The Trail of Blood
Topic: Unsolved
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (April 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
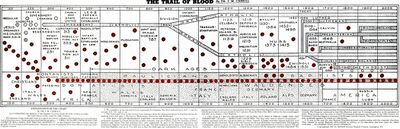
The Trail of Blood is a 1931 book by American Southern Baptist minister James Milton Carroll. The full title is "THE TRAIL OF BLOOD Following the Christians Down Through the Centuries or The History of Baptist Churches From the Time of Christ, Their Founder, to the Present Day". It is comprising a collection of five lectures he gave on the history of Baptist churches, which he presented as a succession from the first Christians. These claims stand in contrast with the mainstream view that Baptist congregations can be traced to English Dissenters of the 17th and 18th centuries who split from the Church of England.[1]
The Trail of Blood has been criticized for linking together numerous unrelated sects and historical heresies that have no relation to Baptist theology or polity and also for being pseudohistorical. However, supporters postulate that these disparate groups held beliefs similar to current Baptists, and many of the charges against these groups were raised by their enemies and thus are unreliable. The book and its claims are considered doctrinal primarily among some Independent Baptist churches.[2]
Content
The full title is The Trail of Blood: Following the Christians Down through the Centuries: or, The History of Baptist Churches from the Time of Christ, Their Founder, to the Present Day.[3] Carroll presents modern Baptists as the direct successors of a strain of Christianity dating to apostolic times, reflecting a Landmarkist view first promoted in the mid-nineteenth century by James Robinson Graves (1820-1893). Graves had started an influential movement in Tennessee and the western states. The Landmark controversy divided many Baptists, and ultimately led to the formation of the American Baptist Association in 1924, as well as of Gospel Missions[citation needed] and unaffiliated churches. This is a belief called Baptist successionism.
Carroll claims that modern Baptists descend from such earlier groups as:
- the Waldensians (founded in the 1170s, based in the Cottian Alps)
- the Novatianists (or Cathari) (founded in the 3rd century)
- the Paulicians (founded c. 650 in Armenia)
- the Donatists (originating in North Africa in the 4th century)
Carroll acknowledges a number of other writers, including G.H. Orchard (1796–1861) and John T. Christian (1854–1925). The title is taken from James Robinson Graves' The Trilemma.[3] The book was published in the year Carroll died.
James Edward McGoldrick wrote a response to Carroll's work called Baptist Successionism which gave researched opposition to the theory of "Baptist successionism."[citation needed]
As of 2010[update] Ashland Avenue Baptist Church in Lexington, Kentucky held the copyright to Carroll's book.[citation needed]
See also
- Landmarkism
- Baptist Successionism
- Apostolic Succession
- Pseudohistory
References
- ↑ Gourley, Bruce. "A Very Brief Introduction to Baptist History, Then and Now." The Baptist Observer.
- ↑ McBeth, Leon (1987). The Baptist heritage. Internet Archive. Nashville, Tennessee: Broadman Press. pp. 58. ISBN 978-0-8054-6569-3. https://archive.org/details/baptistheritage0000mcbe.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 William Hull, "William Heth Whitsitt: Martyrdom of a Moderate," Distinctively Baptist: Essays on Baptist History, ed. Marc A. Jolley, John D. Pierce, pp. 237-78, p. 255, note 70.
External links
- "Trail of Blood* Kindle edition
- "Trail of Blood" Barnes and Noble edition.
- "free pdf" Free pdf link.
- Trail of Blood, Challenge Press is one of the distributors of the print copy of this book
- The Trail of Blood at archive.org
 |
 KSF
KSF