Prograph
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
 | |
| Paradigm | multi-paradigm: object-oriented, visual, dataflow |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Acadia University |
| Developer | Various |
| First appeared | 1983 |
| OS | Cross-platform: Classic MacOS, Microsoft Windows, macOS |
| License | Proprietary |
| Major implementations | |
| Prograph CPX, Marten | |
| Influenced by | |
| functional programming, dataflow diagrams | |
Prograph is a visual, object-oriented, dataflow, multiparadigm programming language that uses iconic symbols to represent actions to be taken on data. Commercial Prograph software development environments such as Prograph Classic and Prograph CPX were available for the Apple Macintosh and Windows platforms for many years but were eventually withdrawn from the market in the late 1990s. Support for the Prograph language on macOS has recently reappeared with the release of the Marten software development environment.[1]
History
Research on Prograph started at Acadia University in 1982 as a general investigation into dataflow languages, stimulated by a seminar on functional languages conducted by Michael Levin. Diagrams were used to clarify the discussion, leading to the insight: "since the diagrams are clearer than the code, why not make the diagrams themselves executable!" Thus Prograph - Programming in Graphics - was born as a visual dataflow language. This work was led by Dr. Tomasz Pietrzykowski, with Stan Matwin and Thomas Muldner co-authoring early papers. From 1983 to 1985, research prototypes were built on a Three Rivers PERQ graphics workstation (in Pascal, with the data visualized as fireballs moving down datalinks), and a VAX with a Tektronix terminal, and an experimental compiler was programmed in an IBM PC. This work was continued at Technical University of Nova Scotia by Pietrzykowski and Dr. Philip Cox, including a version done in Prolog.
In 1985, work began on a commercialisable prototype on the Macintosh, the only widely available, low-priced computer with high-level graphics support available at the time. In early 1986, this prototype was taken over by The Gunakara Sun Systems (later renamed to TGS Systems) for commercialisation, TGS formerly being a consulting firm formed by Pietrzykowski at Acadia University. Working with Pietrzykowski and Cox, Terry Kilshaw hired and managed the original development team, with Jim Laskey as the lead developer. In 1987 Mark Szpakowski suggested the merger of object-orientation with visual dataflow, creating an "objectflow" system. After almost four years of development, the first commercial release, v1.2, was introduced at the OOPSLA conference in New Orleans in October 1989. This product won the 1989 MacUser Editor's Choice Award for Best Development Tool. Version 2.0, released in July 1990, added a compiler to the system.
TGS changed its name to Prograph International (PI) in 1990. Although sales were slow, development of a new version, Prograph CPX (Cross-Platform eXtensions) was undertaken in 1992, that was intended to build fully cross-platform applications. This version was released in 1993, and was immediately followed by development of a client-server application framework. Despite increasing sales, the company was unable to sustain operating costs, and following a failed financing attempt in late 1994, went into receivership in early 1995.
As the receivership proceeded, the management and employees of PI formed a new company, Pictorius, which acquired the assets of PI. Shortly afterwards, development of a Windows version of Prograph CPX was begun. Although it was never formally released, versions of Windows Prograph were regularly made available to Prograph CPX customers, some of whom ported existing applications written in Macintosh Prograph, with varying degrees of success.
After management changes at the new company, emphasis shifted from tools development to custom programming and web application development. In April 2002 the web development part of the company was acquired by the Paragon Technology Group of Bermuda and renamed Paragon Canada. The Pictorius name and rights to the Prograph source code were retained by McLean Watson Capital, a Toronto-based investments firm which had heavily funded Pictorius. A reference to Pictorius appeared for a time on the former's Portfolio page, but has since disappeared. The Windows version of CPX was later released for free use, and was available for some time for download from the remnants of the Pictorius website (link below).
A group of Prograph users ("Prographers") calling themselves "The Open Prograph Initiative" (OPI) formed in the late 1990s with the goal of keeping Prograph viable in the face of OS advances by Apple and Microsoft. For a time, the group also sought to create a new open-source visual programming language to serve as Prograph's successor, but with the advent of Andescotia's Marten visual programming environment, participation in the group essentially ceased.
The Prograph language is supported by the Marten IDE from Andescotia Software.[1]
Description
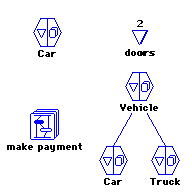
During the 1970s program complexity was growing considerably, but the tools used to write programs were generally similar to those used in the 1960s. This led to problems when working on larger projects, which would become so complex that even simple changes could have side effects that are difficult to fully understand. Considerable research into the problem led many to feel that the problem was that existing programming systems focused on the logic of the program, while in reality the purpose of a program was to manipulate data. If the data being manipulated is the important aspect of the program, why isn't the data the "first class citizen" of the programming language? Working on that basis, a number of new programming systems evolved, including object-oriented programming and dataflow programming.
Prograph took these concept further, introducing a combination of object-oriented methodologies and a completely visual environment for programming. Objects are represented by hexagons with two sides, one containing the data fields, the other the methods that operate on them. Double-clicking on either side would open a window showing the details for that object; for instance, opening the variables side would show class variables at the top and instance variables below. Double-clicking the method side shows the methods implemented in this class, as well as those inherited from the superclass. When a method itself is double-clicked, it opens into another window displaying the logic.

In Prograph a method is represented by a series of icons, each icon containing an instructions (or group of them). Within each method the flow of data is represented by lines in a directed graph. Data flows in the top of the diagram, passes through various instructions, and eventually flows back out the bottom (if there is any output).
Several features of the Prograph system are evident in this picture of a database sorting operation. The upper bar shows that this method, concurrent sort, is being passed in a single parameter, A Database Object. This object is then fed, via the lines, into several operations. Three of these extract a named index (indexA etc.) from the object using the getter operation (the unconnected getter output passes on the "whole" object), and then passes the extracted index to a sort operation. The output of these sort operations are then passed, along with a reference to the original database, to the final operation, update database. The bar at the bottom of the picture represents the outputs of this method, and in this case there are no connections to it and so this method does not return a value. Also note that although this is a method of some class, there is no self; if self is needed, it can be provided as an input or looked up.
In a dataflow language the operations can take place as soon as they have valid inputs for all of their connections. That means, in traditional terms, that each operation in this method could be carried out at the same time. In the database example, all of the sorts could take place at the same time if the computer were capable of supplying the data. Dataflow languages tend to be inherently concurrent, meaning they are capable of running on multiprocessor systems "naturally", one of the reasons that it garnered so much interest in the 1980s.
Loops and branches are constructed by modifying operations with annotations. For instance, a loop that calls the doit method on a list of input data is constructed by first dragging in the doit operator, then attaching the loop modifier and providing the list as the input to the loop. Another annotation, "injection", allows the method itself to be provided as an input, making Prograph a dynamic language to some degree.
Execution
The integrated Prograph development and execution environment also allowed for visual debugging. The usual breakpoint and single-step mechanisms were supported. Each operation in a data flow diagram was visually highlighted as it executed. A tooltip-like mechanism displayed data values when the mouse was held over a data-link when stopped in debug mode. Visual display of the execution stack allowed for both roll-back and roll-forward execution. For many users the visual execution aspects of the language were as important as its edit-time graphical facilities.
The most important run-time debugging feature was the ability to change the code on the fly while debugging. This allowed for bugs to be fixed while debugging without the need to recompile.
Critique
Several problems with the Prograph system are also evident in this method implementation.
Prograph code could be commented using labels. In initial versions, the majority of the included classes were unlabeled. It was often necessary to consult the documentation to determine the proper inputs to a method. This was largely addressed in subsequent versions, but the methods were never documented to the point that the comments explained how and why the methods worked.
Developers had to pay attention to routing of wiring, and to commenting inputs and outputs, to keep their diagrammatic code clean. In the Prograph Database Operation example above, two of the paths cross because one of the wires from the input bar must flow to a certain input on the update operation. This could be avoided by simply dragging and repositioning the 'indexA' and 'sort' icons to be inside the leftmost wire, but in general terms there was no way to avoid this sort of literal spaghetti code.
Another problem was a profusion of windows. When moving around the Prograph workspace, the IDE generally required a new window to be opened to see the contents of methods.
See also
- Visual programming language
- Spreadsheet 2000, a unique spreadsheet written in Prograph
- LabVIEW, a graphical programming application.
- PWCT
Further reading
- Cox, P.T.; Pietrzykowski, T. (1984), "Advanced Programming Aids in Prograph", Technical Report 8408, Halifax, Nova Scotia: School of Computer Science, Technical University of Nova Scotia.
- Cox, P.T.; Mulligan, I.J. (1984), "Compiling the graphical functional language Prograph", Technical Report 8402, Halifax, Nova Scotia: School of Computer Science, Technical University of Nova Scotia.
- Matwin, S.; Pietrzykowski, T. (1985), "Prograph: A Preliminary Report", Computer Languages 10 (2): 91–126, doi:10.1016/0096-0551(85)90002-5.
- Kilshaw, Terry (May 1991), "Prograph Primitives", MacTech Magazine 7 (5), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.07/07.05/PrographPrimitive/index.html.
- Kilshaw, Terry (January 1992), "Prograph 2.5", MacTech Magazine 8 (1), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.08/08.01/Prograph2.5/index.html.
- Kilshaw, Terry (January 1993), "A Pictorial Button Class in Prograph", MacTech Magazine 9 (1), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.09/09.01/PictButton/index.html.
- Kilshaw, Terry (March 1994), "A Review of Prograph CPX 1.0", MacTech Magazine 10 (3): 64–74, http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.10/10.03/PrographReview/index.html.
- Schmucker, Kurt (November 1994), "Prograph CPX - A Tutorial", MacTech Magazine 10 (11), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.10/10.11/PrographCPXTutorial/index.html.
- Shafer, Dan (1994), The Power of Prograph CPX, U.S.A: The Reader Network, ISBN 1-881513-02-5.
- Schmucker, Kurt (January 1995), "Commands and Undo in Prograph CPX", MacTech Magazine 11 (1), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.11/11.01/CommandsandUndoCPX/index.html.
- Schmucker, Kurt (March 1995), "Filters & Sieves in Prograph CPX", MacTech Magazine 11 (3), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.11/11.03/PrographUndo/index.html.
- Schmucker, Kurt (May 1995), "MacApp and Prograph CPX - A Comparison", MacTech Magazine 11 (5), http://www.mactech.com/articles/mactech/Vol.11/11.05/MacAppandPrograph/index.html.
References
External links
- Pictorius - Pictorius's home page, no longer even having a DNS record. The Prograph downloads could for a time still be found at https://archive.today/20010425093223/http://192.219.29.95/prograph.html, but this link now times out.
- Articles on Prograph - 10 articles on Prograph, covering history and language
- Prograph CPX - A Tutorial - an excellent article on the system, dating to shortly after the original release of Prograph CPX
- Visual Programming Languages: A Survey - includes a short overview of the Prograph system
- The Open Prograph Initiative - Home page of the group interested in creating an open source version of Prograph
- Visual Programming with Prograph CPX - Textbook on Prograph CPX
- [1] - December 28, 2011 announcement of beta release of Marten.
- [2] - The Computer Chronicles - Visual Programming Languages (1993)
 |
 KSF
KSF