Hirsutism physical examination
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
|
Hirsutism Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Medical Therapy |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hirsutism physical examination On the Web |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Hirsutism physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hirsutism physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]: Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: ; Rasam Hajiannasab M.D.[2], Ahmed Younes M.B.B.CH [3]
Overview[edit | edit source]
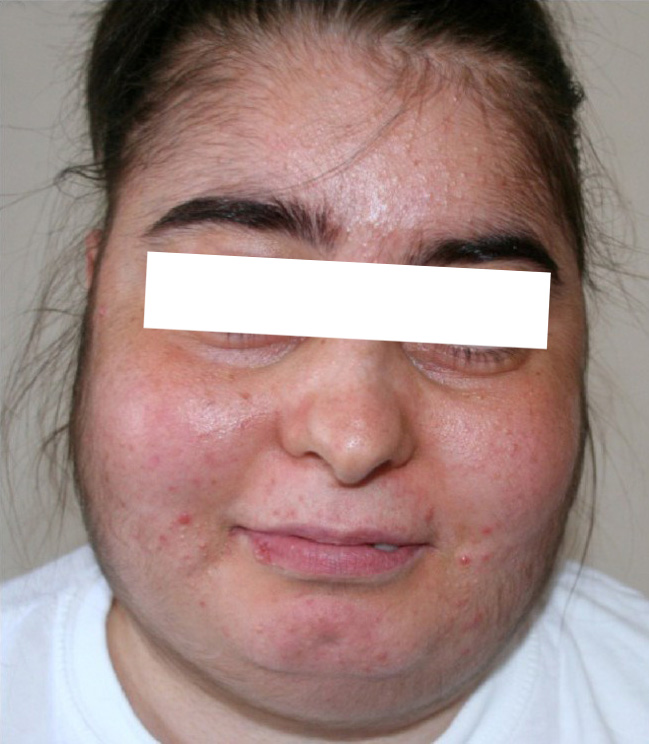
Patients with hirsutism usually appear normal and in no acute distress. The degree of hirsutism can be estimated using the Ferriman-Gallwey score.
Physical Examination[edit | edit source]
General[edit | edit source]
Patients with hirsutism usually appear normal and in no acute distress. The degree of hirsutism can be estimated using the Ferriman-Gallwey score.[1]
Appearance[edit | edit source]
- Patients with hirsutism usually appear normal and in no acute distress.
Skin[edit | edit source]
- generalized increase in growth of the hair on all of the body (hypertrichosis).[1]
- The skin of the abdomen may show striae in the cases of Cushing syndrome.
| Upper lip | 0-4 |
|---|---|
| Chin | 0-4 |
| Chest | 0-4 |
| Leg | 0-4 |
| Thigh | 0-4 |
| Upper arm | 0-4 |
| Forearm | 0-4 |
| Upper back | 0-4 |
| Lower back | 0-4 |
| Upper abdomen | 0-4 |
| Lower abdomen | 0-4 |
Neck[edit | edit source]
- The neck is usually supple without any masses.
Lungs[edit | edit source]
- The lungs are usually clear to auscultation.
Abdomen[edit | edit source]
- Inspection may show central obesity if Cushing syndrome is present.[2]
- Palpation of the abdomen may reveal masses in the iliac fossae if PCO is the cause of hirsutism.
Heart[edit | edit source]
- Auscultation of the heart reveals normal S1, S2, with no rubs, gallops, or murmurs.
Extremities[edit | edit source]
- The extremities may show wasting in the cases of Cushing syndrome.
Neurologic[edit | edit source]
- Patient is usually oriented to time, person, and place with average motor and sensory functions.
References[edit | edit source]
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Hirsutism_physical_examination8 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF