Aerobiz Supersonic
Topic: Software
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
| Aerobiz Supersonic | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Koei |
| Publisher(s) | Koei |
| Series | Koei Executive Series |
| Platform(s) | Super NES Genesis PC-98 (Japanese) Windows (Japanese) MS-DOS (Chinese, Korean) |
| Release | Super NESGenesis |
| Genre(s) | Business simulation |
| Mode(s) | Single-player, multiplayer |
Aerobiz Supersonic, known as Air Management II: Kōkū Ō wo Mezase (エアーマネジメントII 航空王をめざせ) in Japan, is a business simulation video game released for the Super Nintendo Entertainment System by Koei in North America in August 1994. It was later ported to the Genesis. It is a sequel to Koei's previous airline simulation game, Aerobiz.
Gameplay
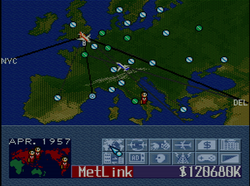
In the game, which is somewhat similar to its predecessor, the player is the CEO of a start-up international airline. The player competes with three other such companies (either AI-controlled or other players) for dominance in the worldwide travel industry. Such dominance is obtained by purchasing slots in various airports around the world, and flying routes to and from those slots. Once a route is created, the player has control of what type of planes fly the route, the price of airfare, and numerous other variables. The winning conditions for the player's airline are evaluated at the end of each year. These are to have a regional hub in every region, have the highest passenger total of all airlines during the given year in four to seven regions (depending on difficulty level), one of which must be the player's home region, and have a profit during the given year.
The game includes numerous historical events that can help or hinder airline performance. Four different eras of play are available for the player to choose. They include 1955–1975 (which depicts the dawn of jet airplanes), 1970–1990 (which depicts a period of instability, oil crises, and the end of the Cold War), 1985–2005 (which depicts the present day of economic prosperity and relative stable peace), and 2000–2020 (which depicts the replacement of jet planes with supersonic airplanes, the European Union extending to Russia, and countries trying to get airlines to fund alternative fuel research). This futuristic era was chosen by SG and Koei to be illustrated by San Francisco illustrator Marc Ericksen for the packaging art, showing two executives conferring over a holographic aircraft design in a futuristic airline terminal.
Airlines must be able to achieve the goals assigned to them within 20 years; only one airline can achieve this victory with no draws permitted. If none of the airlines can achieve the goal, then all airlines lose because stalemates are not permitted at the end of the game. Tiebreakers are also not permitted because games are not usually designed to be in ties at the end of the 20-year contest. In the rare instance that all airlines go bankrupt simultaneously, then all airlines would also lose.
Events
Historical events
The simulation includes numerous historical events, including:
- Summer Olympic Games accurate up to Sydney 2000. The 1976 Summer Olympics were in Montreal, although the game has them in Toronto.
- The downfall of colonialism
- The ejection of Singapore from Malaysia
- The rise of Fidel Castro (1959)
- The Suez Crisis
- The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971
- The Yom Kippur War
- An international oil crisis (1973)
- The Iran–Iraq War
- Operation Desert Storm
- Perestroika
- The destruction of the Berlin Wall and the reunification of Germany
- Fall of the Soviet Union
- The retrocession of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China
- The growth of the European Union
Hypothetical events
The simulation also includes hypothetical events, including:
- After 2000, the Summer Olympics start occurring in random selection of the game's major cities.
- Ukraine joining the European Union in July 1998.
- Belarus joining the European Union in January 1999.
- Switzerland joining the European Union in July 2003.
- Russia joining the European Union in October 2005.
- Civil war in random cities at random times (although in the game, they often occur in Lima, Peru, which had a civil war in real time).
- The introduction and quick obsolescence of commercial supersonic aircraft (2007–2016).
- Global oil crisis in the mid-late 2010s.
- The nations of the world asking the airlines for money to find alternatives to fossil fuels.
- A volcanic eruption in New Zealand.
- Floods in Thailand[3] and Vancouver, Canada[4] (both events corresponding with global climate change).
- An earthquake in São Paulo.
Major players in the game
Eastern Bloc
From the beginning of the game until 1986, the Eastern Bloc countries are stuck with tense relations with Western Europe, North America, and countries in the British Commonwealth. In particular, their worst-possible relationship with the United States, United Kingdom, and Japan means airlines located in the Eastern Bloc cannot buy from the big American planemakers of the time, Boeing, Lockheed, and McDonnell-Douglas. However, they have normal-excellent relations with African countries, Middle Eastern countries, countries in Central America, South America, and some Asian countries. Furthermore, relations with France are decent enough that Eastern Bloc companies can buy from countries based there like Airbus and Sud Aviation, though at a markup. Airplanes from Eastern Bloc countries are, in general, represented as undersized and inefficient gas-guzzlers that can only do medium-range flights as their longest routes, but their base cost is cheaper and they can perform certain specialty roles well.
After perestroika in 1986, airlines from these countries can purchase airplanes from the United States thanks to normalization of relations. These airplanes become even cheaper following the collapse of the Eastern Bloc in 1989-1991. In the game's hypothetical then-future scenario (2000-2020) Russia enters the EU in 2005, making Airbus prices cheaper. Ilyushin and Tupolev airplanes remain very cheap and become more efficient than earlier models.
Western Bloc
Western Europe
With normal-tense relations with Eastern European countries until around 1985, airlines that are headquartered in Western European countries must either purchase cheap airplanes from the "local" market or order slightly more expensive planes from the United States of America. After Perestroika, they can purchase from any plane manufacturing company. Joining the European Union in the mid-1990s makes airplanes cheaper or more expensive depending on relations with the United States prior to the founding of the EU.
North America
North America's situation in the game is identical to the situation found by Western European countries. The only difference is that planes from American companies are cheaper than planes from Western European countries. Since North America has a higher tourism rating than Europe until the 1990s, North America–based airlines can afford more airplanes and routes for a better risk-profit potential than European-based airlines.
People's Republic of China and other countries
Normalized relations with both the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. allows all planes to be purchased by airlines headquartered in the People's Republic of China regardless of the year. However, improving relations with either country will reduce the price of the airplanes - giving the player a choice of acquiring either inefficient Soviet-made planes or efficient American-made planes at bargain prices. Like the People's Republic of China, countries that are not strongly affiliated with either NATO or Warsaw Pact may purchase from any manufacturer as long as relations are not tense (red). Relations with the country must be at least normal (orange) in order to purchase airplanes from that country.
Reception
Electronic Gaming Monthly gave the Super NES version a 7.2 out of 10, deeming it a different type of game that is more geared towards to strategy.[5] They gave the later Genesis version a 6.6 out of 10 and opined that Koei managed to make a unique strategy game while also being entertaining.[6]
Next Generation gave the Genesis version of the game three stars out of five, and said that sim fans will be pleased with the level of detail in the game.[7]
VideoGames selected it as a runner-up for 1994's Best Strategy Game award, which was won by Equinox.[8]
References
- ↑ "Fact File: Aerobiz Supersonic". Electronic Gaming Monthly (65): 310-312. December 1994. https://archive.org/details/Electronic_Gaming_Monthly_65/page/n337/mode/2up. Retrieved January 10, 2022.
- ↑ "Software List (Software Licensee Release)" (in ja). Sega Corporation. https://www.sega.jp/history/hard/megadrive/software_l.html.
- ↑ Hypothetical flooding of Thailand at flood.firetree.net
- ↑ Hypothetical flooding of Vancouver, Canada at flood.firetree.net
- ↑ "Review Crew: Aerobiz Supersonic". Electronic Gaming Monthly (Sendai Publishing) (59): 33. June 1994.
- ↑ "Review Crew: Aerobiz Supersonic". Electronic Gaming Monthly (Sendai Publishing) (66): 40. January 1995.
- ↑ "Finals". Next Generation (Imagine Media) (7): 77. July 1995.
- ↑ "VideoGames Best of '94". VideoGames - The Ultimate Gaming Magazine (74 (March 1995)): 44–7. February 1995. https://archive.org/details/Video_Games_The_Ultimate_Gaming_Magazine_Issue_74_March_1995/page/n45/mode/2up.
External links
- MobyGames is a commercial database website that catalogs information on video games and the people and companies behind them via crowdsourcing. This includes over 300,000 games for hundreds of platforms.[1] Founded in 1999, ownership of the site has changed hands several times. It has been owned by Atari SA since 2022.
Features
Edits and submissions to the site (including screenshots, box art, developer information, game summaries, and more) go through a verification process of fact-checking by volunteer "approvers".[2] This lengthy approval process after submission can range from minutes to days or months.[3] The most commonly used sources are the video game's website, packaging, and credit screens. There is a published standard for game information and copy-editing.[4] A ranking system allows users to earn points for contributing accurate information.[5]
Registered users can rate and review games. Users can create private or public "have" and "want" lists, which can generate a list of games available for trade with other registered users. The site contains an integrated forum. Each listed game can have its own sub-forum.
