Fascia of Colles
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
|
WikiDoc Resources for Fascia of Colles |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Fascia of Colles Most cited articles on Fascia of Colles |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Fascia of Colles |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Fascia of Colles at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Fascia of Colles Clinical Trials on Fascia of Colles at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Fascia of Colles NICE Guidance on Fascia of Colles
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Fascia of Colles Discussion groups on Fascia of Colles Patient Handouts on Fascia of Colles Directions to Hospitals Treating Fascia of Colles Risk calculators and risk factors for Fascia of Colles
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Fascia of Colles |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
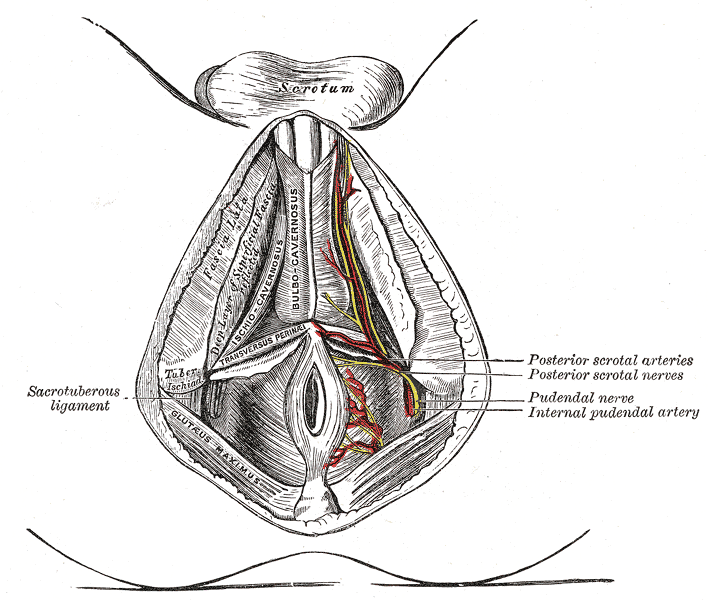
The deep layer of superficial fascia (fascia of Colles) is thin, aponeurotic in structure, and of considerable strength, serving to bind down the muscles of the root of the penis.
It separates the skin from the superficial perineal space.
Relations
[edit | edit source]In front, it is continuous, with the dartos tunic, the deep fascia of the penis, the fascia of the spermatic cord, and Scarpa's fascia upon the anterior wall of the abdomen;
On either side it is firmly attached to the margins of the rami of the pubis and ischium, lateral to the crus penis and as far back as the tuberosity of the ischium.
Posteriorly, it curves around the Transversi perinæi superficiales to join the lower margin of the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
In the middle line, it is connected with the superficial fascia and with the median septum of the Bulbocavernosus.
This fascia not only covers the muscles in this region, but at its back part sends upward a vertical septum from its deep surface, which separates the posterior portion of the subjacent space into two.
Additional images
[edit | edit source]-
The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
External links
[edit | edit source]- Template:WhoNamedIt
- Template:NormanAnatomy (Template:NormanAnatomyFig, Template:NormanAnatomyFig)
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "Anterior Abdominal Wall: Layers of the Superficial Fascia"
 KSF
KSF