Theatre Europe
Topic: Software
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
| Theatre Europe | |
|---|---|
 North American cover art | |
| Developer(s) | Personal Software Services |
| Publisher(s) | Personal Software Services |
| Designer(s) | Alan Steel Sean Pearce David Bolton |
| Series | Strategic Wargames |
| Platform(s) | Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Amstrad CPC, Atari 8-bit, Apple II, Einstein |
| Release | |
| Genre(s) | Turn-based strategy |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
Theatre Europe is a turn-based strategy video game developed and published by Personal Software Services (PSS). It was first released in the United Kingdom for the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Amstrad CPC and Atari 8-bit family home computers in 1985. It was later released in France by ERE Informatique in 1986, and was released in the United States by Datasoft later that year. A port for the Tatung Einstein was released in 1989, in the UK. It is the fifth installment of the Strategic Wargames series.
The game is set during a fictional war in Europe between NATO and the Warsaw Pact, in which both sides use nuclear and chemical weapons. The developers used information and statistics on military strength from the Ministry of Defence and the Soviet embassy in London. The objective is to fight conventional battles in continental Europe, whilst trying to avoid a worldwide nuclear holocaust. During the game, capital cities and their civilian populations are destroyed by nuclear weapons. The game ends once either side is forced to surrender or if the entire population of Europe perishes. To request a nuclear strike, the player was required to call a dedicated telephone number to hear an automated message giving the authorisation code.
Theatre Europe was criticized by the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND) and The Sun newspaper. Some high street retail chains refused to sell the game upon release. The game received critical acclaim for its accuracy, playability and value for money. It won the "Best Strategy Game" award at the 1985 Golden Joystick Awards and was nominated for "Game of the Year".
PSS released a 16-bit follow-up game in 1989, Conflict.[1][2]
Gameplay
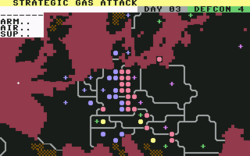
The game is a turn-based strategy and revolves around a fictional conflict between the powers of NATO and allies of the Warsaw Pact.[3] The player has the choice of choosing either NATO or the Warsaw Pact (collectively referred to as Soviet forces), or a "demo" computer versus computer option, where the game plays itself.[4][5] The game takes place over a period of 30 in-game days, in which one day is equal to one "round".[4][6] There are three types of difficulty; level one, in which unless provoked, the enemy will not use nuclear weapons, whilst levels two and three will enable the enemy to use nuclear and chemical attacks to prevent the player from winning the game.[5]
The main feature of the game is focused on a map of Europe and western Russia, which displays accurate terrain such as mountain ranges, major cities, borders and all military forces belonging to each side. The game also features an arcade sequence which involves shooting down enemy units in order to secure combat bonuses; this gameplay mode, however, can be ignored by changing the game's settings.[4] If the arcade sequences are turned on, the player will be notified to choose a battle on the map. Depending on the area chosen, an illustration of a battle commencing in countryside or a city is presented with various forms of military equipment including aeroplanes, helicopters and tanks. The player must shoot down and destroy enemy units using their cursor, in similar style to Missile Command.[5] The outcome of the arcade sequence will affect the game;[4] performing poorly will result in severe losses throughout that round.[5]
After combat has been resolved, the player must move and assemble their forces in continental Europe, which is known as the movement phase.[7] Two special units are exclusively available to the Warsaw Pact: "the 1st Airborne Army which can be flown directly behind enemy lines, and the 1st Amphibious Army which can move over the sea to a tactical attack point".[5] Units are moved by cursor, and only one may be moved at a time. Once all units have been moved within a round, the attack phase will begin. Any amount of friendly units may attack an opposing army; however, once a unit has been dispatched for battle it cannot be stopped until the current attack phase concludes.[5][6] During the attacking phase, a separate screen displaying combat information, such as enemy numbers and casualties, is displayed.[8] If the screen detailing the attacking phase has been turned off in the settings, the battle will instead be decided on warrants of air superiority and armaments.[5]

After battle sequences, the player will have the opportunity to rebuild their units by allocating a quantity of armament supplies, such as air support, which can be issued to any friendly unit on the map. After rebuilding ground units, the game will move onto an "air phase", which consists of commanding aircraft such as aeroplanes, bombers and a limited number of reserve air units.[5] Several options for allocating air forces include: counter air strikes, reconnaissance on enemy movement, interdiction, assault breakers, and deep strikes.[8][5] Counter air strikes involve attacks on enemy air bases, whereas interdiction involves aircraft being sent behind enemy lines in order to attack supply and movement networks. If interdiction aircraft are discovered in enemy territory, there will be a chance that the side will respond with a retaliatory nuclear strike.[5] The remaining three aircraft options are to attack a single unit, strike enemy territory, and attack railways in order to disable enemy reinforcements, respectively.[3]
