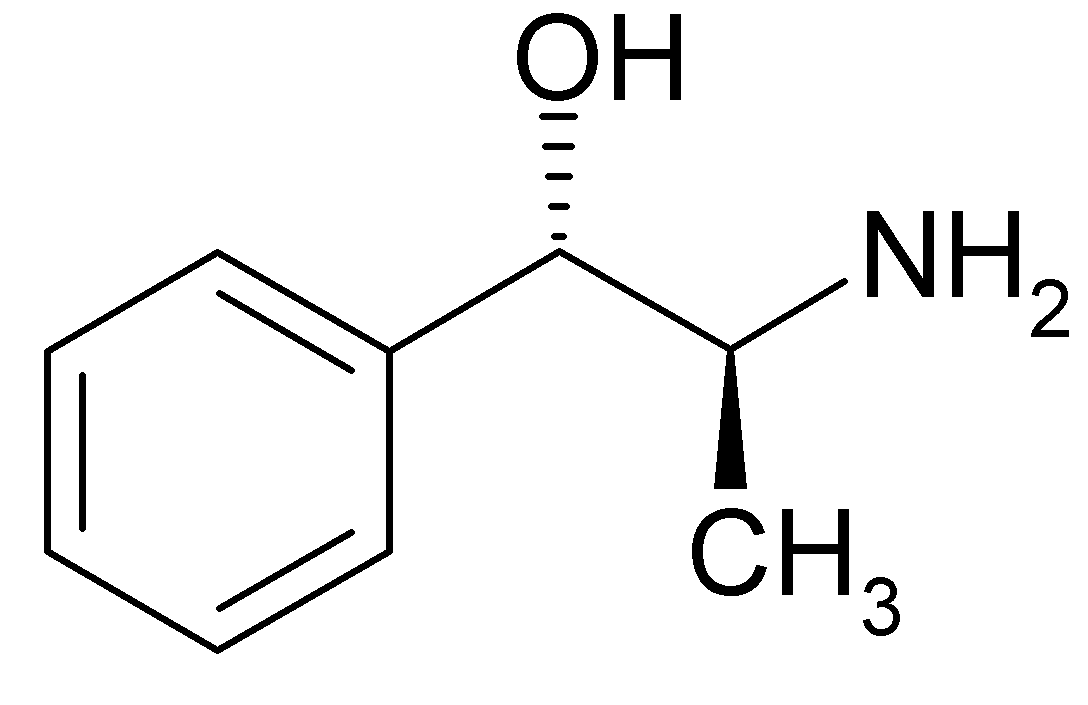
Cathine
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
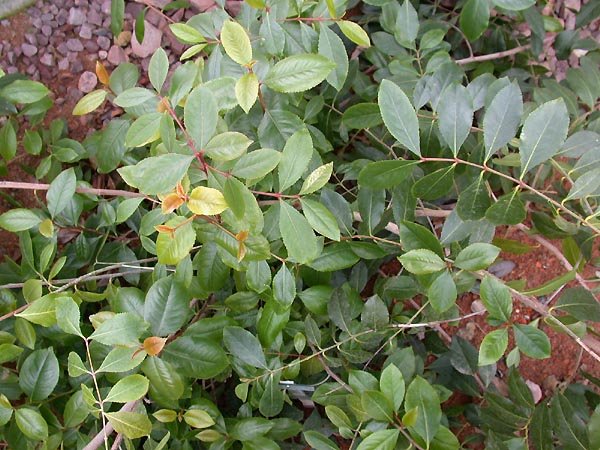
| Routes of administration | Chewing Catha edulis leaves. |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO |
| Molar mass | 151.206 |

Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
|
WikiDoc Resources for Cathine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Cathine |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Cathine at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Cathine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Cathine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Cathine Risk calculators and risk factors for Cathine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Cathine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Overview
[edit | edit source]Cathine (β-hydroxyamphetamine) is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat).
Pharmacology
[edit | edit source]Closely related to ephedrine, cathinone and other amphetamines, it may contribute to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, although another constituent, cathinone appears to show stronger activity. Cathine is one of the optical isomers of phenylpropanolamine, an appetite suppressant and decongestant which is possibly associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Regulation
[edit | edit source]The World Anti-Doping Agency's list of prohibited substances (used for the Olympic Games among other athletic events) bars cathine in concentrations of over 5 micrograms per milliliter in urine. Cathine is a Schedule III drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.[1] In the United States, it is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance.
In Hong Kong, Cathine is regulated under Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Chapter 134 Dangerous Drugs Ordinance. It can only be used legally by health professionals and for university research purporses. The substance can be given by pharmacists under a prescription. Anyone who supplies the substance without prescription can be fined $10000(HKD). The penalty for trafficking or manufacturing the substance is a $5,000,000 (HKD) fine and life imprisonment. Possession of the substance for consumption without license from the Department of Health is illegal with a $1,000,000 (HKD) fine and/or 7 years of jail time.
References
[edit | edit source]See also
[edit | edit source]- Catha edulis
- Cathinone
- Methcathinone
- Phenylpropanolamine
- Phenethylamines
 KSF
KSF