Filariasis laboratory findings
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 5 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 5 min
|
Filariasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Filariasis laboratory findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Filariasis laboratory findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Filariasis laboratory findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Elsaiey, MBBCH [2]
Overview[edit | edit source]
Labarotary findings consistent with the diagnosis of filariasis include identifying microfilariae on thick blood film stained with Giemsa stain. The blood sample is drawn at night as the microfilaria circulate at night. There are also PCR assays available for making the diagnosis.
Laboratory Findings[edit | edit source]
Identification of microfilariae by microscopic examination is the most accuarte diagnostic procedure. Examination of blood samples allows the identification of microfilariae of Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Brugia timori, Loa loa, Mansonella perstans, and M. ozzardi. It is important to time the blood collection with the known periodicity of the microfilariae. The blood sample can be a thick smear, stained with Giemsa or hematoxylin and eosin. For increased sensitivity, concentration techniques can be used. Concentration techniques include centrifugation of the blood sample lyzed in 2% formalin (Knott's technique), or filtration through a nucleopore membrane.
Preparing blood smears[edit | edit source]
Capillary (fingerstick) blood: Since microfilariae concentrate in the peripheral capillaries, thick and thin smears prepared from fingerstick blood are recommended.
- Thick smears
- Thick smears consist of a thick layer of dehemoglobinized (lysed) red blood cells (RBCs).
- Thick smears allow a more efficient detection of parasites (increased sensitivity).
- Thin smears consist of blood spread in a layer such that the thickness decrease.
Microscopy[edit | edit source]
Wuchereria bancrofti[edit | edit source]
- The microfilaria of wuchereria bancrofti is sheathed and measure 240-300 µm in stained blood smears and 275-320 µm in 2% formalin.
- They have a gently curved body and a tail that is tapered to a point.
- The nuclear column (the cells that constitute the body of the microfilaria) is loosely packed; the cells can be visualized individually and do not extend to the tip of the tail. Microfilariae circulate in the blood.
Shown below is an image of microfilariae of W. bancrofti in thick blood smears stained with Giemsa.

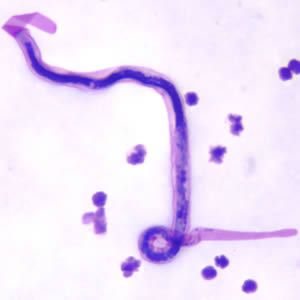
Brugia Malayi[edit | edit source]
- Microfilariae of Brugia malayi are sheathed and in stained blood smears measure 175-230 µm.
- In 2% formalin they are longer, measuring 240-300 µm.
- The tail is tapered, with a significant gap between the terminal and subterminal nuclei.
- Microfilaria circulate in the blood.
Shown below is an image of microfilaria of B. malayi in a thick blood smear, stained with Giemsa.
Brugia Timori[edit | edit source]
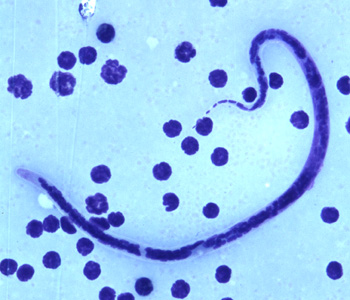
- Microfilaria of Brugia timori are sheathed and measure on average 310 µm in stained blood smears and 340 µm in 2% formalin.
- Microfilaria of B. timori differ from B. malayi by a having a longer cephalic space, a sheath that does not stain with Giemsa, and a larger number of single-file nuclei towards the tail. Microfilariae circulate in the blood.
Shown below is an image of microfilariae of B. timori in a thick blood smear from a patient from Indonesia, stained with Giemsa and captured at 500x oil magnification.
Onchocerca volvulus[edit | edit source]
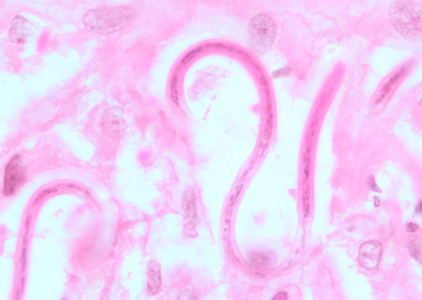
- Microfilariae of Onchocerca volvulus are unsheathed and measure 300-315 µm in length.
- The tail tapers to a point and is often sharply bent.
- The nuclei do not extend to the tip of the tail. Microfilariae typically reside in skin but may be found in blood or urine during heavy infections, or invade the eye and cause a condition known as river blindness.
Shown below is an image of microfilariae of O. volvulus from a skin nodule of a patient from Zambia, stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Antigen detection[edit | edit source]
- Detection of the filarial antigens has become one of the sensitive and specific diagnostic procedures to diagnose filariasis.[1]
- The antigen detecting tests include the following:
- ELISA
- Immunochromatographic technique (ICT) and it includes:
- Alere filariasis test strip
- Card-based assay for qualitative results
Special Procedures for Detecting Microfilariae[edit | edit source]
Blood microfilariae:
- Anticoagulated (EDTA) venous blood (1 ml) should be concentrated by one of the following methods:
- Centrifugation (Knott’s technique)
- Prepare 2% formaldehyde (2 ml of 37% formaldehyde + 98 ml H2O).
- Mix 9 ml of this 2% formaldehyde with 1 ml of patient’s venous blood. Centrifuge at 500 × g for 10 minutes; discard supernatant. Sediment is composed of WBCs and microfilariae (if present).
- Examine as temporary wet mounts.
- Prepare thick and thin smears; allow to dry; dip in absolute methanol before Giemsa staining to enhance staining of microfilariae.
- Filtration
- Place Millipore® or Nucleopore® membrane filter (5 µm pore) in filter holder with syringe attachment.
- Mix 1 ml of venous blood (in EDTA) with 10 ml of 10% Teepol® 610 (Shell Co.); allow to stand for several minutes to allow lysis; transfer to a 10 ml Luer-Loc® syringe; attach the filter apparatus.
- Force the solution through the 5 µm pore filter, followed by several syringes of water to wash out the remaining blood, then 1 or 2 syringes full of air to clear excess fluid.
- Prepare a temporary wet mount by removing the filter and placing it on a glass slide, adding a drop of stain or dye and a coverslip.
- For permanent preparations, pass 2 to 3 ml of methanol through the filter while it is still in the holder; remove filter and dry it on a glass slide; then stain it with Giemsa stain, horizontally (so that the filter does not wash off the slide); coverslip filter before examining.
- Centrifugation (Knott’s technique)
Gallery[edit | edit source]
-
Micrograph of the posterior end of a Brugia malayi microfilaria in a thick blood smear using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Micrograph of the posterior end of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria in blood smear using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Micrograph of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria in a thick blood smear using Giemsa stain technique. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Micrograph of the internal structure of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Photomicrograph reveals morphologic details at the anterior end of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilarial parasite in a blood smear using Giemsa stain (1000X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Weil GJ, Ramzy RM (2007). "Diagnostic tools for filariasis elimination programs". Trends Parasitol. 23 (2): 78–82. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2006.12.001. PMID 17174604.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Public Health Image Library (PHIL)".
 KSF
KSF![Micrograph of the posterior end of a Brugia malayi microfilaria in a thick blood smear using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](https://www.wikidoc.org/images/e/e7/Filariasis13.jpeg)
![Micrograph of the posterior end of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria in blood smear using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](https://www.wikidoc.org/images/9/9a/Filariasis12.jpeg)
![Micrograph of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria in a thick blood smear using Giemsa stain technique. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](https://www.wikidoc.org/images/6/65/Filariasis11.jpeg)
![Micrograph of the internal structure of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria using Giemsa stain. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](https://www.wikidoc.org/images/5/5c/Filariasis10.jpeg)
![Photomicrograph reveals morphologic details at the anterior end of a Wuchereria bancrofti microfilarial parasite in a blood smear using Giemsa stain (1000X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](https://www.wikidoc.org/images/0/0d/Filariasis08.jpeg)