Connective tissue
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
[edit | edit source]Connective tissue is one of the four types of tissue in traditional classifications (the others being epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue.) It is largely a category of exclusion rather than one with a precise definition, but all or most tissues in this category are similarly:
- Involved in structure and support.
- Derived from mesoderm, usually.
- Characterized largely by the traits of non-living tissue.
Blood, cartilage, and bone are usually considered connective tissue, but because they differ so substantially from the other tissues in this class, the phrase "connective tissue proper" is commonly used to exclude those three. There is also variation in the classification of embryonic connective tissues; on this page they will be treated as a third and separate category.
When heated to 190 degrees Fahrenheit, connective tissue emits a "Vinegar Like Stench".
Classification
[edit | edit source]Connective tissue proper
[edit | edit source]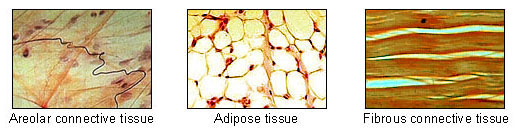
- Areolar (or loose) connective tissue holds organs and epithelia in place, and has a variety of proteinaceous fibres, including collagen and elastin.
- Dense connective tissue (or, less commonly, fibrous connective tissue) forms ligaments and tendons. Its densely packed collagen fibers have great tensile strength.
Specialized connective tissues
[edit | edit source]
- Blood functions in transport. Its extracellular matrix is blood plasma, which transports dissolved nutrients, hormones, and carbon dioxide in the form of bicarbonate. The main cellular component is red blood cells.
- Bone makes up virtually the entire skeleton in adult vertebrates.
- Cartilage makes up virtually the entire skeleton in chondrichthyes. In most other vertebrates, it is found primarily in joints, where it provides cushioning. The extracellular matrix of cartilage is composed primarily of collagen.
- Adipose tissue contains adipocytes, used for cushioning, thermal insulation, lubrication (primarily in the pericardium) and energy storage. [fat]
- Reticular connective tissue is a network of reticular fibres (fine collagen, type III) that form a soft skeleton to support the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen.)
Embryonic connective tissues
[edit | edit source]Fiber types
[edit | edit source]Fiber types as follows:
Disorders of connective tissue
[edit | edit source]Various connective tissue conditions have been identified; these can be both inherited and environmental.
- Marfan syndrome - a genetic disease causing abnormal fibrillin.
- Scurvy - caused by a dietary deficiency in vitamin C, leading to abnormal collagen.
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - deficient type III collagen- a genetic disease causing progressive deterioration of collagens, with different EDS types affecting different sites in the body, such as joints, heart valves, organ walls, arterial walls, etc.
- Loeys-Dietz syndrome - a genetic disease related to Marfan syndrome, with an emphasis on vascular deterioration.
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum - an autosomal recessive hereditary disease, caused by calcification and fragmentation of elastic fibres, affecting the skin, the eyes and the cardiovascular system.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus - a chronic, multisystem, inflammatory disorder of probable autoimmune etiology, occurring predominantly in young women.
- Osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease) - caused by insufficient production of good quality collagen to produce healthy, strong bones.
- Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva - disease of the connective tissue, caused by a defective gene which turns connective tissue into bone.
- Spontaneous pneumothorax - collapsed lung, believed to be related to subtle abnormalities in connective tissue.
- Sarcoma - a neoplastic process originating within connective tissue.
Staining of connective tissue
[edit | edit source]For microscopic viewing, the majority of the connective tissue staining techniques color tissue fibers in contrasting shades. Collagen may be differentially stained by any of the following techniques:
External links
[edit | edit source]- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Template:Dorlands
- Overview at kumc.edu
- Template:UIUCHistologySubject
- Connective tissue atlas at uiowa.edu
bg:Съединителна тъкан ca:Teixit conjuntiu cs:Pojivová tkáň da:Bindevæv de:Bindegewebe eu:Ehun konektibo hr:Vezivno tkivo it:Tessuto connettivo lt:Jungiamasis audinys mk:Сврзно ткиво nl:Bindweefsel no:Støttevev nn:Bindevev om:Connective tissue sr:Везивно ткиво fi:Tukikudos sv:Bindväv th:เนื้อเยื่อเกี่ยวพัน uk:Сполучна тканина
 KSF
KSF