family of objects is the "most general" object which admits a morphism to each of the given objects.
Definition
Product of two objects
Fix a category Let and be objects of A product of and is an object typically denoted equipped with a pair of morphisms satisfying the following universal property:
- For every object and every pair of morphisms there exists a unique morphism such that the following diagram commutes:
Whether a product exists may depend on or on and If it does exist, it is unique up to canonical isomorphism, because of the universal property, so one may speak of the product. This has the following meaning: if is another product, there exists a unique isomorphism such that and .
The morphisms and are called the canonical projections or projection morphisms; the letter (pronounced pi) alliterates with projection. Given and the unique morphism is called the product of morphisms and and is denoted
Product of an arbitrary family
Instead of two objects, we can start with an arbitrary family of objects indexed by a set
Given a family of objects, a product of the family is an object equipped with morphisms satisfying the following universal property:
- For every object and every -indexed family of morphisms there exists a unique morphism such that the following diagrams commute for all
The product is denoted If then it is denoted and the product of morphisms is denoted
Equational definition
Alternatively, the product may be defined through equations. So, for example, for the binary product:
- Existence of is guaranteed by existence of the operation
- Commutativity of the diagrams above is guaranteed by the equality: for all and all
- Uniqueness of is guaranteed by the equality: for all [1]
As a limit
The product is a special case of a limit. This may be seen by using a discrete category (a family of objects without any morphisms, other than their identity morphisms) as the diagram required for the definition of the limit. The discrete objects will serve as the index of the components and projections. If we regard this diagram as a functor, it is a functor from the index set considered as a discrete category. The definition of the product then coincides with the definition of the limit, being a cone and projections being the limit (limiting cone).
Universal property
Just as the limit is a special case of the universal construction, so is the product. Starting with the definition given for the universal property of limits, take as the discrete category with two objects, so that is simply the product category The diagonal functor assigns to each object the ordered pair and to each morphism the pair The product in is given by a universal morphism from the functor to the object in This universal morphism consists of an object of and a morphism which contains projections.
Examples
In the category of sets, the product (in the category theoretic sense) is the Cartesian product. Given a family of sets the product is defined as with the canonical projections Given any set with a family of functions the universal arrow is defined by
Other examples:
- In the category of topological spaces, the product is the space whose underlying set is the Cartesian product and which carries the product topology. The product topology is the coarsest topology for which all the projections are continuous.
- In the category of modules over some ring the product is the Cartesian product with addition defined componentwise and distributive multiplication.
- In the category of groups, the product is the direct product of groups given by the Cartesian product with multiplication defined componentwise.
- In the category of graphs, the product is the tensor product of graphs.
- In the category of relations, the product is given by the disjoint union. (This may come as a bit of a surprise given that the category of sets is a subcategory of the category of relations.)
- In the category of algebraic varieties, the product is given by the Segre embedding.
- In the category of semi-abelian monoids, the product is given by the history monoid.
- In the category of Banach spaces and short maps, the product carries the l∞ norm.[2]
- A partially ordered set can be treated as a category, using the order relation as the morphisms. In this case the products and coproducts correspond to greatest lower bounds (meets) and least upper bounds (joins).
Discussion
An example in which the product does not exist: In the category of fields, the product does not exist, since there is no field with homomorphisms to both and
Another example: An empty product (that is, is the empty set) is the same as a terminal object, and some categories, such as the category of infinite groups, do not have a terminal object: given any infinite group there are infinitely many morphisms so cannot be terminal.
If is a set such that all products for families indexed with exist, then one can treat each product as a functor [3] How this functor maps objects is obvious. Mapping of morphisms is subtle, because the product of morphisms defined above does not fit. First, consider the binary product functor, which is a bifunctor. For we should find a morphism We choose This operation on morphisms is called Cartesian product of morphisms.[4] Second, consider the general product functor. For families we should find a morphism We choose the product of morphisms
A category where every finite set of objects has a product is sometimes called a Cartesian category[4] (although some authors use this phrase to mean "a category with all finite limits").
The product is associative. Suppose is a Cartesian category, product functors have been chosen as above, and denotes a terminal object of We then have natural isomorphisms These properties are formally similar to those of a commutative monoid; a Cartesian category with its finite products is an example of a symmetric monoidal category.
Distributivity
For any objects of a category with finite products and coproducts, there is a canonical morphism where the plus sign here denotes the coproduct. To see this, note that the universal property of the coproduct guarantees the existence of unique arrows filling out the following diagram (the induced arrows are dashed):
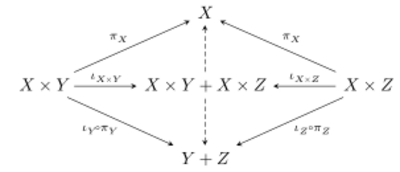
The universal property of the product then guarantees a unique morphism induced by the dashed arrows in the above diagram. A distributive category is one in which this morphism is actually an isomorphism. Thus in a distributive category, there is the canonical isomorphism
See also
- Coproduct – the dual of the product
- Diagonal functor – the left adjoint of the product functor.
- Limit and colimits – Mathematical concept
- Equalizer – Set of arguments where two or more functions have the same value
- Inverse limit – Construction in category theory
- Cartesian closed category – Type of category in category theory
References
- ↑ Lambek J., Scott P. J. (1988). Introduction to Higher-Order Categorical Logic. Cambridge University Press. p. 304.
- ↑ Qiaochu Yuan (June 23, 2012). "Banach spaces (and Lawvere metrics, and closed categories)". https://qchu.wordpress.com/2012/06/23/banach-spaces-and-lawvere-metrics-and-closed-categories/.
- ↑ Lane, S. Mac (1988). Categories for the working mathematician (1st ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag. p. 37. ISBN 0-387-90035-7.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Michael Barr, Charles Wells (1999). Category Theory – Lecture Notes for ESSLLI. p. 62. http://www.let.uu.nl/esslli/Courses/barr/barrwells.ps.
- Adámek, Jiří; Horst Herrlich; George E. Strecker (1990). Abstract and Concrete Categories. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-60922-6. http://katmat.math.uni-bremen.de/acc/acc.pdf.
- Barr, Michael; Charles Wells (1999). Category Theory for Computing Science. Les Publications CRM Montreal (publication PM023). http://www.math.mcgill.ca/triples/Barr-Wells-ctcs.pdf. Retrieved 2016-03-21. Chapter 5.
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1998). Categories for the Working Mathematician. Graduate Texts in Mathematics 5 (2nd ed.). Springer. ISBN 0-387-98403-8.
- Definition 2.1.1 in Borceux, Francis (1994). Handbook of categorical algebra. Encyclopedia of mathematics and its applications 50–51, 53 [i.e. 52]. 1. Cambridge University Press. p. 39. ISBN 0-521-44178-1. https://archive.org/details/handbookofcatego0000borc/page/39.
External links
- Interactive Web page which generates examples of products in the category of finite sets. Written by Jocelyn Paine.
- Product in nLab
 |
 KSF
KSF