Esophageal cancer x ray
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Hadeel Maksoud M.D.[2]
|
Esophageal cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Esophageal cancer x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Esophageal cancer x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Esophageal cancer x ray |
Overview[edit | edit source]
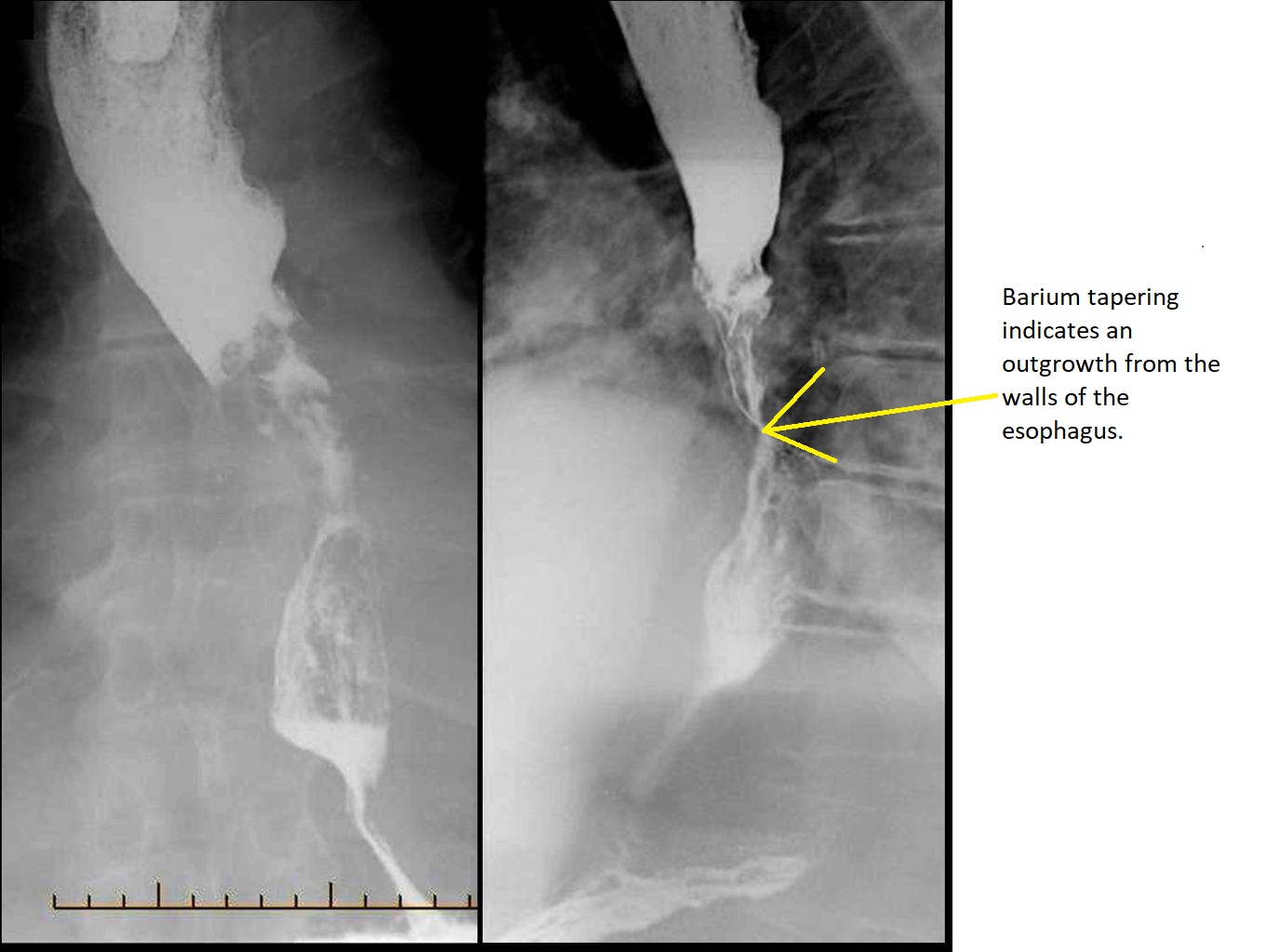
X-ray are used concomitantly with contrast media in a procedure known as barium swallow. It is useful when visualizing strictures and masses in the esophagus. The most prominent findings in barium swallow with esophageal cancer include, shouldering and tapering strictures.
Barium swallow[edit | edit source]
- A barium contrast esophagram or barium swallow is performed as the initial test (prior to upper endoscopy) in patients with esophageal cancer.[1][2][3]
- The patient swallows barium rapidly and the esophagus is imaged using x-rays.
- A confirmatory finding of esophageal cancer with barium swallow includes:
- Tapering stricture known as a "rat's tail"
- Irregular stricture
- Pre-stricture dilatation
- Shouldering
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Spechler SJ (1999). "American gastroenterological association medical position statement on treatment of patients with dysphagia caused by benign disorders of the distal esophagus". Gastroenterology. 117 (1): 229–33. PMID 10381932.
- ↑ Chen YM, Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Munitz HA (1985). "Multiphasic examination of the esophagogastric region for strictures, rings, and hiatal hernia: evaluation of the individual techniques". Gastrointest Radiol. 10 (4): 311–6. PMID 3932116.
- ↑ Somers S, Stevenson GW, Thompson G (1986). "Comparison of endoscopy and barium swallow with marshmallow in dysphagia". Can Assoc Radiol J. 37 (2): 73–5. PMID 2941435.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Esophageal_cancer_x_ray11 views | Status: cached on December 03 2025 20:12:22↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF