Human height
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 23 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 23 min
|
WikiDoc Resources for Human height |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Human height Most cited articles on Human height |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Human height |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Human height at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Human height at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Human height
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Human height Discussion groups on Human height Patient Handouts on Human height Directions to Hospitals Treating Human height Risk calculators and risk factors for Human height
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Human height |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Overview
[edit | edit source]Human height varies according to both "nature" and "nurture". The particular human genome that an individual inherits is a large part of the first variable (nature), and a combination of health and environmental factors present before adulthood (when growth stops) are a major part of the second determinant ("nurture"). Hereditary factors include both genes and chromosomes, and are inborn. Environmental factors are events that occur before adult height is reached, such as diet, exercise, and living conditions.
When populations share genetic background and environmental factors, average height is frequently characteristic within the group. Exceptional height variation (around 20% deviation from average) within such a population is usually due to gigantism or dwarfism; which are medical conditions due to specific genes or to endocrine abnormalities. In regions of extreme poverty or prolonged warfare, environmental factors like malnutrition during childhood and/or adolescence may account for marked reductions in adult stature even without the presence of any of these medical conditions. This is one reason that immigrant populations from regions of extreme poverty to regions of plenty may show an increase in stature, despite sharing the same gene pool.
The average height for each sex within a population is significantly different, with adult males being (on average) taller than adult females. This difference may be attributed to sex chromosomal differences, XY (male) as opposed to XX (female). Women ordinarily reach their greatest height at a younger age than men. Vertical growth stops when the long bones stop lengthening, which occurs with the closure of epiphyseal plates. These plates are bone growth centers that disappear ("close") under the hormonal surges brought about by the completion of puberty. Puberty generally occurs several years earlier in young women than in young men, and so final adult height is reached earlier in women. Adult height for one sex in a particular ethnic group follows more or less a normal distribution.
Adult height between ethnic groups often differs significantly, as presented in detail in the chart below. For example, the average height of women from the Czech Republic is currently greater than that of men from Malawi. This may be due to genetic differences, to childhood lifestyle differences (nutrition, sleep patterns, physical labor) or to both.
At 2.57 metres (8 ft 5.5 in), Leonid Stadnyk is the world's tallest living man and is from Ukraine. The tallest man in modern history was Robert Pershing Wadlow from Alton, Illinois, who was born in 1918 and stood 8 ft 11.1 inches (2.72 m) at the time of his death in 1940.
The maximal height that an individual attains in adulthood is not maintained throughout life if that life is a very long one. Again, depending on chromosomal (male v. female), genetic, and environmental factors, there is shrinkage of stature that may begin in middle age in some individuals but is universal in the extremely aged. This decrease in height is due to such factors as decreased height of inter-vertebral discs because of dessication, atrophy of soft tissues, and postural changes secondary to degenerative disease.
Average adult height around the world
[edit | edit source]Below are average adult heights by country. (The original studies and sources should be consulted for details on methodology and the exact populations measured, surveyed, or considered.)
| Country/Region | Average male height | Average female height | Sample population / age range |
Methodology | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 172.6 cm (5 ft 8 in) | 160.7 cm (5 ft 3.3 in) | 18-19 | Measured | 2001 | [1] |
| Australia | 177.4 cm (5' 10.2") | 163.9 cm (5' 4.5") | 18-24 | Measured | 1995 | [2] |
| Australia | 174.8 cm (5' 8.8") | 161.4 cm (5' 3.5") | 18+ | Measured | 1995 | [2] |
| Bahrain | 165.1 cm (5' 5") | 154.7 cm (5' 1") | 19+ | Measured | 2002 | [3] |
| Brazil | 169.0 cm (5' 6.5") | 158.0 cm (5' 2.2") | 21-65 | Measured | 2003 | [4][5] |
| Cameroon | 170.6 cm (5' 7.2") | 161.3 cm (5' 3.5") | Urban | Measured | 2003 | [6] |
| Canada | 174.0 cm (5' 8.5") | 161.0 cm (5' 3.4") | Measured | 2005 | [7] | |
| China (PRC) | 164.8 cm (5' 4.9") | 154.5 cm (5' 0.8") | 30-65 | Measured | 1997 | [8] |
| China (PRC) | 170.2 cm (5' 7") | 158.6 cm (5' 2.5") | Urban, 17 | Measured | 2002 | [9] |
| China (PRC) | 165.3 cm (5' 5.5") | 157.0 cm (5' 2") | Rural, 17 | Measured | 2002 | [10] |
| Côte d’Ivoire | 170.1 cm (5' 7") | 159.1 cm (5' 2.7") | 25-29 | Measured | 1985-1987 | [11] |
| Czech Republic | 180.3 cm (5' 11") | 167.3 cm (5' 6.0") | 18 | Measured | 2005 | [12] |
| Denmark | 180.6 cm (5' 11.1") | Conscripts, 19 | 2006 | [13] | ||
| Dinaric Alps | 185.6 cm (6' 1.0") | 171 cm | 17 | Measured | 2005 | [14] |
| Estonia | 179.1 cm (5' 10.5") | 17 | [15] | |||
| Finland | 174.7 cm (5' 9.5") | 163.5 cm (5' 4.3") | Self-reported | 2000 | [16] | |
| Finland | 178.2 cm (5' 10") | 164.7 cm (5' 4.7") | 15-64 | Self-reported | [17] | |
| France | 174.1 cm (5' 8.5") | 161.9 cm (5' 3.7") | 20+ | Measured | 2003 | [18] |
| France | 177.0 cm (5' 9.6") | 164.6 cm (5' 4.8") | 20-29 | Measured | 2003 | [19] |
| Ghana | 169.46 cm (5' 6.7") | 158.53 cm (5' 2.4") | 25-29 | Measured | 1987-1989 | [20] |
| Gambia | 168.0 cm (5' 6.1") | 157.8 cm (5' 2.2") | Rural, 21-49 | Measured | [21] | |
| Germany | 178.1 cm (5' 10") | 165 cm (5' 4.9") | Entire population | [22][23] | ||
| Germany | 180.3 cm (5' 11") | 167 cm (5' 6") | 18-19 | 2005 | [22][23] | |
| Guatemala (Maya people) | 157.5 cm (5' 2") | 142.2 cm (4' 6") | 20 | [24] | ||
| Iceland | 181.7 cm (5' 11.5") | 167.6 cm (5' 6") | 20 | [25] | ||
| India | 165.3 cm (5' 5") | 152.1 cm (5' 0") | 20 | Measured | 2005-2006 | [26] |
| India | 161.2 cm (5' 3.5") | 152.1 cm (5' 0") | Rural, 17 | 2002 | [27] | |
| Indonesia | 158.0 cm (5' 2.2") | 147.0 cm (4' 10.0") | 50+ | Self-reported | 1997 | [28] |
| Indonesia, East Bali | 162.4 cm (5' 3.9") | 151.3 cm (4' 11.5") | 19-23 | Measured | 1995 | [29] |
| Iran | 170.27 cm (5' 7.0") | 157.2cm (5' 1.9") | 20+ | Measured | 2005 | [30] |
| Iraq | 165.4 cm (5' 5.1") | 155.8 cm (5' 1.3") | 18-44 | Measured | 1999-2000 | [31] |
| Israel | 175.6 cm (5' 9.2") | 162.7 cm (5' 4.1") | 20-30 | 1980-2000 | [32] | |
| Italy - Middle & North | 176.9 cm (5' 9.7") | 163.2 cm (5' 4.2") | 20 | 1994-2000 | [33] | |
| Italy - South | 174.2 cm (5' 8.0") | 160.8 cm (5' 3.3") | 20 | 1994-2000 | [33] | |
| Japan | 170.8 cm (5' 7.2") | 158.0 cm (5' 2.1") | 17 | 2005 | [34] | |
| Japan | 172.2 cm (5' 7.8") | 158.8 cm (5' 2.6") | 25-29 | 2006 | [35] | |
| Korea, South | 173.9 cm (5' 8.5") | 161.1 cm (5' 3.4") | 17 | 2006 | [36] | |
| Korea, South | 175.0 cm (5' 8.8") | 161.9 cm (5' 3.7") | 19-24 | 2007 | [37] | |
| Ulsan, South Korea | 175.0 cm (5' 8.8") | 161.0 cm (5' 3.4") | 17 | 2006 | [38] | |
| Gyeongbuk, South Korea | 173.3 cm (5' 8.2") | 161.0 cm (5' 3.4") | 17 | 2006 | [38] | |
| Lithuania | 176.3 cm (5' 9.4") | 20 | [39] | |||
| Malaysia | 164.7 cm (5' 4.8") | 153.3 cm (5' 0.2") | 20+ | Measured | 1996 | [40] |
| Malta | 169 cm (5' 6.5") | 159 cm (5' 2.6") | 2003 | [41] | ||
| Malta | 175.2 cm (5' 9") | 163.8 cm (5' 4.5") | 25-34 | [41] | ||
| Malawi | 166 cm (5' 5.3") | 155 cm (5' 1.1") | Urban, 16-60 | Measured | 2000 | [42] |
| Mali | 171.3 cm (5' 7.4") | 160.4 cm (5' 3.2") | Rural | Measured | 1992 | [43] |
| Mexico, State of Morelos | 167 cm (5' 5.7") | 155 cm (5' 1.1") | Self-reported | 1998 | [44] | |
| Netherlands | 184.8 cm (6' 0.8") | 168.7 cm (5' 6.4") | 20-30 | 2004 | [45] | |
| New Zealand | 177.0 cm (5' 9.7") | 165.0 cm (5' 5") | 19-45 | 1993 | [46] | |
| Nigeria | 163.8 cm (5' 4.5") | 157.8 cm (5' 2.1") | 25-74 | Measured | 1994-1996 | |
| Norway | 179.9 cm (5' 10.8") | 167.2 cm (5' 5.9") | Male 18-19; female unknown | [48] | ||
| Philippines | 163.5 cm (5' 4.4") | 151.8 cm (4' 11.8") | 20-39 | Measured | 2003 | [49] |
| Portugal | 172.8 cm (5' 8") | Conscipts, 21 | 1998-99 | [50] | ||
| Poland | 177.8 cm (5' 10") | Conscripts, 18 | 2005 | [51] | ||
| Singapore | 172.0 cm (5' 7.8") | 160 cm (5' 3") | 17-25 | 2003 | [52] | |
| South Africa | 169.0 cm (5' 6.5") | 159.0 cm (5' 2.5") | 25-64 | Measured | 1998 | [53] |
| Spain | 170 cm (5' 7") | 161 cm (5' 3.3") | Entire population | Self-reported | 2003 | [54] |
| Spain | 173 cm (5' 8") | 164.3 cm (5' 4.6") | 18-29 | Self reported | 2003 | [54] |
| Catalonia, Spain | 173.0 cm (5' 8") | 164 cm (5' 4.6") | 18 | