Octave of Easter
Topic: Religion
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
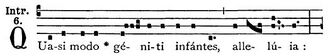
The Octave of Easter is the eight-day period (octave) in Eastertide that starts on Easter Sunday and concludes with the following Sunday.
| Part of a series on |
| Christianity |
|---|
|
|
External
The Octave of a feast refers to an eight-day festal period commencing with that feast. In the ordinary form of the Roman Rite, Easter is one of two solemnities that carries an octave, the second being Christmas Day. In the extraordinary form of the Roman Rite, many solemnities carry octaves.
The name Quasimodo came from the Latin text of the traditional Introit for this day, which begins "Quasi modo geniti infantes..." from 1 Peter 2:2,[1] roughly translated as "As newborn babes [desire the rational milk without guile]...".[1Pt 2:2] Literally, quasi modo means "as if in [this] manner".
Western churches

On the Octave Day of Easter, called Saint Thomas Sunday in the East, the Gospel reading is always John 20:19-29, relating the appearance of Christ to his disciples, with Thomas the Apostle present, on the Sunday following his resurrection. A traditional name in English is Low Sunday, perhaps given this name because of the contrast with the high festival of Easter on the preceding Sunday,[2] or the word "Low" may be a corruption of Latin Laudes, the first word of a sequence in use in the Sarum Rite.[3] Another name is Quasimodo Sunday, from the first words of the introit in Latin.[4]
Easter Week was known as ebdomada alba (white week) or in albis (in white), because of the white robes that those who had been baptized at the Easter Vigil used at the celebrations each day until Saturday.[5] The pre-Tridentine edition of the Roman Missal, published in 1474, called Saturday in albis, short for in albis depositis or in albis deponendis (of removal of the white garments), a name that was kept in the Tridentine versions of the Missal for that Saturday. In the 1604 edition of the Tridentine Missal, but not in the original 1570 edition, the description in albis was applied also to the following Sunday, the octave day of Easter.[6]
The name in albis was dropped in the 1969 revision of the Roman Missal, which calls this Sunday the Second Sunday of Easter. In the third edition of this Missal, promulgated in 2000 but published only in 2002, the Sunday took what is now its official name: "Second Sunday of Easter or of Divine Mercy".
Octave day
"The Octave Day of Easter" refers only to the last day of the Octave. Another name is White Sunday. It is also called Low Sunday, particularly in the Anglican Communion. It may be called Thomas Sunday, especially among Byzantine Rite Christians.
Divine Mercy Sunday
On 30 April 2000, the second Sunday of Easter was designated as Divine Mercy Sunday (or the Feast of Mercy) by Pope John Paul II, who fulfilled the wish which Jesus revealed to saint Faustina Kowalska, saying that any Catholic who goes to Confession – the Sacrament of Penance – then receives the Holy Eucharist on this day will be liberated from any punishment after death.
The Saturday before Divine Mercy Sunday is the culmination of the novena to the Divine Mercy of Jesus, a devotion given to St. Faustina (Maria Faustina Kowalska), and is based upon an entry in her diary stating that anyone who participates in the Mass and receives the sacraments of Confession and the Eucharist on this day is assured by Jesus of full remission of their sins and punishments. The devotion was actively promoted by Pope John Paul II, who canonized St. Faustina and designated the Sunday after Easter as the Sunday of the Divine Mercy (Dominica II Paschae seu de divina misericordia) in the General Roman Calendar.[7] John Paul II, who died in April 2005 on the vigil of Divine Mercy Sunday, was beatified on Divine Mercy Sunday, 1 May 2011, by his successor, Pope Benedict XVI.[8] and was canonized, with Pope John XXIII on Divine Mercy Sunday, 27 April 2014, by Pope Francis.
Chile

In Chile , mainly in Santiago Metropolitan Region, on Quasimodo Sunday is celebrated the Cuasimodo Feast.[citation needed] Huasos in adorned carriages or bicycles accompany the priest to give communion to the infirm.
Byzantine Rite churches
Antipascha is the name given to the eighth day of Pascha (Easter) in the Eastern Orthodox and certain Eastern Catholic churches. According to the Synaxarium, "On this Sunday, the second Sunday of Pascha, we celebrate the Antipascha, that is to say the re-dedication of the Resurrection of Christ, and also commemorate the event of the Holy Apostle Thomas' touching the wounds of Christ."[9]
Thomas Sunday and Renewal Sunday are other names by which this Sunday is known. The former name refers to the event commemorated that day, described in the Gospel passage read that day at the Divine Liturgy, (John 20:19-31), which recounts the story of Christ appearing to the Apostle Thomas in order to dispel the latter's doubt about the Resurrection.[10] Among Eastern Christians Thomas is not so much remembered as "doubting Thomas," but is rather remembered for his confession of faith: "My Lord and my God," thus being the first to publicly proclaim the two natures of Christ: human and divine. The latter name reflects that on that day the celebration of the Resurrection is repeated and renewed.
The entire week from Pascha to Thomas Sunday, known as Bright Week, is considered to be one continuous day.
Literary note
- Quasimodo, protagonist of the 1831 French novel Notre Dame de Paris (most often called in English The Hunchback of Notre Dame) by Victor Hugo, was found abandoned on the doorsteps of Notre Dame Cathedral on the Sunday after Easter, AD 1467. In the words of the novel:
He [sc. archdeacon Claude Frollo, Quasimodo's adoptive father] baptized his adopted child and called him Quasimodo; whether it was that he chose thereby to commemorate the day when he had found him, or that he meant to mark by that name how incomplete and imperfectly molded the poor little creature was. Indeed, Quasimodo, one-eyed, hunchbacked, and bow-legged, could hardly be considered as anything more than an almost.[11]
References
- ↑ The full line is Quasi modo geniti infantes, rationabile, sine dolo lac concupiscite, from Catholic Encyclopedia listing for Low Sunday. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ↑ The Chambers Dictionary (Allied Publishers 1998 ISBN 978-8-18606225-8), p. 954
- ↑ C. Frederick Barbee, Paul F. M. Zahl (editors), The Collects of Thomas Cranmer (Eerdmans 2006 ISBN 978-0-80281759-4), p. 52
- ↑ Elizabeth Knowles (editor), The Oxford Dictionary of Phrase and Fable (Oxford University Press 2006 ISBN 978-0-19157856-4)
- ↑ Patrick Regan, Advent to Pentecost (Liturgical Press 2012), pp. 242-243
- ↑ Regan 2012, pp. 246-249
- ↑ A Divine Mercy Resource by Richard Torretto (2010), pp. 188-190. ISBN 1-450-23236-1.
- ↑ "Pope paves way to beatification of John Paul II". bbc.news.co.uk. 14 January 2011. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-12191423. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ↑ "Synaxarion: ANTIPASCHA - Thomas Sunday". Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ↑ Sokolof, Archpriest Dimitrii (2001) [1899]. Manual of the Orthodox Church's Divine Services. Jordanville, New York: Holy Trinity Monastery. pp. 109. ISBN 0-884-65067-7. http://www.ccel.org/ccel/sokolof/services.toc.html.
- ↑ Hugo, Victor (1996) [1831]. The Hunchback of Notre-Dame. Penguin Books. pp. 147–148. ISBN 978-01-4062-222-5.
External links
- Thomas Sunday Orthodox icon and synaxarium
 Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Low Sunday". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Low Sunday". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.- Feast of Mercy
- What is Divine Mercy Sunday? Find out the basics
| Preceded by Easter Sunday |
Sundays of the Roman Catholic liturgical calendar Octave of Easter (Quasimodo Sunday) Divine Mercy Sunday (Dominica in albis) 2nd Sunday of Easter |
Succeeded by Jubilate Sunday 3rd Sunday of Easter |
 KSF
KSF