The game allows the player to request chemical and nuclear tactical strikes against the enemy. A chemical attack is automatically targeted at an enemy capital city, and will conclude with a readout announcing the outcome of the attack, such as civilian casualties. In order to launch a strategic nuclear attack, the player is given 30 seconds to call a dedicated 1-800 telephone number and obtain a special authorisation code from the automated answerphone message (the authorisation code was 'Midnight Sun').[9][5][3][10] Once the authorisation code has been received, the player will be given three separate options on how to proceed. Standby mode will postpone the nuclear launch, whereas a strategic launch will involve one nuclear warhead targeting a city. The third option, known as "Fire-Plan", will issue a full-scale nuclear strike across Europe and results in a nuclear holocaust, which will end the game.[5][3][8]
Release
Richard Cockayne in an interview with Your Computer magazine in 1986[10]
In an interview with Your Computer magazine, Gary Mays stated that Theatre Europe received heavy criticism from the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND).[10] The CND accused the developers of "bad taste", despite Cockayne claiming that the organisation never "looked into the product". During development of the game, Cockayne and Mays obtained figures and statistics of various military strength from the Ministry of Defence and the Soviet embassy in London.[3] Cockayne asserted that the statistics the developers gained were realistically plausible, stating that he would let the "horrifying results speak for themselves" during the game.[10] Game designer Alan Steel stated that during testing, he was "alarmed" to discover when the computer played itself, the Warsaw Pact always won a conventional war overwhelmingly, forcing NATO to either surrender or begin a nuclear war. Steel adjusted the game to give NATO a chance to win.[3] Theatre Europe was first released in the United Kingdom for the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Amstrad CPC and Atari 8-bit home computers in 1985. It was then re-released in France and the United States for those consoles in 1986.[11] Due to lobbying from the CND, high street outlets such as Boots and John Menzies refused to sell the game in their stores, with the former finding it "morally offensive".[12]
Reception
| Reception | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
The game received critical acclaim upon release. Gwyn Hughes of Your Sinclair defended the accuracy and morality of the game, stating that it was not in "bad taste" and that the game was a "well researched program", which he thought would give the player an insight into the nature of modern war.[4] Philippa Irving of Crash similarly stated that Theatre Europe offered more than a usual "run-of-the-mill" war game and heralded its simplistic nature, adding that novice gamers would "get in to it with ease".[5] John Gilbert of Sinclair User added scepticism over the developer's intention of making something "so serious" as opposed to their other titles; however he praised the game as a "brilliant, if chilling" simulation.[7] A reviewer writing for ZX Computing similarly stated that the game was "superbly chilling" and "extremely" well-presented.[15] A reviewer of Computer and Video Games criticised the inferior graphics on the ZX Spectrum, stating that they were "a bit flawed" in comparison to the Commodore 64 version.[6]
Bill Harrington reviewed the game for Computer Gaming World, and stated that " TE does a credible job of demonstrating the perils of escalation and dramatizing how slippery the slope to nuclear war might be, but is basically a game in search of a market."[16]
Computer Gamer noted that the game attracted media attention, despite the objective of the game discouraging the use of nuclear weapons. Reed praised the presentation and gameplay, also stating that the use of a joystick and keyboard is "excellent".[8] A reviewer from Zzap!64 heralded the presentation and value for money, stating that it is overall "very special indeed". The reviewer also gave praise to the sound, suggesting that the game featured "one of the best pieces of micro music ever".[3] Antic stated that the Atari 8-bit version's "execution is uneven". The magazine reported that the arcade portion "quickly becomes a nuisance" and NATO could not defeat the Warsaw Pact because of lack of balance, flaws that did not exist in the Commodore 64 version.[17] Peter Connor of Advanced Computer Entertainment said that Theatre Europe was a "gift", in regards to its value of money and level of playability.[13] In a 1994 survey of wargames Computer Gaming World gave the title two-plus stars out of five, stating that it was "rendered obsolete by history and game play".[18]
The game won the "Best Strategy Game" award at the 1985 Golden Joystick Awards and was nominated for "Game of the Year".[14]
References
- ↑ Railton, Ken (October 1989). "Games - Conflict Europe". ST Format (Future plc) (3): 74. http://www.atarimania.com/atari-magazine-issue-st-format-issue-03_1144.html.
- ↑ Rignall, Julian (August 1989). "Review - Conflict in Europe [sic"]. Computer and Video Games (Future plc) (93): 74. https://archive.org/details/cvg-magazine-093b/page/n73/mode/2up.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Wade, Bob (June 1985). "Theatre Europe review (Zzap!)". Zzap!64 (2): 18–20. https://archive.org/stream/zzap64-magazine-002/ZZap_64_Issue_002_1985_Jun#page/n17/mode/2up.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Hughes, Gwyn (August 1986). "Theatre Europe review". Your Sinclair (8): 67. http://www.ysrnry.co.uk/articles/theatreeurope.htm. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 Irving, Philippa (July 1986). "Theatre Europe review (Crash)". Crash (30): 54, 55. http://www.crashonline.org.uk/30/t_europe.htm. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Theatre Europe review (CVG)". Computer and Video Games (61): 43. October 1986. http://wos.meulie.net/pub/sinclair/magazines/C+VG/Issue061/Pages/CVG06100043.jpg.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Gilbert, John (August 1986). "Theatre Europe review". Sinclair User (53): 61. http://wos.meulie.net/pub/sinclair/magazines/SinclairUser/Issue053/Pages/SinclairUser05300061.jpg.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Staff (August 1986). "Theatre Europe review". Computer Gamer (17): 95. https://archive.org/details/Computer_Gamer_Issue_17_1986-08_Argus_Press_GB/page/n94/mode/1up?view=theater.
- ↑ Daniel Goldberg (20 October 2015). The State of Play: Creators and Critics on Video Game Culture. Seven Stories Press. ISBN 978-1-60980-640-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=yXnWBQAAQBAJ.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 "History of PSS". Your Computer 6 (6): 84–85. 13 June 1986. https://archive.org/stream/your-computer-magazine-1986-06/YourComputer_1986_06#page/n83/mode/2up. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ↑ "Theatre Europe release list". CBS. http://www.giantbomb.com/theatre-europe/3030-5111/.
- ↑ Schofield, Jack (29 August 1985). "Futures (Micro-Guardian): Anyone for Armageddon? / Computer war games". The Guardian.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Connor, Peter (December 1987). "Theatre Europe review". Advanced Computer Entertainment (3): 90. https://archive.org/stream/ace-magazine-03/ACE_Issue_03_1987_Dec#page/n89/mode/1up.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Golden Joystick Awards". Computer and Video Games (EMAP) (55): 90. May 1986. https://archive.org/stream/Computer_Video_Games_Issue_055_1986-05_EMAP_Publishing_GB/Computer__Video_Games_Issue_055_1986-05_EMAP_Publishing_GB#page/n89/mode/2up.
- ↑ "Theatre Europe and Iwo Jima review". ZX Computing (86): 43. August 1986. http://wos.meulie.net/pub/sinclair/magazines/ZXComputing/Issue8608/Pages/ZXComputing860800043.jpg.
- ↑ Harrington, Bill (Aug–Sep 1987). "Theatre Europe: Datasoft Goes To War". Computer Gaming World 1 (39): 32–33.
- ↑ Stanoch, John (June 1987). "Theatre Europe". Antic. http://www.atarimagazines.com/v6n2/ProductReviews.html.
- ↑ Brooks, M. Evan (January 1994). "War In Our Time / A Survey Of Wargames From 1950-2000". Computer Gaming World: 194–212. http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1994&pub=2&id=114.
External links
- MobyGames is a commercial database website that catalogs information on video games and the people and companies behind them via crowdsourcing. This includes over 300,000 games for hundreds of platforms.[1] Founded in 1999, ownership of the site has changed hands several times. It has been owned by Atari SA since 2022.
Features
Edits and submissions to the site (including screenshots, box art, developer information, game summaries, and more) go through a verification process of fact-checking by volunteer "approvers".[2] This lengthy approval process after submission can range from minutes to days or months.[3] The most commonly used sources are the video game's website, packaging, and credit screens. There is a published standard for game information and copy-editing.[4] A ranking system allows users to earn points for contributing accurate information.[5]
Registered users can rate and review games. Users can create private or public "have" and "want" lists, which can generate a list of games available for trade with other registered users. The site contains an integrated forum. Each listed game can have its own sub-forum.
History

MobyGames was founded on March 1, 1999, by Jim Leonard and Brian Hirt, and joined by David Berk 18 months later, the three of which had been friends since high school.[6][7] Leonard had the idea of sharing information about computer games with a larger audience. The database began with information about games for IBM PC compatibles, relying on the founders' personal collections. Eventually, the site was opened up to allow general users to contribute information.[5] In a 2003 interview, Berk emphasized MobyGames' dedication to taking video games more seriously than broader society and to preserving games for their important cultural influence.[5]
In mid-2010, MobyGames was purchased by GameFly for an undisclosed amount.[8] This was announced to the community post factum , and the site's interface was given an unpopular redesign.[7] A few major contributors left, refusing to do volunteer work for a commercial website.{{Citation needed|date=June 2025} On December 18, 2013, MobyGames was acquired by Jeremiah Freyholtz, owner of Blue Flame Labs (a San Francisco-based game and web development company) and VGBoxArt (a site for fan-made video game box art).[9] Blue Flame Labs reverted MobyGames' interface to its pre-overhaul look and feel,[10] and for the next eight years, the site was run by Freyholtz and Independent Games Festival organizer Simon Carless.[7]
On November 24, 2021, Atari SA announced a potential deal with Blue Flame Labs to purchase MobyGames for $1.5 million.[11] The purchase was completed on 8 March 2022, with Freyholtz remaining as general manager.[12][13][14] Over the next year, the financial boost given by Atari led to a rework of the site being built from scratch with a new backend codebase, as well as updates improving the mobile and desktop user interface.[1] This was accomplished by investing in full-time development of the site instead of its previously part-time development.[15]
In 2024, MobyGames began offering a paid "Pro" membership option for the site to generate additional revenue.[16] Previously, the site had generated income exclusively through banner ads and (from March 2014 onward) a small number of patrons via the Patreon website.[17]
See also
- IGDB – game database used by Twitch for its search and discovery functions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sheehan, Gavin (2023-02-22). "Atari Relaunches The Fully Rebuilt & Optimized MobyGames Website". https://bleedingcool.com/games/atari-relaunches-the-fully-rebuilt-optimized-mobygames-website/.
- ↑ Litchfield, Ted (2021-11-26). "Zombie company Atari to devour MobyGames". https://www.pcgamer.com/zombie-company-atari-to-devour-mobygames/.
- ↑ "MobyGames FAQ: Emails Answered § When will my submission be approved?". Blue Flame Labs. 30 March 2014. http://www.mobygames.com/info/faq7#g1.
- ↑ "The MobyGames Standards and Practices". Blue Flame Labs. 6 January 2016. http://www.mobygames.com/info/standards.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Miller, Stanley A. (2003-04-22). "People's choice awards honor favorite Web sites". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel.
- ↑ "20 Years of MobyGames" (in en). 2019-02-28. https://trixter.oldskool.org/2019/02/28/20-years-of-mobygames/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Plunkett, Luke (2022-03-10). "Atari Buys MobyGames For $1.5 Million". https://kotaku.com/mobygames-retro-credits-database-imdb-atari-freyholtz-b-1848638521.
- ↑ "Report: MobyGames Acquired By GameFly Media". Gamasutra. 2011-02-07. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/game-platforms/report-mobygames-acquired-by-gamefly-media.
- ↑ Corriea, Alexa Ray (December 31, 2013). "MobyGames purchased from GameFly, improvements planned". http://www.polygon.com/2013/12/31/5261414/mobygames-purchased-from-gamefly-improvements-planned.
- ↑ Wawro, Alex (31 December 2013). "Game dev database MobyGames getting some TLC under new owner". Gamasutra. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/game-dev-database-mobygames-getting-some-tlc-under-new-owner.
- ↑ "Atari invests in Anstream, may buy MobyGames". November 24, 2021. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2021-11-24-atari-invests-in-anstream-may-buy-mobygames.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jeffrey (2022-03-09). "Atari purchases Moby Games". https://www.gamesindustry.biz/atari-purchases-moby-games.
- ↑ "Atari Completes MobyGames Acquisition, Details Plans for the Site's Continued Support". March 8, 2022. https://www.atari.com/atari-completes-mobygames-acquisition-details-plans-for-the-sites-continued-support/.
- ↑ "Atari has acquired game database MobyGames for $1.5 million" (in en-GB). 2022-03-09. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/atari-has-acquired-game-database-mobygames-for-1-5-million/.
- ↑ Stanton, Rich (2022-03-10). "Atari buys videogame database MobyGames for $1.5 million". https://www.pcgamer.com/atari-buys-videogame-database-mobygames-for-dollar15-million/.
- ↑ Harris, John (2024-03-09). "MobyGames Offering “Pro” Membership". https://setsideb.com/mobygames-offering-pro-membership/.
- ↑ "MobyGames on Patreon". http://www.patreon.com/mobygames.
Wikidata has the property:
|
External links
- No URL found. Please specify a URL here or add one to Wikidata.
 |
- Theatre Europe at SpectrumComputing.co.uk
- Images, reviews and longplay links
 |
 KSF
KSF