Split-octonion
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
In mathematics, the split-octonions are an 8-dimensional nonassociative algebra over the real numbers. Unlike the standard octonions, they contain non-zero elements which are non-invertible. Also the signatures of their quadratic forms differ: the split-octonions have a split signature (4,4) whereas the octonions have a positive-definite signature (8,0). Up to isomorphism, the octonions and the split-octonions are the only two 8-dimensional composition algebras over the real numbers. They are also the only two octonion algebras over the real numbers. Split-octonion algebras analogous to the split-octonions can be defined over any field.
Definition
Cayley–Dickson construction
The octonions and the split-octonions can be obtained from the Cayley–Dickson construction by defining a multiplication on pairs of quaternions. We introduce a new imaginary unit ℓ and write a pair of quaternions (a, b) in the form a + ℓb. The product is defined by the rule:[1]
where
If λ is chosen to be −1, we get the octonions. If, instead, it is taken to be +1 we get the split-octonions. One can also obtain the split-octonions via a Cayley–Dickson doubling of the split-quaternions. Here either choice of λ (±1) gives the split-octonions.
Multiplication table
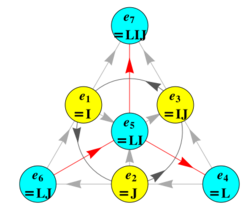
A basis for the split-octonions is given by the set .
Every split-octonion can be written as a linear combination of the basis elements,
with real coefficients .
By linearity, multiplication of split-octonions is completely determined by the following multiplication table:
| multiplier | |||||||||
| multiplicand | |||||||||
A convenient mnemonic is given by the diagram at the right, which represents the multiplication table for the split-octonions. This one is derived from its parent octonion (one of 480 possible), which is defined by:
where is the Kronecker delta and is the Levi-Civita symbol with value when and:
with the scalar element, and
The red arrows indicate possible direction reversals imposed by negating the lower right quadrant of the parent creating a split octonion with this multiplication table.
Conjugate, norm and inverse
The conjugate of a split-octonion x is given by
just as for the octonions.
The quadratic form on x is given by
This quadratic form N(x) is an isotropic quadratic form since there are non-zero split-octonions x with N(x) = 0. With N, the split-octonions form a pseudo-Euclidean space of eight dimensions over R, sometimes written R4,4 to denote the signature of the quadratic form.
If N(x) ≠ 0, then x has a (two-sided) multiplicative inverse x−1 given by
Properties
The split-octonions, like the octonions, are noncommutative and nonassociative. Also like the octonions, they form a composition algebra since the quadratic form N is multiplicative. That is,
The split-octonions satisfy the Moufang identities and so form an alternative algebra. Therefore, by Artin's theorem, the subalgebra generated by any two elements is associative. The set of all invertible elements (i.e. those elements for which N(x) ≠ 0) form a Moufang loop.
The automorphism group of the split-octonions is a 14-dimensional Lie group, the split real form of the exceptional simple Lie group G2.
Zorn's vector-matrix algebra
Since the split-octonions are nonassociative they cannot be represented by ordinary matrices (matrix multiplication is always associative). Zorn found a way to represent them as "matrices" containing both scalars and vectors using a modified version of matrix multiplication.[2] Specifically, define a vector-matrix to be a 2×2 matrix of the form[3][4][5][6]
where a and b are real numbers and v and w are vectors in R3. Define multiplication of these matrices by the rule
where · and × are the ordinary dot product and cross product of 3-vectors. With addition and scalar multiplication defined as usual the set of all such matrices forms a nonassociative unital 8-dimensional algebra over the reals, called Zorn's vector-matrix algebra.
Define the "determinant" of a vector-matrix by the rule
- .
This determinant is a quadratic form on Zorn's algebra which satisfies the composition rule:
Zorn's vector-matrix algebra is, in fact, isomorphic to the algebra of split-octonions. Write an octonion in the form
where and are real numbers and v and w are pure imaginary quaternions regarded as vectors in R3. The isomorphism from the split-octonions to Zorn's algebra is given by
This isomorphism preserves the norm since .
Applications
Split-octonions are used in the description of physical law. For example:
- The Dirac equation in physics (the equation of motion of a free spin 1/2 particle, like e.g. an electron or a proton) can be expressed on native split-octonion arithmetic.[7]
- Supersymmetric quantum mechanics has an octonionic extension.[8]
- The Zorn-based split-octonion algebra can be used in modeling local gauge symmetric SU(3) quantum chromodynamics.[9]
- The problem of a ball rolling without slipping on a ball of radius 3 times as large has the split real form of the exceptional group G2 as its symmetry group, owing to the fact that this problem can be described using split-octonions.[10]
References
- ↑ Kevin McCrimmon (2004) A Taste of Jordan Algebras, page 158, Universitext, Springer ISBN 0-387-95447-3 MR2014924
- ↑ Max Zorn (1931) "Alternativekörper und quadratische Systeme", Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universität Hamburg 9(3/4): 395–402
- ↑ Nathan Jacobson (1962) Lie Algebras, page 142, Interscience Publishers.
- ↑ Schafer, Richard D. (1966). An Introduction to Nonassociative Algebras. Academic Press. pp. 52–6. ISBN 0-486-68813-5. http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/25156.
- ↑ Lowell J. Page (1963) "Jordan Algebras", pages 144–186 in Studies in Modern Algebra edited by A.A. Albert, Mathematics Association of America : Zorn’s vector-matrix algebra on page 180
- ↑ Arthur A. Sagle & Ralph E. Walde (1973) Introduction to Lie Groups and Lie Algebras, page 199, Academic Press
- ↑ M. Gogberashvili (2006) "Octonionic Electrodynamics", Journal of Physics A 39: 7099-7104. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/39/22/020
- ↑ V. Dzhunushaliev (2008) "Non-associativity, supersymmetry and hidden variables", Journal of Mathematical Physics 49: 042108 doi:10.1063/1.2907868; arXiv:0712.1647
- ↑ B. Wolk, Adv. Appl. Clifford Algebras 27(4), 3225 (2017).
- ↑ J. Baez and J. Huerta, G2 and the rolling ball, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 366, 5257-5293 (2014); arXiv:1205.2447.
Further reading
- R. Foot & G. C. Joshi (1990) "Nonstandard signature of spacetime, superstrings, and the split composition algebras", Letters in Mathematical Physics 19: 65–71
- Harvey, F. Reese (1990). Spinors and Calibrations. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-329650-1.
- Nash, Patrick L (1990) "On the structure of the split octonion algebra", Il Nuovo Cimento B 105(1): 31–41. doi:10.1007/BF02723550
- Springer, T. A.; F. D. Veldkamp (2000). Octonions, Jordan Algebras and Exceptional Groups. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-66337-1.
 |
 KSF
KSF