Eastern culture
Topic: Social
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
Eastern culture, also known as Eastern civilization and historically as Oriental culture, is an umbrella term for the diverse cultural heritages of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, artifacts and technologies of the Eastern world.
While there is no singular and catch-all "Eastern culture", there are subgroups within it, such as countries within East Asia, Southeast Asia, or South Asia, as well as syncretism within these regions. These include the spread of Eastern religions such as Buddhism or Hinduism, the usage of Chinese characters or Brahmic scripts, language families, the fusion of cuisines, and traditions, among others.
Terminology
The East, as a geographical area, is unclear and undefined. More often, the ideology of a state's inhabitants is what will be used to categorize it as an Eastern society. There is some disagreement about what nations should or should not be included in the category and at what times. Many parts of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire are considered to be distinct from the West and therefore labelled as eastern by most scholars. The Byzantine Empire was primarily influenced by Eastern practices due to its proximity and cultural similarity to Iran and Arabia, thus lacking features seen as "Western". Both Eastern and Western European authors have often perceived Byzantium as a body of religious, political, and philosophical ideas contrary to those of the West.
It is difficult to determine which individuals fit into which category, and the East–West contrast is sometimes criticized as relativistic and arbitrary.[1][2][3] Globalism has spread Western ideas so widely that almost all modern cultures are, to some extent, influenced by aspects of Eastern culture. Stereotypical views of "the East" have been labeled Orientalism, paralleling Occidentalism—the term for the 19th-century stereotyped views of "the West".
As Europeans discovered the wider world, old concepts adapted. The area that had formerly been considered the Orient ("the East") became the Near East as the interests of the European powers interfered with Meiji Japan and Qing China for the first time in the 19th century.[4] Thus, the Sino-Japanese War in 1894–1895 occurred in the Far East while the troubles surrounding the decline of the Ottoman Empire simultaneously occurred in the Near East.[lower-alpha 1] The term Middle East in the mid-19th century included the territory east of the Ottoman Empire, but West of China—Greater India and Greater Persia—is now used synonymously with "Near East" in most languages.
Traditions
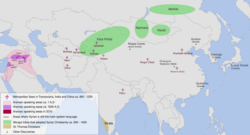
While there is no singular Eastern culture of the Eastern world, there are subgroups within it, such as countries within East Asia, Southeast Asia, or South Asia, as well as syncretism within these regions. These include the spread of Eastern religions such as Buddhism or Hinduism, the usage of Chinese characters or Brahmic scripts, language families, the fusion of cuisines, and traditions, among others. Eastern culture has developed many themes and traditions. Some important ones are listed below:
Religion
- Eastern religions (see also Eastern philosophy)
- Taoic religions (a.k.a. East Asian religions)
- Chinese folk religion – a general term covering a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora.
- Confucianism – a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China that developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius.
- Taoism – an ancient Chinese school of philosophical thought and religion that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao. The Tao Te Ching, a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi, together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism.
- Shinto – an ancient religion that originated in Japan . Its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion.
- Korean shamanism – an animistic ethnic religion of Korea dating back to prehistory and consists of the worship of gods and ancestors as well as nature spirits.
- Manchu shamanism – an animistic and polytheistic religion practiced by most of the Manchu people, believing in several gods and spirits, led by a universal sky god who is the source of all life and creation.
- Tengrism – an ancient ethnic and state Turko-Mongolic religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on folk shamanism, animism and generally centered around the titular sky god Tengri.
- Mongolian shamanism – the animistic and shamanic ethnic religion that has been practiced in Mongolia and its surrounding areas (including Buryatia and Inner Mongolia) at least since the age of recorded history.
- Shamanism in Siberia – religio-cultural practices of shamanism followed by a large minority of people in Siberia, and regarded by some researchers as the heartland of shamanism.
- Indian religions
- Hinduism – an ancient faith that evolved from the Vedic religion of North India.
- Buddhism – an ancient religion and philosophical tradition based on a series of original teachings attributed to Gautama Buddha.
- Jainism – an ancient religion that traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four Tirthankaras (supreme preachers of Dharma), the last of whom was Mahāvīra.
- Sikhism – a relatively new religion that developed in the warring plains of 15th-century Punjab in an atmosphere of ideological war between Islam and Hinduism. Its followers retain spiritual as well as martial qualities.
- Taoic religions (a.k.a. East Asian religions)
- Abrahamic religions (see also religion in the Middle East)
- Christianity – the majority of the modern world adheres to this faith, although it is no longer widely practiced in its native continent of Asia. Since the faith spread to Europe in antiquity, the notion of "Europe" and the "Western world" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christianity and the Christian world". Many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.[5] In Asia, Cyprus, Georgia, Armenia, Russia, the Philippines and East Timor are the only Christian-majority countries,[6] though there are also minority Christian populations in the Levant, Anatolia, Fars, and Kerala that have preserved their ancient beliefs, adhering to Syriac Christianity (i.e. Assyrian and Maronite people), an Eastern Christian sect.[7] Significant Christian communities are also found in Central Asia, China, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Japan, Macau, Malaysia, South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan and Vietnam.[6]
- Islam – the majority of the world's Muslim population has always lived in Asia, due to Islam spreading and becoming the dominant religion of West Asia, Central Asia and Southeast Asia.
- Judaism – the ancient religion of the Israelites or Hebrews of the Fertile Crescent,[8] who lived in what is now Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon. They eventually evolved into the Ashkenazi, Sephardic, and Mizrahi Jews and Samaritans of today.
- Druze faith – an esoteric ethnoreligious group that resides primarily in Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan.[9]
- Zoroastrianism – the ancient monotheistic state religion of Sassanid Iran.
Cinema
- East Asian cinema
- Chinese cinema
- Hong Kong cinema
- Japanese cinema
- Korean cinema
- North Korean cinema
- South Korean cinema
- Mongolian cinema
- Taiwanese cinema
- Southeast Asian cinema
- Cambodian cinema
- Burmese cinema
- Filipino cinema
- Indonesian cinema
- Laotian cinema
- Malaysian cinema
- Singaporean cinema
- Thai cinema
- Vietnamese cinema
- South Asian cinema
- Afghan cinema
- Bangladeshi cinema
- Bhutanese cinema
- Indian cinema
- Assamese cinema
- Bengali cinema
- Bhojpuri cinema
- Chhattisgarhi cinema
- Deccani cinema
- Dogri cinema
- Gujarati cinema
- Haryanvi cinema
- Hindi cinema
- Kannada cinema
- Kashmiri cinema
- Konkani cinema
- Malayalam cinema
- Meitei cinema
- Marathi cinema
- Oriya cinema
- Punjabi cinema
- Rajasthani cinema
- Sanskrit cinema
- Tamil cinema
- Telugu cinema
- Tulu cinema
- Pakistani cinema
- Lollywood
- Nepali cinema
- Sri Lankan cinema
- Central Asian cinema
- Kazakh cinema
- Kyrgyz cinema
- Tajik cinema
- Turkmen cinema
- Uzbek cinema
- West Asian cinema
- Arab cinema
- Armenian cinema
- Azerbaijani cinema
- Bahraini cinema
- Cypriot cinema
- Egyptian cinema
- Emirati cinema
- Georgian cinema
- Iranian cinema
- Iraqi cinema
- Israeli cinema
- Jewish cinema
- Jordanian cinema
- Kuwaiti cinema
- Lebanese cinema
- Omani cinema
- Palestinian cinema
- Qatari cinema
- Saudi Arabian cinema
- Syrian cinema
- Turkish cinema
- Yemeni cinema
- North Asian cinema
- Russian cinema
Cuisine
- East Asian cuisine
- Chinese cuisine
- Anhui cuisine
- Beijing cuisine
- Cantonese cuisine
- Chinese aristocrat cuisine
- Chinese imperial cuisine
- Chinese Islamic cuisine
- Hakka cuisine
- Henan cuisine
- Hubei cuisine
- Hunan cuisine
- Guizhou cuisine
- Jiangsu cuisine
- Huaiyang cuisine
- Jiangxi cuisine
