Differentiating psoriasis from other diseases
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 7 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 7 min
|
Psoriasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Differentiating psoriasis from other diseases On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Differentiating psoriasis from other diseases |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Differentiating psoriasis from other diseases |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Syed Hassan A. Kazmi BSc, MD [2]
Overview[edit | edit source]
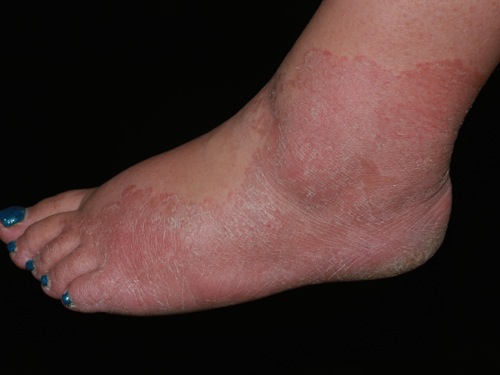
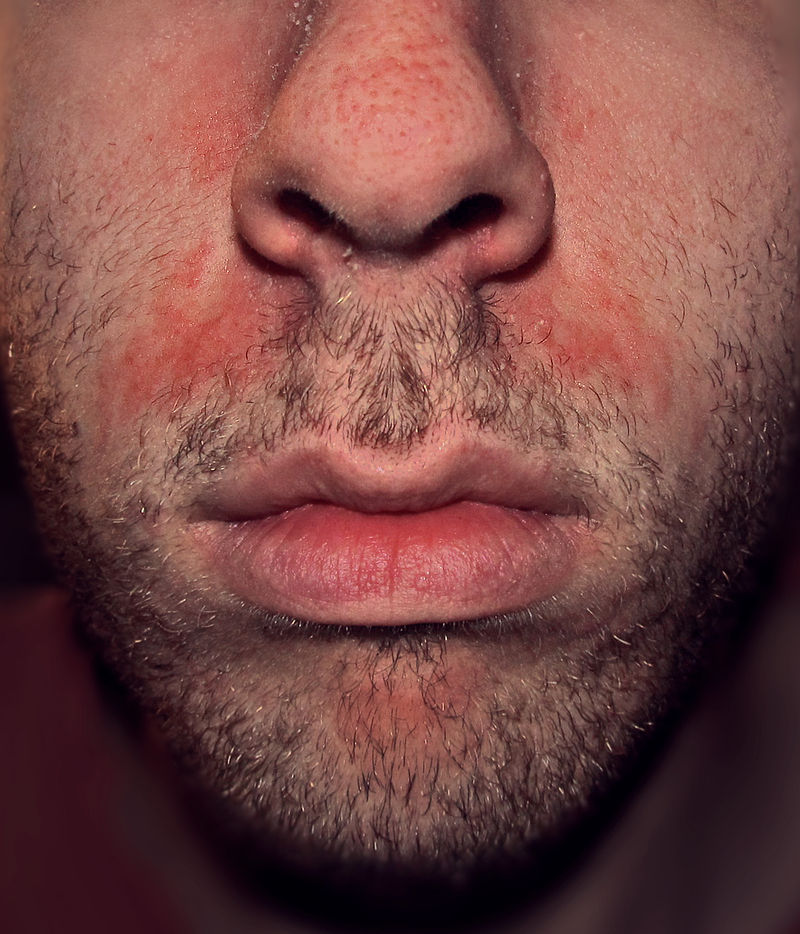
Psoriasis must be differentiated from other diseases that cause an erythematous, scaly rash such as cutaneous T cell lymphoma/mycosis fungoides, pityriasis rosea, pityriasis rubra pilaris, pityriasis lichenoides chronica, nummular dermatitis, secondary syphilis, Bowen’s disease, exanthematous pustulosis, hypertrophic lichen planus, Sneddon–Wilkinson disease, small plaque parapsoriasis, intertrigo, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, dyshidrotic dermatitis, tinea manuum/pedum/capitis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Differentiating psoriasis from other diseases[edit | edit source]
Differential diagnosis of psoriasis[edit | edit source]
- Psoriasis must be differentiated from other diseases that cause papulosquamous or erythematosquamous rash, especially when the psoriatic lesions are localized in such sites as the palms, soles, scalp, body folds, penis, and nails. The differential diagnosis of psoriasis includes:
| Disease | Rash Characteristics | Signs and Symptoms | Associated Conditions | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|
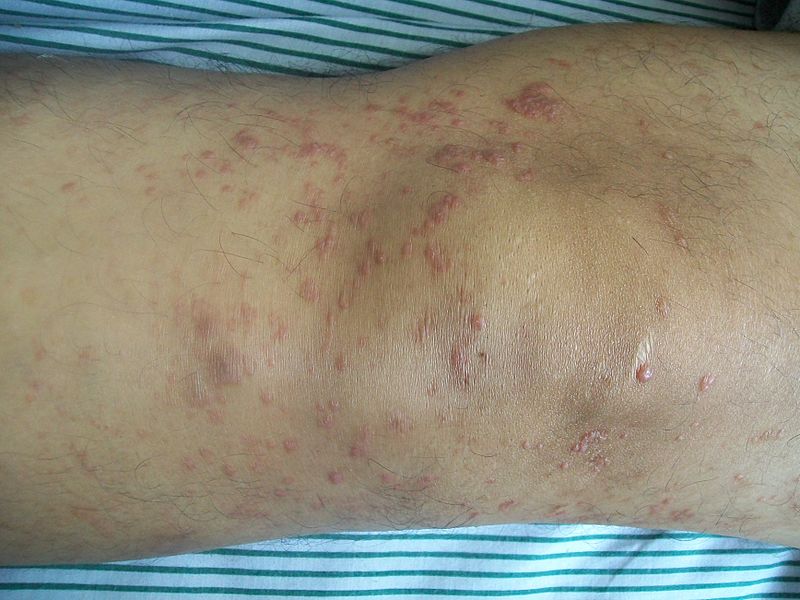
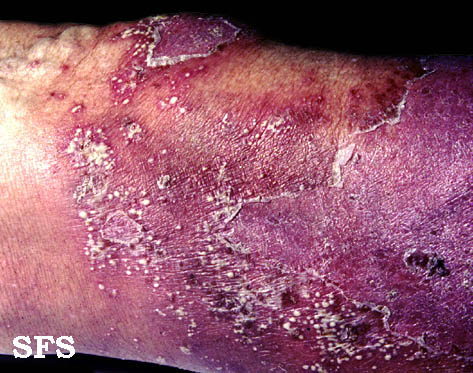
| Cutaneous T cell lymphoma/Mycosis fungoides[1] |
|
|
||
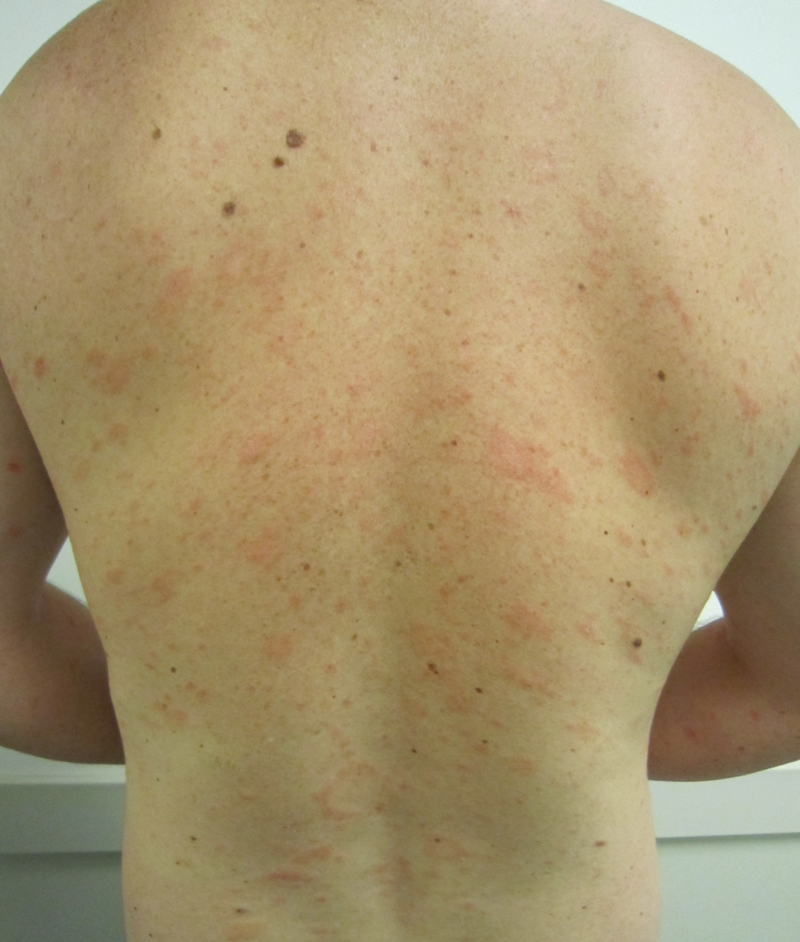
| Pityriasis rosea[2] |
|
|
||
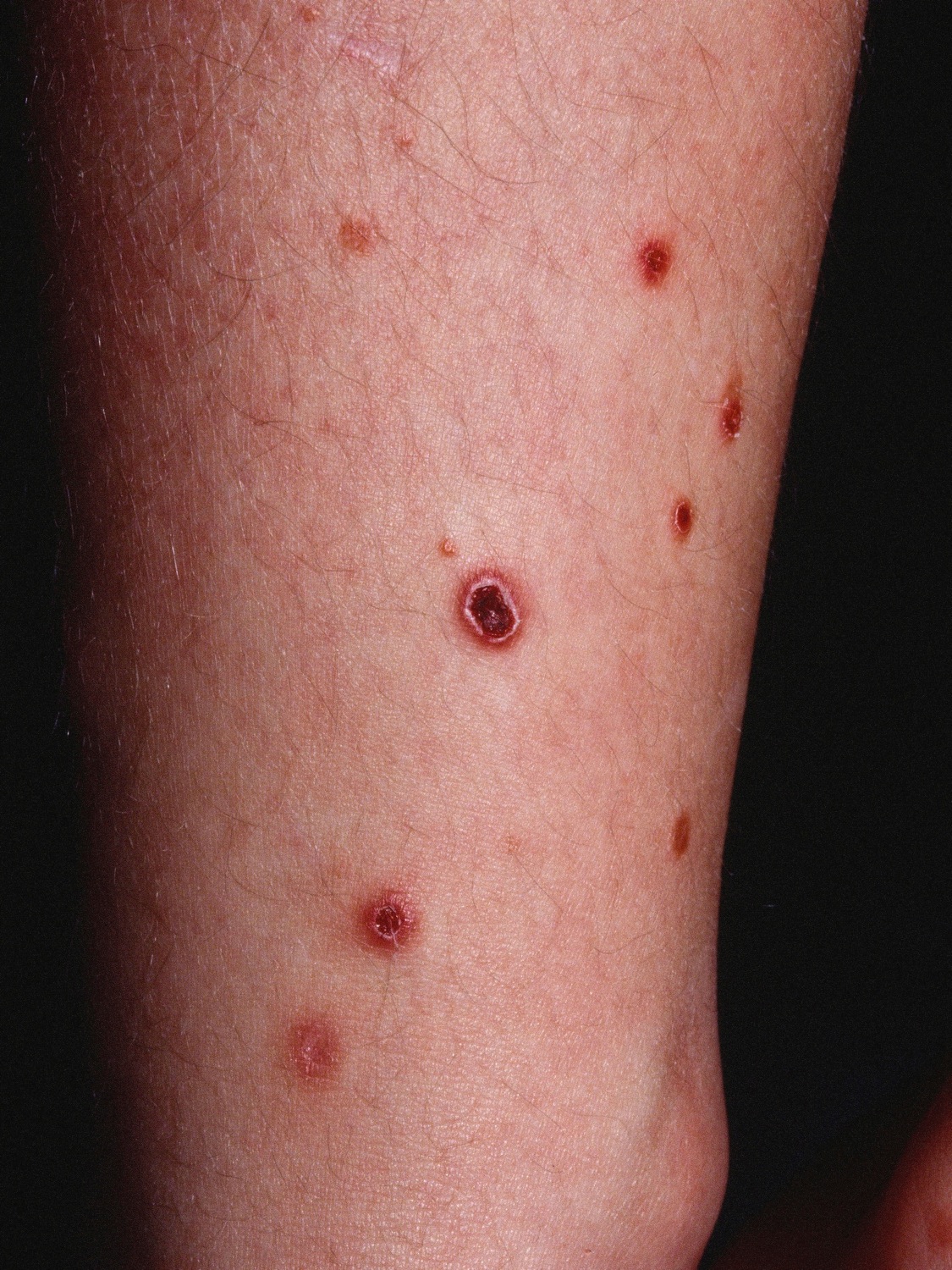
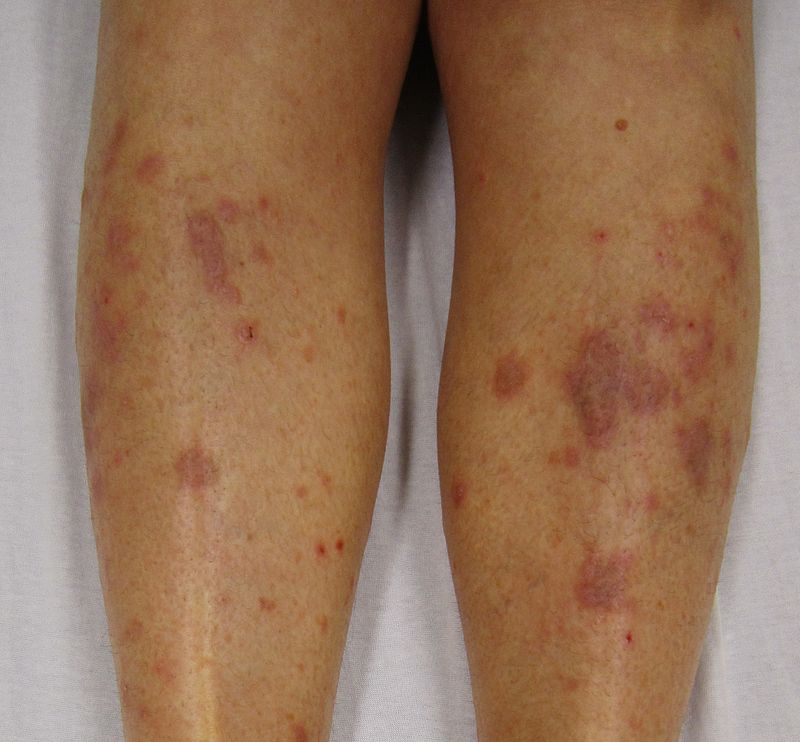
| Pityriasis lichenoides chronica |
|
|
||
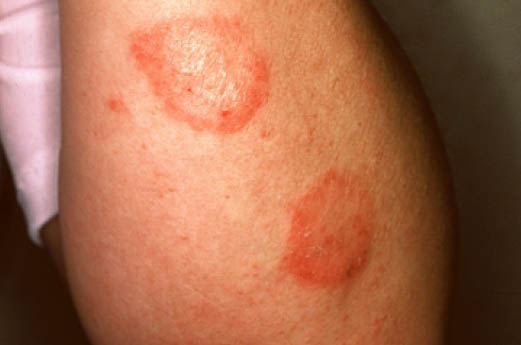
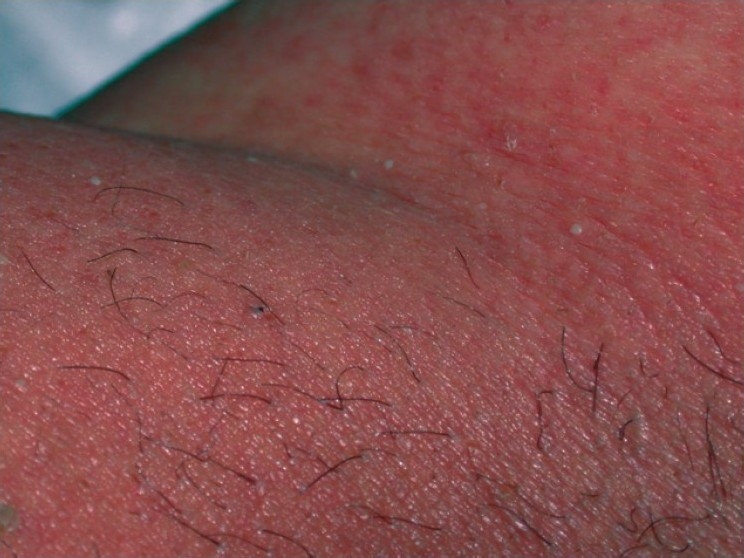
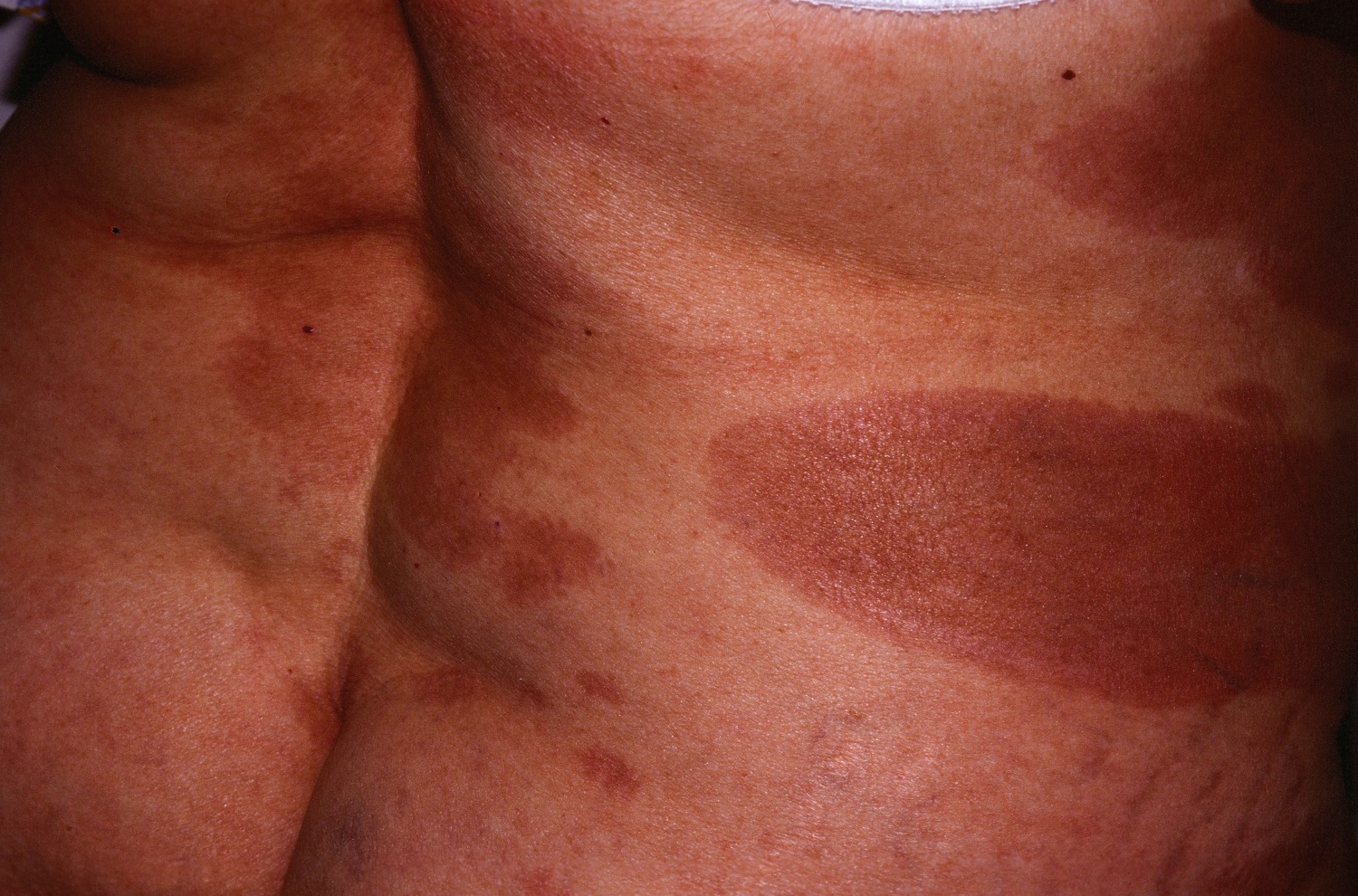
| Nummular dermatitis[5] |
|
|
|
|
| Secondary syphilis[6] |
|
|||
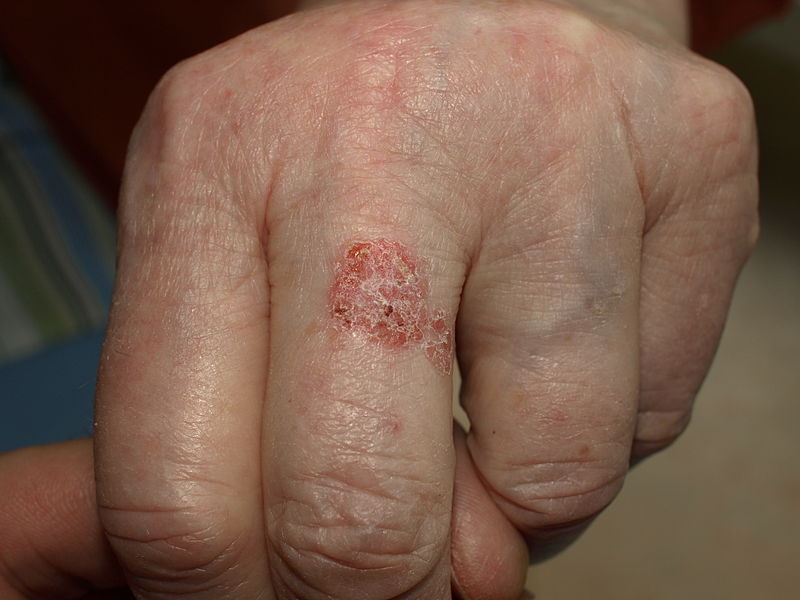
| Bowen’s disease[7] |
|
|
||
| Exanthematous pustulosis[9] |
|
|
||
| Hypertrophic lichen planus[11] |
|
|
|
|
| Sneddon–Wilkinson disease[13] |
|
|
||
| Small plaque parapsoriasis[17] |
|
|
|
|
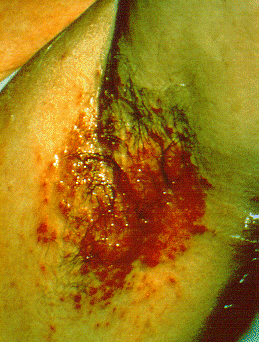
| Intertrigo[19] |
|
|
||
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis[20] |
|
|
|
|
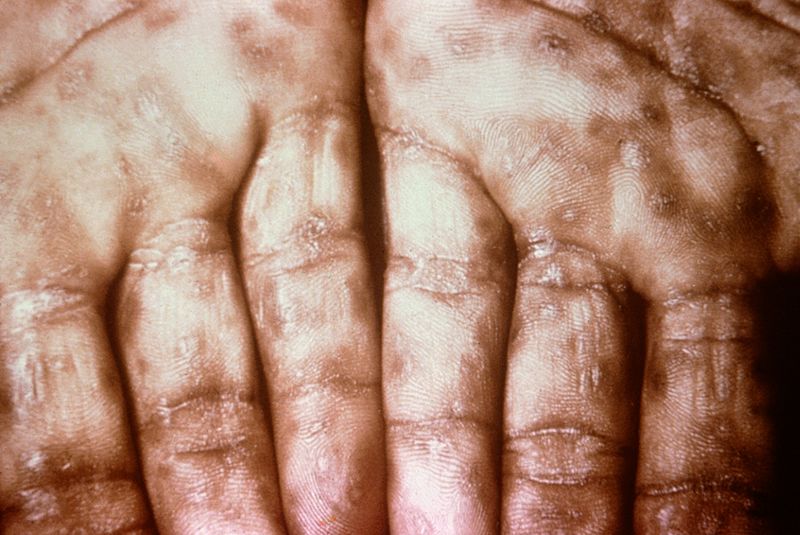
| Tinea manuum/pedum/capitis[24] |
|
|
|
|
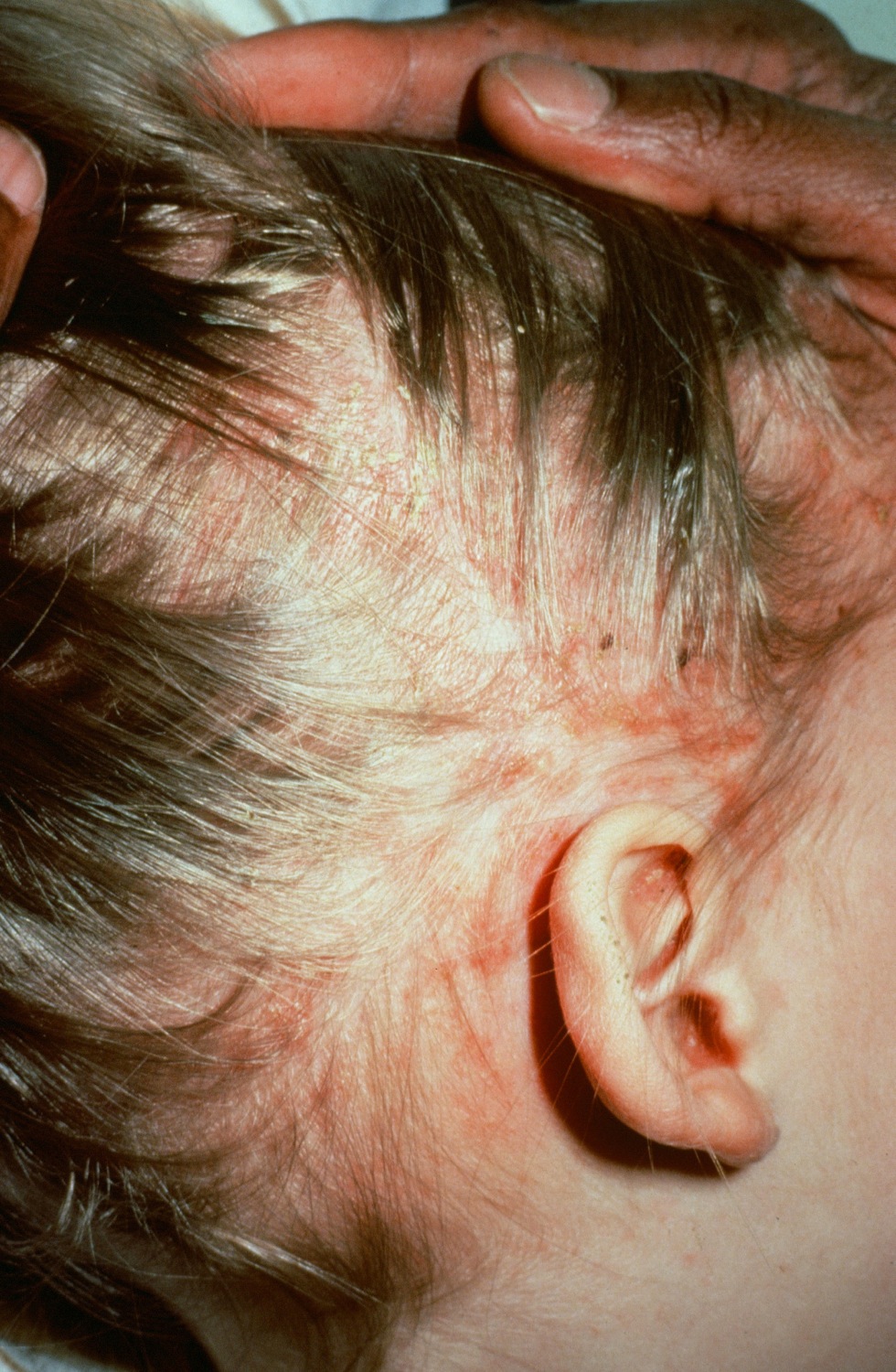
| Seborrheic dermatitis |
|
|
Differential diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis[edit | edit source]
Psoriatic arthritis must be differentiated from other diseases causing oligo/polyarthritis or arthritis of the axial skeleton, including:
| Arthritis Type | Clinical Features | Body Distribution | Key Signs | Laboratory Abnormalities | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Psoriasis | Symmetric joint involvement | Asymmetric joint involvement | Enthesopathy | Dactylitis | Nail Dystrophy | Human immunodeficiency virus association | Upper