History

MobyGames was founded on March 1, 1999, by Jim Leonard and Brian Hirt, and joined by David Berk 18 months later, the three of which had been friends since high school.[6][7] Leonard had the idea of sharing information about computer games with a larger audience. The database began with information about games for IBM PC compatibles, relying on the founders' personal collections. Eventually, the site was opened up to allow general users to contribute information.[5] In a 2003 interview, Berk emphasized MobyGames' dedication to taking video games more seriously than broader society and to preserving games for their important cultural influence.[5]
In mid-2010, MobyGames was purchased by GameFly for an undisclosed amount.[8] This was announced to the community post factum , and the site's interface was given an unpopular redesign.[7] A few major contributors left, refusing to do volunteer work for a commercial website.{{Citation needed|date=June 2025} On December 18, 2013, MobyGames was acquired by Jeremiah Freyholtz, owner of Blue Flame Labs (a San Francisco-based game and web development company) and VGBoxArt (a site for fan-made video game box art).[9] Blue Flame Labs reverted MobyGames' interface to its pre-overhaul look and feel,[10] and for the next eight years, the site was run by Freyholtz and Independent Games Festival organizer Simon Carless.[7]
On November 24, 2021, Atari SA announced a potential deal with Blue Flame Labs to purchase MobyGames for $1.5 million.[11] The purchase was completed on 8 March 2022, with Freyholtz remaining as general manager.[12][13][14] Over the next year, the financial boost given by Atari led to a rework of the site being built from scratch with a new backend codebase, as well as updates improving the mobile and desktop user interface.[1] This was accomplished by investing in full-time development of the site instead of its previously part-time development.[15]
In 2024, MobyGames began offering a paid "Pro" membership option for the site to generate additional revenue.[16] Previously, the site had generated income exclusively through banner ads and (from March 2014 onward) a small number of patrons via the Patreon website.[17]
See also
- IGDB – game database used by Twitch for its search and discovery functions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sheehan, Gavin (2023-02-22). "Atari Relaunches The Fully Rebuilt & Optimized MobyGames Website". https://bleedingcool.com/games/atari-relaunches-the-fully-rebuilt-optimized-mobygames-website/.
- ↑ Litchfield, Ted (2021-11-26). "Zombie company Atari to devour MobyGames". https://www.pcgamer.com/zombie-company-atari-to-devour-mobygames/.
- ↑ "MobyGames FAQ: Emails Answered § When will my submission be approved?". Blue Flame Labs. 30 March 2014. http://www.mobygames.com/info/faq7#g1.
- ↑ "The MobyGames Standards and Practices". Blue Flame Labs. 6 January 2016. http://www.mobygames.com/info/standards.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Miller, Stanley A. (2003-04-22). "People's choice awards honor favorite Web sites". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
- ↑ "20 Years of MobyGames" (in en). 2019-02-28. https://trixter.oldskool.org/2019/02/28/20-years-of-mobygames/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Plunkett, Luke (2022-03-10). "Atari Buys MobyGames For $1.5 Million". https://kotaku.com/mobygames-retro-credits-database-imdb-atari-freyholtz-b-1848638521.
- ↑ "Report: MobyGames Acquired By GameFly Media". Gamasutra. 2011-02-07. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/game-platforms/report-mobygames-acquired-by-gamefly-media.
- ↑ Corriea, Alexa Ray (December 31, 2013). "MobyGames purchased from GameFly, improvements planned". http://www.polygon.com/2013/12/31/5261414/mobygames-purchased-from-gamefly-improvements-planned.
- ↑ Wawro, Alex (31 December 2013). "Game dev database MobyGames getting some TLC under new owner". Gamasutra. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/game-dev-database-mobygames-getting-some-tlc-under-new-owner.
- ↑ "Atari invests in Anstream, may buy MobyGames". November 24, 2021. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2021-11-24-atari-invests-in-anstream-may-buy-mobygames.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jeffrey (2022-03-09). "Atari purchases Moby Games". https://www.gamesindustry.biz/atari-purchases-moby-games.
- ↑ "Atari Completes MobyGames Acquisition, Details Plans for the Site's Continued Support". March 8, 2022. https://www.atari.com/atari-completes-mobygames-acquisition-details-plans-for-the-sites-continued-support/.
- ↑ "Atari has acquired game database MobyGames for $1.5 million" (in en-GB). 2022-03-09. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/atari-has-acquired-game-database-mobygames-for-1-5-million/.
- ↑ Stanton, Rich (2022-03-10). "Atari buys videogame database MobyGames for $1.5 million". https://www.pcgamer.com/atari-buys-videogame-database-mobygames-for-dollar15-million/.
- ↑ Harris, John (2024-03-09). "MobyGames Offering “Pro” Membership". https://setsideb.com/mobygames-offering-pro-membership/.
- ↑ "MobyGames on Patreon". http://www.patreon.com/mobygames.
Wikidata has the property:
|
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
 |
 KSF
KSF