- Northeastern Chinese cuisine
- Manchu cuisine
- Jilin cuisine
- Liaoning cuisine
- Shaanxi cuisine
- Shandong cuisine
- Shanghai cuisine
- Shanxi cuisine
- Sichuan cuisine
- Teochew cuisine
- Tianjin cuisine
- Tibetan cuisine
- Uyghur cuisine
- Yunnan cuisine
- Zhejiang cuisine
- Hong Kong cuisine
- Japanese cuisine
- Ainu cuisine
- Japanese regional cuisine
- Okinawan cuisine
- Nagoya cuisine
- Korean cuisine
- Korean regional cuisine
- Korean royal court cuisine
- Korean temple cuisine
- North Korean cuisine
- South Korean cuisine
- Macanese cuisine
- Mongolian cuisine
- Taiwanese cuisine
- Chinese cuisine
- Southeast Asian cuisine
- Bruneian cuisine
- Burmese cuisine
- Cambodian cuisine
- Christmas Island cuisine
- East Timorese cuisine
- Eurasian cuisine of Singapore and Malaysia
- Filipino cuisine
- Indonesian cuisine
- Acehnese cuisine
- Arab Indonesian cuisine
- Balinese cuisine
- Banjar cuisine
- Batak cuisine
- Betawi cuisine
- Chinese Indonesian cuisine
- Indo cuisine
- Indonesian Indian cuisine
- Javanese cuisine
- Madurese cuisine
- Makassar cuisine
- Minahasan cuisine
- Padang cuisine
- Palembang cuisine
- Sundanese cuisine
- Lao cuisine
- Malay cuisine
- Malaysian cuisine
- Malaysian Chinese cuisine
- Malaysian Indian cuisine
- Sabahan cuisine
- Sarawakian cuisine
- Peranakan cuisine
- Singaporean cuisine
- Thai cuisine
- Vietnamese cuisine
- South Asian cuisine
- Afghan cuisine
- Balochi cuisine
- Bangladeshi cuisine
- Bengali cuisine
- Bhutanese cuisine
- Cuisine of the Indian subcontinent
- Hazara cuisine
- Indian cuisine
- Anglo-Indian cuisine
- Arunachalese cuisine
- Assamese cuisine
- Bihari cuisine
- Bhojpuri cuisine
- Buddhist cuisine
- Goan cuisine
- Goan Catholic cuisine
- Gujarati cuisine
- Indian Chinese cuisine
- Indian fast food
- Jharkhandi cuisine
- Maharashtrian cuisine
- Malvani cuisine
- Manipuri cuisine
- Meghalayan cuisine
- Mizo cuisine
- Naga cuisine
- North Indian cuisine
- Kashmiri cuisine
- Rajasthani cuisine
- Cuisine of Uttar Pradesh
- Awadhi cuisine
- Cuisine of Uttarakhand
- Kumaoni cuisine
- Cuisine of Odisha
- Sikkimese cuisine
- South Indian cuisine
- Chettinad cuisine
- Karnataka cuisine
- Mangalorean cuisine
- Mangalorean Catholic cuisine
- Mangalorean cuisine
- Kerala cuisine
- Saraswat cuisine
- Telangana cuisine
- Hyderabadi cuisine
- Telugu cuisine
- Udupi cuisine
- Tripuri cuisine
- Maithil cuisine
- Maldivian cuisine
- Mughlai cuisine
- Nepalese cuisine
- Pakistani cuisine
- Lahori cuisine
- Pakistani Chinese cuisine
- Saraiki cuisine
- Sindhi cuisine
- Cuisine of Karachi
- Parsi cuisine
- Pashtun cuisine
- Punjabi cuisine
- Sri Lankan cuisine
- Tamil cuisine
- Central Asian cuisine
- Bukharan Jewish cuisine
- Kazakh cuisine
- Koryo-saram cuisine
- Kyrgyz cuisine
- Tajik cuisine
- Turkmen cuisine
- Uzbek cuisine
- West Asian cuisine
- Arab cuisine
- Armenian cuisine
- Assyrian cuisine
- Azerbaijani cuisine
- Bahraini cuisine
- Cypriot cuisine
- Eastern Arabian cuisine
- Egyptian cuisine
- Emirati cuisine
- Georgian cuisine
- Iranian cuisine
- Caspian cuisine
- Iraqi cuisine
- Israeli cuisine
- Jordanian cuisine
- Kurdish cuisine
- Kuwaiti cuisine
- Lebanese cuisine
- Levantine cuisine
- Mizrahi Jewish cuisine
- Omani cuisine
- Ossetian cuisine
- Palestinian cuisine
- Qatari cuisine
- Saudi Arabian cuisine
- Syrian cuisine
- Syrian Jewish cuisine
- Turkish cuisine
- Yemeni cuisine
- North Asian cuisine
- Russian cuisine
- Buryat cuisine
- Chukchi cuisine
- Cuisine of Commander Islands
- Sakha cuisine
- Yamal cuisine
- Yup'ik cuisine
- Russian cuisine
Cultures
- East Asian culture
- Culture of China
- Culture of Hong Kong
- Culture of Macau
- Culture of Mongolia
- Culture of Japan
- Culture of Korea
- Culture of North Korea
- Culture of South Korea
- Culture of Taiwan
- Southeast Asian culture
- Culture of Brunei
- Culture of Cambodia
- Culture of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Culture of East Timor
- Culture of Indonesia
- Culture of Malaysia
- Culture of Myanmar
- Culture of Laos
- Culture of the Philippines
- Culture of Singapore
- Culture of Thailand
- Culture of Vietnam
- South Asian culture
- Culture of Afghanistan
- Culture of Bangladesh
- Culture of Bhutan
- Culture of India
- Culture of the Maldives
- Culture of Nepal
- Culture of Pakistan
- Culture of Sri Lanka
- Central Asian culture
- Culture of Kazakhstan
- Culture of Kyrgyzstan
- Culture of Tajikistan
- Culture of Turkmenistan
- Culture of Uzbekistan
- West Asian culture
- Arab culture
- Culture of Abkhazia
- Culture of Armenia
- Culture of Artsakh
- Assyrian culture
- Culture of Azerbaijan
- Culture of Bahrain
- Culture of Eastern Arabia
- Culture of Egypt
- Culture of Georgia
- Culture of Iraq
- Culture of Iran
- Culture of Israel
- Jewish culture
- Culture of Jordan
- Culture of Kuwait
- Culture of Lebanon
- Culture of Northern Cyprus
- Culture of Palestine
- Culture of Qatar
- Culture of Saudi Arabia
- Culture of Syria
- Culture of Turkey
- Culture of the United Arab Emirates
- Culture of Yemen
- North Asian culture
- Culture of Russia
Medicine
- Oriental medicine
- Ayurveda
- Chinese medicine
- Kampo
- Traditional Korean medicine
- Traditional Filipino medicine
- Traditional Tibetan medicine
- Traditional Vietnamese medicine
Gallery
-
Zhájiàng Miàn (noodles with bean paste) is a traditional northern Chinese dish.
-
Mooncakes with Chinese characters 金門旦黃 (jinmen danhuang).
-
Sushi from Japan has become prevalent even among Westerners.
-
A cup of Japanese matcha tea.
-
Bulgogi, Korean-style marinated sliced meat.
-
Japchae, a kind of Korean noodle dish made with marinated beef and vegetables in soy sauce and sesame oil.
-
Mongolian Buuz.
-
Kaeng kanun, a northern Thai curry made with jackfruit.
-
Tapsilog, a common breakfast meal in the Philippines.
-
Butter chicken and butter naan from India.
-
Mix vegetables curry with garlic kulcha in India.
-
Kebabs are a popular cuisine among Middle Easterners.
-
Armenian khash (or pacha), which is also commonly eaten by Assyrians, Arabs and Kurds.
-
Round challah, a special bread in Jewish cuisine
-
Minangkabau Tari Lilin (candle dance)
-
A movie theater in Qufu, Shandong
-
Ramoji Film City located in Hyderabad, holds the Guinness World Record for the World's largest film studio.[10]
-
Temple of Confucius in Liuzhou, Guangxi, China .
-
The Tian Tan Buddha statue in Hong Kong.
-
Izumo-taisha shrine in Izumo, Japan .
-
A Hindu temple in Sri Lanka.
-
Color drenched Gopis during the Holi celebrations in Krishna Temple, Mathura, India .
-
A Syro-Malabar Catholic bishop holding the Mar Thoma Christian Cross which symbolizes the heritage and identity of the Syrian Church of Saint Thomas Christians of India
-
Assyrian Christians from lake Urmia in north eastern Persia in their traditional costumes.
-
The Monastery of St. Matthew, located atop Mount Alfaf in northern Iraq, is recognized as one of the oldest Christian monasteries in existence.
-
Chaldean Catholic from the town of Alqosh, Iraq.
-
Maronite Church in Lebanon.
-
Mor Hananyo Monastery is located in the Syriac cultural region known as Tur Abdin in Turkey.
-
Great Mosque of Mecca in Saudi Arabia.
-
The Western Wall and Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem.
-
Great synagogue in Afula, Israel
-
Aerial view of Masada, Israel
-
The Druze Maqam Nabi Shu'ayb.
Family
Families have a great importance in Eastern cultures. They teach their children about how the family is their protection and the major source of their identity. Parents expect loyalty from their children. Parents define the law and the children are expected to obey them. This is called filial piety, the respect for one's parents and elders, and it is a concept that originated in China as 孝 (xiao) from Confucian teachings.[11] Children are expected to have self-control, thus making it hard for them to express emotions. They are also expected to show respect through their motions and the way they speak. Children are expected to look after their parents when they grow older.[12] Sons are expected to stay home, while daughters eventually leave and live with their husband's family. In Chinese culture, children are occasionally expected to care for their elders (赡养), and in various diaspora communities one may find Chinese children living with their grandparents.
See also
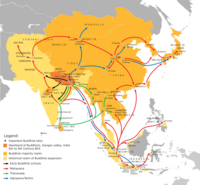
- Eastern religions
- Silk Road transmission of Buddhism
Notes
- ↑ British archaeologist D.G. Hogarth published The Nearer East in 1902, which helped to define the term and its extent, including Albania, Montenegro, southern Serbia and Bulgaria, Greece, Egypt, all Ottoman lands, the entire Arabian Peninsula, and Western parts of Iran.
References
- ↑ Yin Cheong Cheng, New Paradigm for Re-engineering Education. p. 369
- ↑ Ainslie Thomas Embree, Carol Gluck, Asia in Western and World History: A Guide for Teaching. p. xvi
- ↑ Kwang-Sae Lee, East and West: Fusion of Horizons[page needed]
- ↑ Davidson, Roderic H. (1960). "Where is the Middle East?". Foreign Affairs 38 (4): 665–75. doi:10.2307/20029452.
- ↑ Dawson, Christopher; Glenn Olsen (1961). Crisis in Western Education (reprint ed.). p. 108. ISBN 9780813216836.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Global Christianity – A Report on the Size and Distribution of the World's Christian Population". Pew Research Center. https://assets.pewresearch.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2011/12/Christianity-fullreport-web.pdf.
- ↑ Hindson, Edward E.; Mitchell, Daniel R. (1 August 2013) (in en). The Popular Encyclopedia of Church History. Harvest House Publishers. p. 225. ISBN 9780736948074.
- ↑
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Kohler, Kaufmann (1901–1906). "Judaism". in Singer, Isidore. The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/9028-judaism.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Kohler, Kaufmann (1901–1906). "Judaism". in Singer, Isidore. The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/9028-judaism.
- ↑ C. Held, Colbert (2008). Middle East Patterns: Places, People, and Politics. Routledge. p. 109. ISBN 9780429962004. "Worldwide, the Druze number 1 million or so, with about 45 to 50 percent of them living in Syria, 35 to 40 percent living in Lebanon, and less than 10 percent living in Israel. Recently, there has been a growing Druze diaspora."
- ↑ "Ramoji Film City sets record". Business Line. http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/2005/08/03/stories/2005080301301901.htm.
- ↑ "Cultural Values of Asian Patients and Families – Dimensions of Culture". http://www.dimensionsofculture.com/2010/10/cultural-values-of-asian-patients-and-families/.
- ↑ "The Value and Meaning of the Korean Family". http://asiasociety.org/education/value-and-meaning-korean-family.
Bibliography
- Berger, Mark T. (1997). "The triumph of the East? The East-Asian Miracle and post-Cold War capitalism". in Borer, Douglas A.. The rise of East Asia: critical visions of the Pacific century. Routledge. pp. 260–261, 266. ISBN 0-415-16168-1. https://archive.org/details/riseofeastasiacr0000unse/page/260.
 KSF
KSF


















![Ramoji Film City located in Hyderabad, holds the Guinness World Record for the World's largest film studio.[10]](https://handwiki.org/wiki/images/thumb/b/b4/Ramoji_14.jpg/90px-Ramoji_14.jpg)
