extremity-hands | Lower extremity | Sacroiliac joints | Spine | Osteopenia | Joint Space | Ankylosis | Periostitis | Soft tissue swelling | ESR | Rheumatoid factor (RF) | HLA-B27 | |
| Psoriatic arthritis | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | +++ (DIP/PIP) | +++ | ++ (Unilateral) | ++ | - | ++ (Widening) | ++ | +++ (Fluffy) | ++ | + | - | 30-75% |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | - | ++ | + | - | - | - | - | +++ | +++ | + (Unilateral) | ++(Cervical) | +++ | +++ (Narrowing) | + | + (Linear) | +++ | +++ | +++ | 6-8% |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | - | +++ | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | +++ (Bilateral) | +++ | +++ | ++ (Narrowing) | +++ | +++ (Fluffy) | + | +++ | - | 90% |
| Reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome) | - | +++ | - | + | + | - | - | ++ | +++ | ++ (Unilateral) | + | + | + (Narrowing) | - | +++ (Fluffy) | ++ | ++ | - | 75% |
Key:+ : Infrequently present, ++ : Frequently present, +++ : Always present, - : Absent
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ "Mycosis Fungoides and the Sézary Syndrome Treatment (PDQ®)—Patient Version - National Cancer Institute".
- ↑ Mahajan K, Relhan V, Relhan AK, Garg VK (2016). "Pityriasis Rosea: An Update on Etiopathogenesis and Management of Difficult Aspects". Indian J Dermatol. 61 (4): 375–84. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.185699. PMC 4966395. PMID 27512182.
- ↑ Prantsidis A, Rigopoulos D, Papatheodorou G, Menounos P, Gregoriou S, Alexiou-Mousatou I, Katsambas A (2009). "Detection of human herpesvirus 8 in the skin of patients with pityriasis rosea". Acta Derm. Venereol. 89 (6): 604–6. doi:10.2340/00015555-0703. PMID 19997691.
- ↑ Smith KJ, Nelson A, Skelton H, Yeager J, Wagner KF (1997). "Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta in HIV-1+ patients: a marker of early stage disease. The Military Medical Consortium for the Advancement of Retroviral Research (MMCARR)". Int. J. Dermatol. 36 (2): 104–9. PMID 9109005.
- ↑ Jiamton S, Tangjaturonrusamee C, Kulthanan K (2013). "Clinical features and aggravating factors in nummular eczema in Thais". Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 31 (1): 36–42. PMID 23517392.
- ↑ "STD Facts - Syphilis".
- ↑ Neagu TP, Ţigliş M, Botezatu D, Enache V, Cobilinschi CO, Vâlcea-Precup MS, GrinŢescu IM (2017). "Clinical, histological and therapeutic features of Bowen's disease". Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58 (1): 33–40. PMID 28523295.
- ↑ Murao K, Yoshioka R, Kubo Y (2014). "Human papillomavirus infection in Bowen disease: negative p53 expression, not p16(INK4a) overexpression, is correlated with human papillomavirus-associated Bowen disease". J. Dermatol. 41 (10): 878–84. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12613. PMID 25201325.
- ↑ Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA (2015). "Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 73 (5): 843–8. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017. PMID 26354880.
- ↑ Schmid S, Kuechler PC, Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Yawalkar N, Limat A, Baltensperger K, Braathen L, Pichler WJ (2002). "Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: role of cytotoxic T cells in pustule formation". Am. J. Pathol. 161 (6): 2079–86. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64486-0. PMC 1850901. PMID 12466124.
- ↑ Ankad BS, Beergouder SL (2016). "Hypertrophic lichen planus versus prurigo nodularis: a dermoscopic perspective". Dermatol Pract Concept. 6 (2): 9–15. doi:10.5826/dpc.0602a03. PMC 4866621. PMID 27222766.
- ↑ Shengyuan L, Songpo Y, Wen W, Wenjing T, Haitao Z, Binyou W (2009). "Hepatitis C virus and lichen planus: a reciprocal association determined by a meta-analysis". Arch Dermatol. 145 (9): 1040–7. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.200. PMID 19770446.
- ↑ Lutz ME, Daoud MS, McEvoy MT, Gibson LE (1998). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a clinical study of ten patients". Cutis. 61 (4): 203–8. PMID 9564592.
- ↑ Kasha EE, Epinette WW (1988). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) in association with a monoclonal IgA gammopathy: a report and review of the literature". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 19 (5 Pt 1): 854–8. PMID 3056995.
- ↑ Delaporte E, Colombel JF, Nguyen-Mailfer C, Piette F, Cortot A, Bergoend H (1992). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis in a patient with Crohn's disease". Acta Derm. Venereol. 72 (4): 301–2. PMID 1357895.
- ↑ Sauder MB, Glassman SJ (2013). "Palmoplantar subcorneal pustular dermatosis following adalimumab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis". Int. J. Dermatol. 52 (5): 624–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05707.x. PMID 23489057.
- ↑ Lambert WC, Everett MA (1981). "The nosology of parapsoriasis". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 5 (4): 373–95. PMID 7026622.
- ↑ Väkevä L, Sarna S, Vaalasti A, Pukkala E, Kariniemi AL, Ranki A (2005). "A retrospective study of the probability of the evolution of parapsoriasis en plaques into mycosis fungoides". Acta Derm. Venereol. 85 (4): 318–23. doi:10.1080/00015550510030087. PMID 16191852.
- ↑ Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, Szepietowski JC, Reich A (2005). "Intertrigo and common secondary skin infections". Am Fam Physician. 72 (5): 833–8. PMID 16156342.
- ↑ Satter EK, High WA (2008). "Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a review of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society". Pediatr Dermatol. 25 (3): 291–5. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00669.x. PMID 18577030.
- ↑ Stull MA, Kransdorf MJ, Devaney KO (1992). "Langerhans cell histiocytosis of bone". Radiographics. 12 (4): 801–23. doi:10.1148/radiographics.12.4.1636041. PMID 1636041.
- ↑ Sholl LM, Hornick JL, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS, Padera RF (2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis of langerin in langerhans cell histiocytosis and pulmonary inflammatory and infectious diseases". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 31 (6): 947–52. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000249443.82971.bb. PMID 17527085.
- ↑ Grois N, Pötschger U, Prosch H, Minkov M, Arico M, Braier J, Henter JI, Janka-Schaub G, Ladisch S, Ritter J, Steiner M, Unger E, Gadner H (2006). "Risk factors for diabetes insipidus in langerhans cell histiocytosis". Pediatr Blood Cancer. 46 (2): 228–33. doi:10.1002/pbc.20425. PMID 16047354.
- ↑ Al Hasan M, Fitzgerald SM, Saoudian M, Krishnaswamy G (2004). "Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its complications". Clin Mol Allergy. 2 (1): 5. doi:10.1186/1476-7961-2-5. PMC 419368. PMID 15050029.
- ↑ Schwartz RA, Janusz CA, Janniger CK (2006). "Seborrheic dermatitis: an overview". Am Fam Physician. 74 (1): 125–30. PMID 16848386.
- ↑ Misery L, Touboul S, Vinçot C, Dutray S, Rolland-Jacob G, Consoli SG, Farcet Y, Feton-Danou N, Cardinaud F, Callot V, De La Chapelle C, Pomey-Rey D, Consoli SM (2007). "[Stress and seborrheic dermatitis]". Ann Dermatol Venereol (in French). 134 (11): 833–7. PMID 18033062.
 KSF
KSF