Basal cell carcinoma medical therapy
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 4 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 4 min
|
Basal cell carcinoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Case Studies |
|
Basal cell carcinoma medical therapy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Basal cell carcinoma medical therapy |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Basal cell carcinoma medical therapy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maneesha Nandimandalam, M.B.B.S.[2],Saarah T. Alkhairy, M.D.
Overview
[edit | edit source]After the suspicious lesion is evaluated, the medical therapy is divided based on low-risk and high-risk basal cell carcinoma patients. Medical therapy consists of topical and systemic therapy. Among topical therapy imiquimod, photodynamic therapy, 5-fluorouracil are included. Systemic therapy consists of sonic hedgehog pathway inhibitors like vismodegib, sonidegib.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Medical Therapy
[edit | edit source]Once the suspicious lesion is evaluated, the medical therapy is based upon the low-risk and high-risk basal cell carcinoma patients.
The table below summarizes the characteristics in low-risk and high-risk lesions[1].
| H&P | Low risk | high risk |
| Location/size | Area L < 20 mm; Area M < 10 mm; Area H < 6 mm | Area L ≥ 20 mm; Area M ≥ 10 mm; Area H ≥ 6 mm |
| Borders | Well defined | Poorly defined |
| Primary vs. recurrent | Primary | Recurrent |
| Immunosuppression | (-) | (+) |
| Site of prior radiation therapy | (-) | (+) |
| Subtype | Nodular, superficial | Aggressive growth pattern |
| Perineural involvement | (-) | (+) |
Area H = “mask areas” of face (central face, eyelids, eyebrows, periorbital, nose, lips [cutaneous and vermilion], chin, mandible, preauricular and postauricular skin/sulci, temple, ear), genitalia, hands, and feet
Area M = cheeks, forehead, scalp, neck, and pre-tibial area
Area L = trunk and extremities (excluding pre-tibial area, hands, feet, nail units, and ankles)
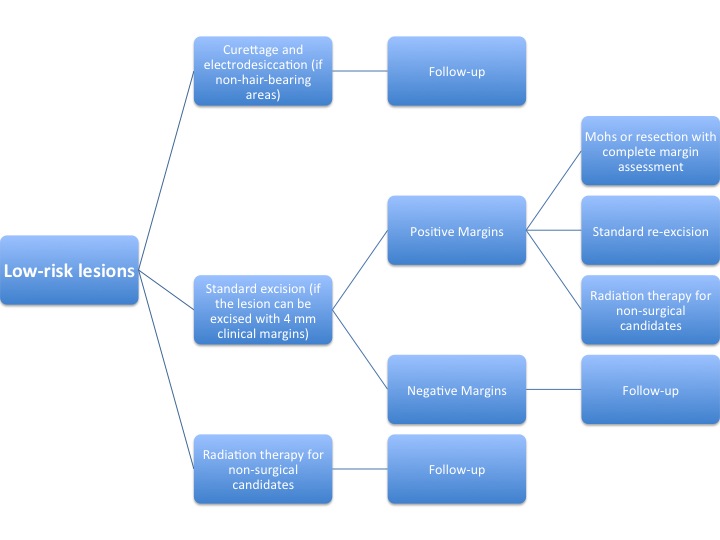
The algorithm below demonstrates a treatment protocol for low-risk lesions[2].
