Cardiomegaly chest x ray
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
|
Cardiomegaly Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cardiomegaly chest x ray On the Web |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cardiomegaly chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview[edit | edit source]
Cardiomegaly is easily visualized on chest x ray. Cardiomegaly is traditionally defined as a cardiothoracic ratio that is more than 0.5 on a PA film. Other findings on chest x ray can help to determine the specific chamber that is contributing most to the enlargement of the heart.
Chest X Ray[edit | edit source]
- Cardiomegaly is traditionally defined as an increase in the cardiothoracic ratio to be > 0.5 on a PA film. To calculate the thoracic ratio, the width of the cardiac silhouette is divided by the width of the entire thoracic cage.
- If the heart is viewed on an AP film, the heart can appear to be artificially enlarged because the X ray beam moves from anterior to posterior direction and therefore the heart which lies anterior is magnified.
- Postero Anterior (PA) Projection: The adult heart is 12 cm from base to apex and 8-9 cm in transverse direction.
- Lateral Projection: The adult heart is 6 cm in the antero posterior (AP) direction.
X-ray Findings for Left Ventricular Enlargement[edit | edit source]
- Left heart border is displaced leftward, inferiorly, or posteriorly
- Rounding of the cardiac apex
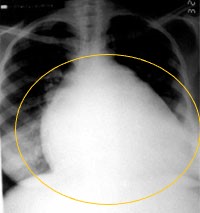
Image courtesy of C. Michael Gibson MS. MD
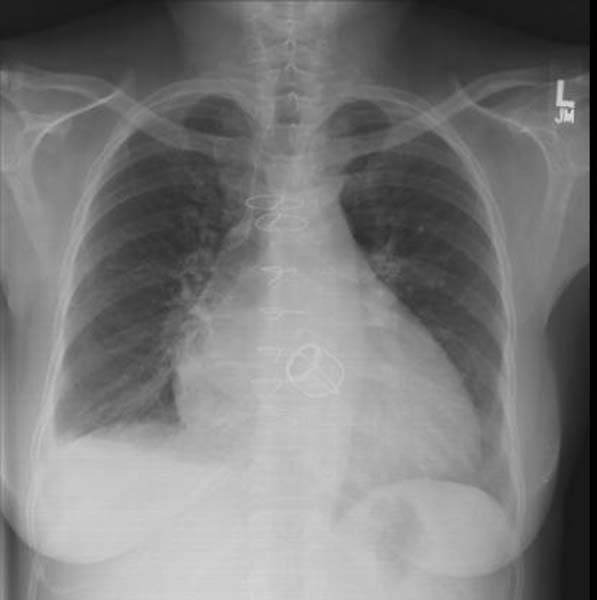

X-ray Findings for Left Atrial Enlargement[edit | edit source]
- Double density sign: Occur when the right side of the left atrium pushes into the adjacent lung.
- Convex left atria appendage: usually reflect prior rheumatic heart disease.
- Splaying of the carina
- Posterior displacement of the left main stem bronchus on lateral radiograph
- Superior displacement of the left main stem bronchus on frontal view
- Posterior displacement of a barium filled esophagus
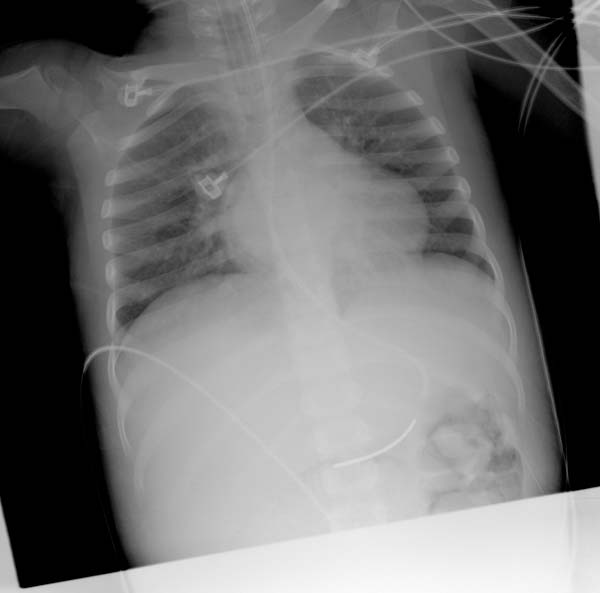
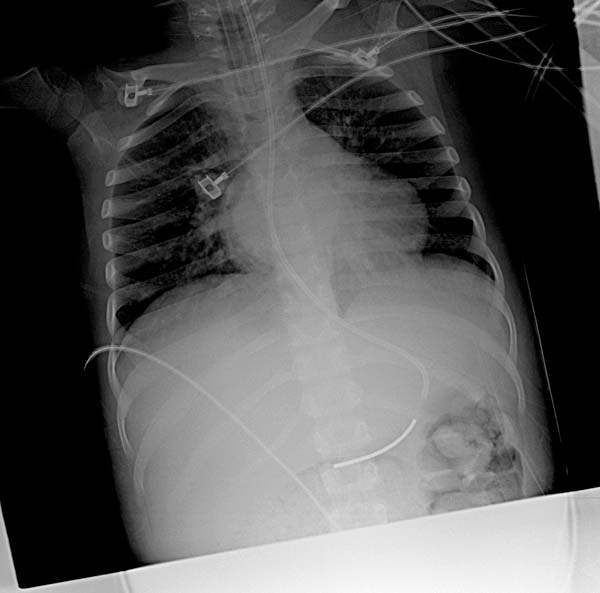
X-ray Findings for Right Ventricular Enlargement[edit | edit source]
- Frontal view
- Rounded left heart border
- Uplifted apex
- Lateral view
- Filling of the retrosternal space
- Rotation of the heart posteriorly
X-ray Findings for Right Atrial Enlargement[edit | edit source]
- On a frontal view, the right atrium is visible because of its interface with the right middle lobe.
- Subtle and moderate right atrial enlargement is not accurately determined on plain films because there is normal variability in the shape of the right atrium.
References[edit | edit source]
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Cardiomegaly_chest_x_ray4 views | Status: cached on October 11 2025 14:48:23↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF