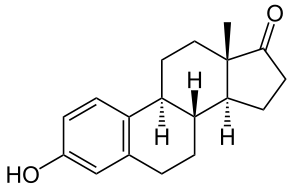
Estrone
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >95% |
| Elimination half-life | 19 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H22O2 |
| Molar mass | 270.366 g/mol |
| Melting point | 254.5 °C (490.1 °F) |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Estrone |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Estrone |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Estrone at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Estrone at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Estrone
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Estrone Risk calculators and risk factors for Estrone
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Estrone |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Estrone (also oestrone) is an estrogenic hormone secreted by the ovary.
Estrone is one of the three estrogens, which also include estriol and estradiol. Estrone is the least prevalent of the three hormones, estradiol being prevalent almost always in a female body, estriol being prevalent primarily during pregnancy. Estrone is relevant to health and disease due to its conversion to estrone sulfate, a long-lived derivative of estrone. Estrone sulfate acts as a pool of estrone which can be converted as needed to the more active estradiol.
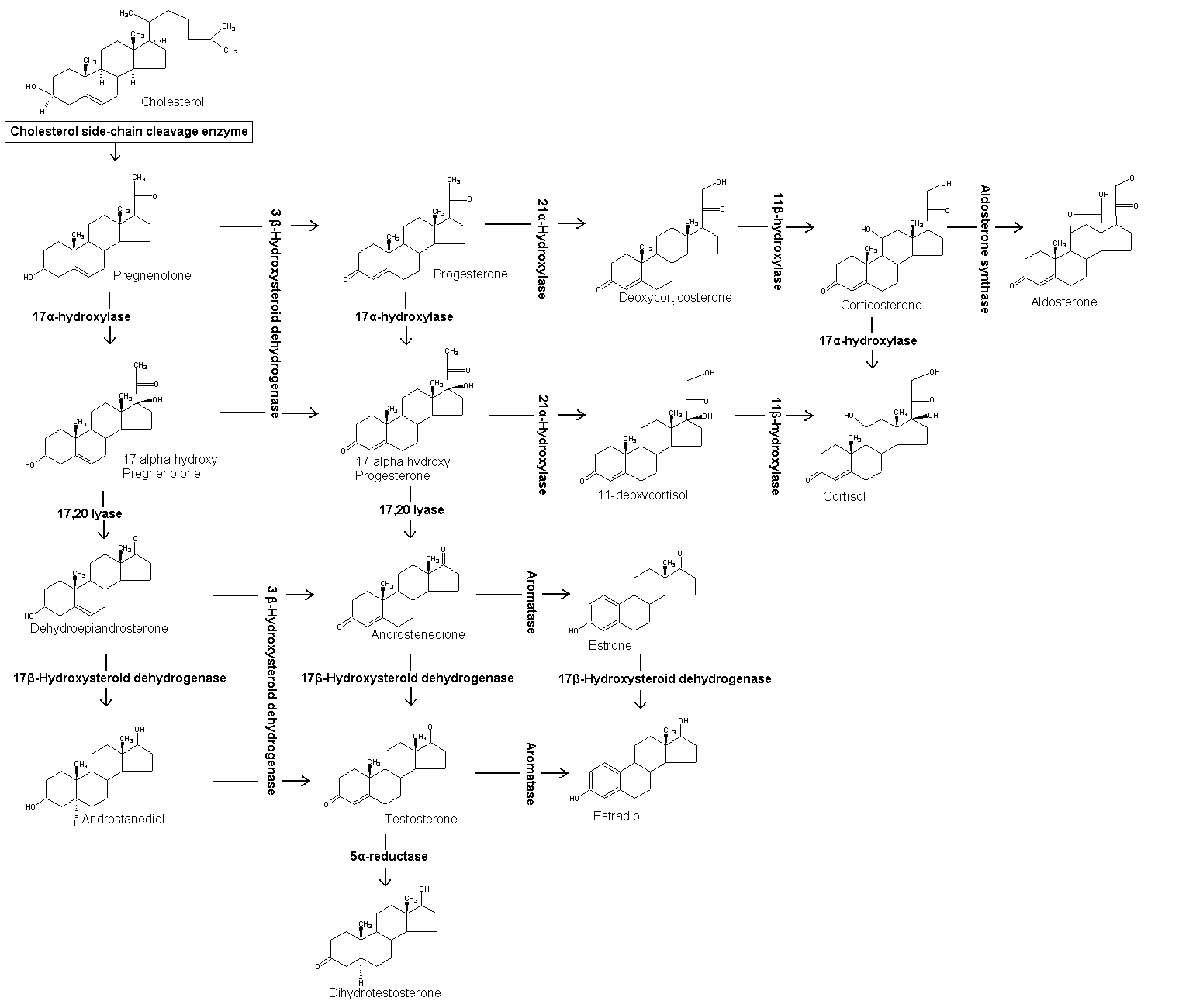
Synthesis[edit | edit source]
Estrone is synthesized via aromatase from androstenedione, a derivative of progesterone. The conversion consists of the de-methylation of C-19 and the aromaticity of the 'A' ring. This reaction is similar to the conversion of testosterone to estradiol.
Additional images[edit | edit source]
-
Androstenedione converting to estrone.
 KSF
KSF