Seam carving
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
Seam carving (or liquid rescaling) is an algorithm for content-aware image resizing, developed by Shai Avidan, of Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL), and Ariel Shamir, of the Interdisciplinary Center and MERL. It functions by establishing a number of seams (paths of least importance) in an image and automatically removes seams to reduce image size or inserts seams to extend it. Seam carving also allows manually defining areas in which pixels may not be modified, and features the ability to remove whole objects from photographs.
The purpose of the algorithm is image retargeting, which is the problem of displaying images without distortion on media of various sizes (cell phones, projection screens) using document standards, like HTML, that already support dynamic changes in page layout and text but not images.[1]
Image Retargeting was invented by Vidya Setlur, Saeko Takage, Ramesh Raskar, Michael Gleicher and Bruce Gooch in 2005.[2] The work by Setlur et al. won the 10-year impact award in 2015[where?].
Seams
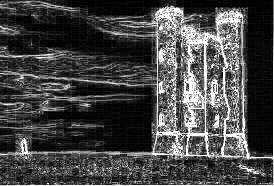
Seams can be either vertical or horizontal. A vertical seam is a path of pixels connected from top to bottom in an image with one pixel in each row.[1] A horizontal seam is similar with the exception of the connection being from left to right. The importance/energy function values a pixel by measuring its contrast with its neighbor pixels.
Process
The below example describes the process of seam carving:
| Step | Image |
|---|---|
| 1) Start with an image. | |
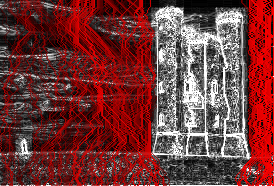
| 2) Calculate the weight/density/energy of each pixel. This can be done by various algorithms: gradient magnitude, entropy, visual saliency, eye-gaze movement.[1] Here we use gradient magnitude. | |
| 3) From the energy, make a list of seams. Seams are ranked by energy, with low energy seams being of least importance to the content of the image. Seams can be calculated via the dynamic programming approach below. | |
| 4) Remove low-energy seams as needed. | |
| 5) Final image. |
The seams to remove depends only on the dimension (height or width) one wants to shrink. It is also possible to invert step 4 so the algorithm enlarges in one dimension by copying a low energy seam and averaging its pixels with its neighbors.[1]
Computing seams
Computing a seam consists of finding a path of minimum energy cost from one end of the image to another. This can be done via Dijkstra's algorithm, dynamic programming, greedy algorithm or graph cuts among others.[1]
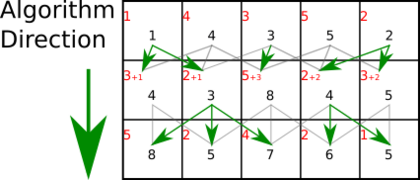
Dynamic programming
Dynamic programming is a programming method that stores the results of sub-calculations in order to simplify calculating a more complex result. Dynamic programming can be used to compute seams. If attempting to compute a vertical seam (path) of lowest energy, for each pixel in a row we compute the energy of the current pixel plus the energy of one of the three possible pixels above it.
The images below depict a DP process to compute one optimal seam.[1] Each square represents a pixel, with the top-left value in red representing the energy value of that pixel. The value in black represents the cumulative sum of energies leading up to and including that pixel.
The energy calculation is trivially parallelized for simple functions. The calculation of the DP array can also be parallelized with some interprocess communication. However, the problem of making multiple seams at the same time is harder for two reasons: the energy needs to be regenerated for each removal for correctness and simply tracing back multiple seams can form overlaps. Avidan 2007 computes all seams by removing each seam iteratively and storing an "index map" to record all the seams generated. The map holds a "nth seam" number for each pixel on the image, and can be used later for size adjustment.[1]
If one ignores both issues however, a greedy approximation for parallel seam carving is possible. To do so, one starts with the minimum-energy pixel at one end, and keep choosing the minimum energy path to the other end. The used pixels are marked so that they are not picked again.[3] Local seams can also be computed for smaller parts of the image in parallel for a good approximation.[4]
Issues
- The algorithm may need user-provided information to reduce errors. This can consist of painting the regions which are to be preserved. With human faces it is possible to use face detection.
- Sometimes the algorithm, by removing a low energy seam, may end up inadvertently creating a seam of higher energy. The solution to this is to simulate a removal of a seam, and then check the energy delta to see if the energy increases (forward energy). If it does, prefer other seams instead.[5]
Implementations
Adobe Systems acquired a non-exclusive license to seam carving technology from MERL,[6] and implemented it as a feature in Photoshop CS4, where it is called Content Aware Scaling.[7] As the license is non-exclusive, other popular computer graphics applications (e. g. GIMP, digiKam, and ImageMagick) as well as some stand-alone programs (e. g. iResizer)[8] also have implementations of this technique, some of which are released as free and open source software.[9][10][11]
Improvements and extensions
- Better energy function and application to video by introducing 2D (time+1D) seams.[5]
- Multi-operator: Combine with cropping and scaling.[13]
- Much faster removal of multiple seams[14]
A 2010 review of eight image retargeting methods found that seam carving produced output that was ranked among the worst of the tested algorithms. It was, however, a part of one of the highest-ranking algorithms: the multi-operator extension mentioned above (combined with cropping and scaling).[15]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Avidan, Shai; Shamir, Ariel (July 2007). "Seam carving for content-aware image resizing" (in en). ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 papers. p. 10. doi:10.1145/1275808.1276390. ISBN 978-1-4503-7836-9.
- ↑ Vidya Setlur; Saeko Takage; Ramesh Raskar; Michael Gleicher; Bruce Gooch (December 2005). "Automatic image retargeting" (in EN). Proceedings of the 4th international conference on Mobile and ubiquitous multimedia - MUM '05. pp. 59–68. doi:10.1145/1149488.1149499. ISBN 0-473-10658-2.
- ↑ Bist; Palakkode (2016). "Parallel Seam Carving". http://www.andrew.cmu.edu/user/abist/results.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Chen-Kuo Chiang; Shu-Fan Wang; Yi-Ling Chen; Shang-Hong Lai (November 2009). "Fast JND-Based Video Carving With GPU Acceleration for Real-Time Video Retargeting". IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 19 (11): 1588–1597. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2009.2031462.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Improved Seam Carving for Video Retargeting. Michael Rubinstein, Ariel Shamir, Shai Avidan. SIGGRAPH 2008.
- ↑ Mitsubishi Electric press release, Business Wire, December 16, 2008.
- ↑ Adobe Photoshop CS4 new feature list.
- ↑ iResizer Content aware image resizing software by Teorex
- ↑ Liquid Rescale, seam carving plug-in for GIMP
- ↑ Announcement of inclusion in digiKam
- ↑ Seam carving capability included in ImageMagick
- ↑ "Improved seam carving with forward energy". https://avikdas.com/2019/07/29/improved-seam-carving-with-forward-energy.html.
- ↑ Multi-operator Media Retargeting. Michael Rubinstein, Ariel Shamir, Shai Avidan. SIGGRAPH 2009.
- ↑ Real-time content-aware image resizing Science in China Series F: Information Sciences, 2009 SCIENCE IN CHINA PRESS.
- ↑ Rubinstein, Michael; Gutierrez, Diego; Sorkine, Olga; Shamir, Ariel (2010). "A Comparative Study of Image Retargeting". ACM Transactions on Graphics 29 (5): 1–10. doi:10.1145/1882261.1866186. http://people.csail.mit.edu/mrub/papers/retBenchmark.pdf. See also the RetargetMe benchmark.
External links
- Interactive demo of seam carving
- Seam Carving demonstration videos:
- on YouTube
- on Ariel Shamir's pages on the Interdisciplinary Center web site (higher resolution)
- Explanation of seam carving (Liquid rescaling) at the ImageMagick website
- Implementation tutorial of seam carving
- HitPaw Video Object Remover
 |
 KSF
KSF