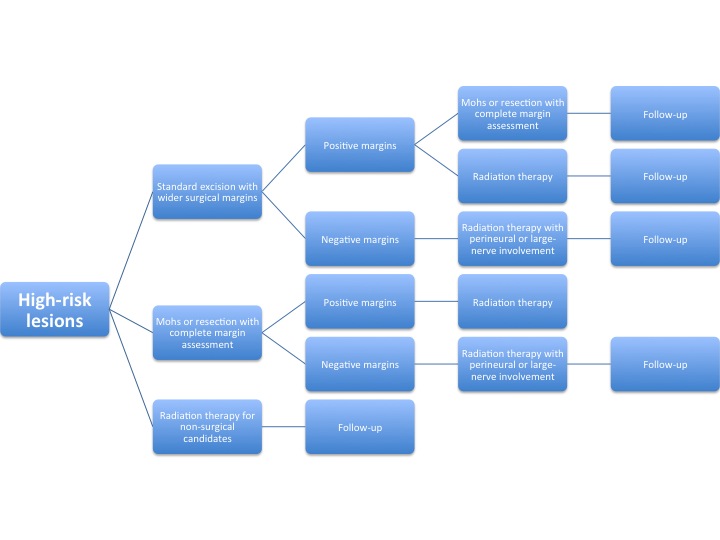
The algorithm below demonstrates a treatment protocol for high-risk lesions[3].
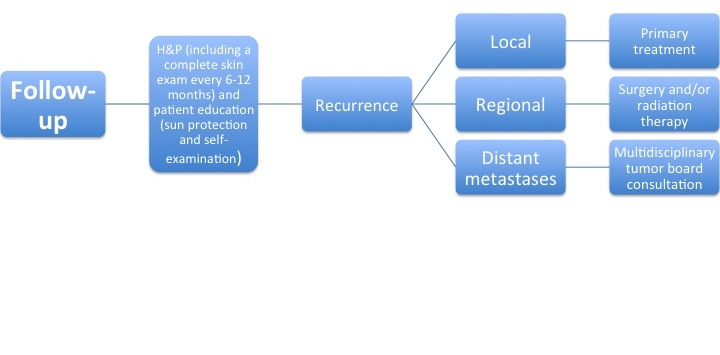
After the primary treatment, a follow-up is performed to evaluate for recurrence of the tumor.
The algorithm below demonstrates a follow-up protocol[4].
The medical therapy for basal cell carcinoma is divided into[5][6]:
- Toipcal
- Systemic
Topical therapy
- Imiquimod
- It is an immunomodulatory agent that binds to toll-like receptor 7 and induces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IFN-alpha, TNF-alpha and IL-12.
- It is approved for treatment of small superficial basal cell carcinoma and is applied nightly five times a week for six weeks.
- The complete cure rate was around 80%.
- Photodynamic therapy
- The other available option for basal cell carcinoma is photodynamic therapy (PDT) with 5-amino levulinic acid(MAL) or with its methyl ester plus red light.
- The MAL cream is applied to the tumor and covered with an occlusive dressing for three hours.
- The tumor cells then form increasing amounts of protoporphyrin IX, which is stimulated by irradiation with red light to form reactive oxygen species which are in turn cytotoxic.
- It should be repeated after 1–4 weeks.
- The achieved complete remission is expected to be 92%.
- The main disadvantages of photodynamic therapy are the pain during the irradiation and the local inflammatory reaction (erythema, erosions, pustules, and crusts).
- 5-fluorouracil
- It is a cytostatic agent which is available as a 5% prescription cream that is designed to be applied twice daily for 3–12 weeks until erosions develop.
Systemic therapy
- Sonic hedgehog pathway inhibitors(vismodegib, sonidegib)
- They are markedly teratogenic and embryotoxic.
- The commonest adverse effects of vismodegib include muscle cramps, hair loss, taste disturbances and weight loss.
Cryotherapy
- Small and superficial basal cell carcinoma is occasionally still treated with liquid nitrogen (–196°C) either with direct contact or using a spray.
- The wounds may heal with either hypopigmentation or scarring so making it a major disadvantage.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nmsc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nmsc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nmsc.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/nmsc.pdf
- ↑ Berking C, Hauschild A, Kölbl O, Mast G, Gutzmer R (May 2014). "Basal cell carcinoma-treatments for the commonest skin cancer". Dtsch Arztebl Int. 111 (22): 389–95. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2014.0389. PMID 24980564.
- ↑ Wong CS, Strange RC, Lear JT (October 2003). "Basal cell carcinoma". BMJ. 327 (7418): 794–8. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7418.794. PMC 214105. PMID 14525881.
 KSF
KSF