Foot
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
Template:Infobox Anatomy Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
The foot is a biological structure found in many animals that is used for locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.
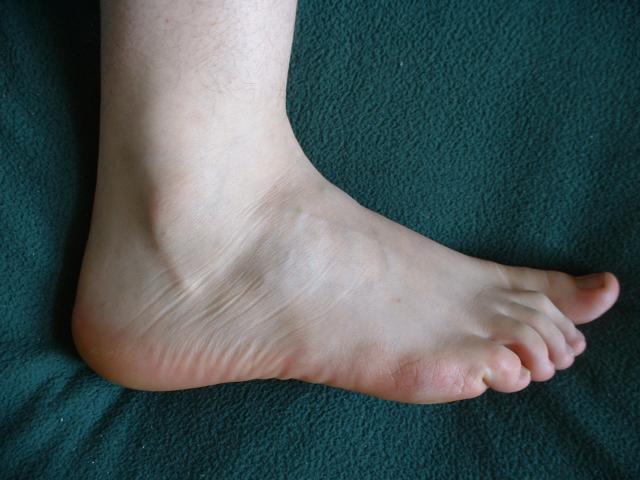
The human foot
[edit | edit source]Anatomy
[edit | edit source]The major bones in the foot are:
- Phalanges: The bones in the toes are called phalanges.
- Metatarsals: The bones in the middle of the foot are called metatarsal bones.
- Cuneiforms: There are three bones in the middle of the foot, towards the centre of the body called cuneiforms.
- Cuboid: The bone sitting adjacent to the cuneiforms on the outside of the foot is called the cuboid.
- Navicular: This bone sits behind the cuneiforms.
- Talus: Also called the ankle bone, the talus sits directly behind the navicular.
- Calcaneus: Also called the heel bone, the calcaneus sits under the talus and behind the cuboid.
The foot also contains sesamoid bones in distal portion of the first metatarsal bone.
Medical aspects
[edit | edit source]Due to their position and function, feet are exposed to a variety of potential infections and injuries, including athlete's foot, bunions, ingrown toenails, Morton's neuroma, plantar fasciitis, plantar warts and stress fractures. In addition, there are several genetic conditions that can affect the shape and function of the feet, including a club foot or flat feet.
A doctor who specializes in the treatment of the feet practices podiatry and is called a podiatrist. A pedorthist specializes in the use and modification of footwear to treat problems related to the lower limbs.
Reflexology is an alternative therapy which involves the stimulation of the nerves and skin of the feet to improve a person's health.
Additional images
[edit | edit source]-
A foot seen from the lateral view.
-
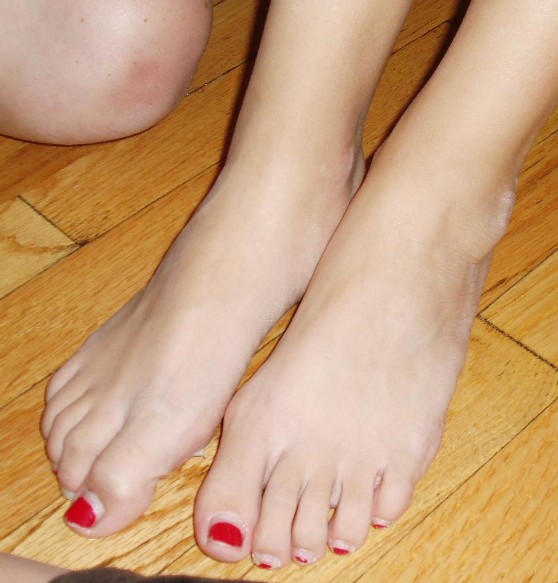
Feet seen from the top.
-
The soles of a male (left) and female (right) foot.
External links
[edit | edit source]| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Foot. |
| File:Wiktionary-logo-en-v2.svg | Look up foot in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Template:Dmoz
- American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons
- American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine
- Association of Reflexologists
- Foot Health
- Epodiatry
- Foot Health Care
- Anatomical illustrations
Template:Human anatomical features
Template:Lower limb general af:Voet an:Piet ast:Pie (anatomía) ca:Peu cy:Troed de:Fuß eo:Piedo ko:발 it:Piede (anatomia) he:כף רגל la:Pes lt:Pėda ms:Kaki nl:Voet (anatomie) no:Fot (kroppsdel) nn:Fot oc:Pè nds:Foot qu:Chaki simple:Foot fi:Jalkaterä sv:Fot uk:Стопа (анатомія) ur:فٹ yi:פוס
 KSF
KSF