Gemstone Warrior
Topic: Software
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
| Gemstone Warrior | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Paradigm Creators |
| Publisher(s) | Strategic Simulations |
| Designer(s) | Peter William Lount Trouba (Paul) Gossen |
| Platform(s) | Apple II, Atari 8-bit, Commodore 64, Macintosh |
| Release | 1984: Apple II 1985: Atari 8-bit,[1] C64 1986: Macintosh |
| Genre(s) | Action-adventure |
| Mode(s) | Single player |
Gemstone Warrior is a video game written by Canadian developer Paradigm Creators for the Apple II and published by Strategic Simulations in 1984.[2][3] It is a 2D action-adventure game where the player controls an armored figure searching for treasure and the pieces of the stolen Gemstone. Gemstone Warrior was SSI's first game to sell over 50,000 copies in North America.[4]
The game was ported to the Commodore 64, Atari 8-bit family, and Macintosh. It was followed by a 1986 sequel, Gemstone Healer, also created by Paradigm.
Plot
The player has to recover the Gemstone, a relic of incredible power forged by the gods and focusing the natural magic of the world. This, they entrusted to Man alone and for a time, there was great prosperity and peace. But the Demons, led by Nicodemius, had managed to boil to the surface and take the Gemstone. Unable to destroy it, Nicodemius fragments it into five pieces and hides them in the Labyrinth, buried deep within the Netherworld. Going into the Netherworld, the protagonist must find and return with the Gemstone.
Gameplay
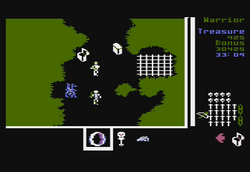
There are three difficulty levels, determining various factors such as the rate at which magic items change their effects and the rate at which more dangerous monsters start appearing.
The game is viewed in a 2D screen displaying the playing area, health, and inventory. The player controls an armored figure that wields a crossbow with a limited supply of bolts that can be replenished by finding more within the dungeon areas. Special "fireballs" can also be launched against foes, although these are limited and are not as common. There are also magical tools and other items that can be collected to provide a variety of benefits such as goblets that can restore health to crystal balls that can annihilate everything on the screen.
The dungeons are filled with a variety of dangers and secret doors. Many brutal monsters fill the caverns ranging from skeletal warriors, exploding gas plants, to nearly invulnerable demons. The player is also able to search the corpses of monsters that remain behind, chests, and coffins for supplies. Monsters do not always respawn in zones, leaving behind only their corpse as a reminder that the player had been there, although some do return to life, such as the skeletons and ghosts.
The goal is to traverse the maze to locate the Labyrinth, find the five pieces of Gemstone within its randomly generated layout, and return to the entrance cavern to escape.
Audio
The title screen in the Atari 8-bit and Commodore C64 versions uses a variation of J.S. Bach's The Well-Tempered Clavier, Prelude 6 in D Minor BWV 851.
Reviews
- Casus Belli #26 (June 1985)[5]
References
- ↑ "Gemstone Warrior". http://www.atarimania.com/game-atari-400-800-xl-xe-gemstone-warrior_2181.html.
- ↑ Barton, Matt (2007-02-23). "Part 2: The Golden Age (1985-1993)". The History of Computer Role-Playing Games. Gamasutra. Archived from the original on 2009-03-12. https://web.archive.org/web/20090312012343/http://www.gamasutra.com/features/20070223b/barton_03.shtml. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ↑ "Gemstone Warrior (Extended Arcade)". Hardcore Computist (27): 21. 1985. https://archive.org/details/computist-scan-27.
- ↑ Maher, Jimmy (2016-03-18). "Opening the Gold Box, Part 3: From Tabletop to Desktop". The Digital Antiquarian. http://www.filfre.net/2016/03/opening-the-gold-box-part-3-from-tabletop-to-desktop/. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ↑ "Ludotique | Article | RPGGeek". https://www.rpggeek.com/rpgissuearticle/139395/ludotique.
External links
- MobyGames is a commercial database website that catalogs information on video games and the people and companies behind them via crowdsourcing. This includes over 300,000 games for hundreds of platforms.[1] Founded in 1999, ownership of the site has changed hands several times. It has been owned by Atari SA since 2022.
Features
Edits and submissions to the site (including screenshots, box art, developer information, game summaries, and more) go through a verification process of fact-checking by volunteer "approvers".[2] This lengthy approval process after submission can range from minutes to days or months.[3] The most commonly used sources are the video game's website, packaging, and credit screens. There is a published standard for game information and copy-editing.[4] A ranking system allows users to earn points for contributing accurate information.[5]
Registered users can rate and review games. Users can create private or public "have" and "want" lists, which can generate a list of games available for trade with other registered users. The site contains an integrated forum. Each listed game can have its own sub-forum.
History

MobyGames was founded on March 1, 1999, by Jim Leonard and Brian Hirt, and joined by David Berk 18 months later, the three of which had been friends since high school.[6][7] Leonard had the idea of sharing information about computer games with a larger audience. The database began with information about games for IBM PC compatibles, relying on the founders' personal collections. Eventually, the site was opened up to allow general users to contribute information.[5] In a 2003 interview, Berk emphasized MobyGames' dedication to taking video games more seriously than broader society and to preserving games for their important cultural influence.[5]
In mid-2010, MobyGames was purchased by GameFly for an undisclosed amount.[8] This was announced to the community post factum , and the site's interface was given an unpopular redesign.[7] A few major contributors left, refusing to do volunteer work for a commercial website.{{Citation needed|date=June 2025} On December 18, 2013, MobyGames was acquired by Jeremiah Freyholtz, owner of Blue Flame Labs (a San Francisco-based game and web development company) and VGBoxArt (a site for fan-made video game box art).[9] Blue Flame Labs reverted MobyGames' interface to its pre-overhaul look and feel,[10] and for the next eight years, the site was run by Freyholtz and Independent Games Festival organizer Simon Carless.[7]
On November 24, 2021, Atari SA announced a potential deal with Blue Flame Labs to purchase MobyGames for $1.5 million.[11] The purchase was completed on 8 March 2022, with Freyholtz remaining as general manager.[12][13][14] Over the next year, the financial boost given by Atari led to a rework of the site being built from scratch with a new backend codebase, as well as updates improving the mobile and desktop user interface.[1] This was accomplished by investing in full-time development of the site instead of its previously part-time development.[15]
In 2024, MobyGames began offering a paid "Pro" membership option for the site to generate additional revenue.[16] Previously, the site had generated income exclusively through banner ads and (from March 2014 onward) a small number of patrons via the Patreon website.[17]
See also
- IGDB – game database used by Twitch for its search and discovery functions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sheehan, Gavin (2023-02-22). "Atari Relaunches The Fully Rebuilt & Optimized MobyGames Website". https://bleedingcool.com/games/atari-relaunches-the-fully-rebuilt-optimized-mobygames-website/.
- ↑ Litchfield, Ted (2021-11-26). "Zombie company Atari to devour MobyGames". https://www.pcgamer.com/zombie-company-atari-to-devour-mobygames/.
- ↑ "MobyGames FAQ: Emails Answered § When will my submission be approved?". Blue Flame Labs. 30 March 2014. http://www.mobygames.com/info/faq7#g1.
- ↑ "The MobyGames Standards and Practices". Blue Flame Labs. 6 January 2016. http://www.mobygames.com/info/standards.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Miller, Stanley A. (2003-04-22). "People's choice awards honor favorite Web sites". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
- ↑ "20 Years of MobyGames" (in en). 2019-02-28. https://trixter.oldskool.org/2019/02/28/20-years-of-mobygames/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Plunkett, Luke (2022-03-10). "Atari Buys MobyGames For $1.5 Million". https://kotaku.com/mobygames-retro-credits-database-imdb-atari-freyholtz-b-1848638521.
- ↑ "Report: MobyGames Acquired By GameFly Media". Gamasutra. 2011-02-07. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/game-platforms/report-mobygames-acquired-by-gamefly-media.
- ↑ Corriea, Alexa Ray (December 31, 2013). "MobyGames purchased from GameFly, improvements planned". http://www.polygon.com/2013/12/31/5261414/mobygames-purchased-from-gamefly-improvements-planned.
- ↑ Wawro, Alex (31 December 2013). "Game dev database MobyGames getting some TLC under new owner". Gamasutra. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/game-dev-database-mobygames-getting-some-tlc-under-new-owner.
- ↑ "Atari invests in Anstream, may buy MobyGames". November 24, 2021. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2021-11-24-atari-invests-in-anstream-may-buy-mobygames.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jeffrey (2022-03-09). "Atari purchases Moby Games". https://www.gamesindustry.biz/atari-purchases-moby-games.
- ↑ "Atari Completes MobyGames Acquisition, Details Plans for the Site's Continued Support". March 8, 2022. https://www.atari.com/atari-completes-mobygames-acquisition-details-plans-for-the-sites-continued-support/.
- ↑ "Atari has acquired game database MobyGames for $1.5 million" (in en-GB). 2022-03-09. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/atari-has-acquired-game-database-mobygames-for-1-5-million/.
- ↑ Stanton, Rich (2022-03-10). "Atari buys videogame database MobyGames for $1.5 million". https://www.pcgamer.com/atari-buys-videogame-database-mobygames-for-dollar15-million/.
- ↑ Harris, John (2024-03-09). "MobyGames Offering “Pro” Membership". https://setsideb.com/mobygames-offering-pro-membership/.
- ↑ "MobyGames on Patreon". http://www.patreon.com/mobygames.
Wikidata has the property:
|
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
- Images of Gemstone Warrior package, manual, and screen shots
- Peter.Lount.com
- Audio interview with Peter Lount
- From the pages of the past, games of yesteryear – Gemstone Warrior
 |
 KSF
KSF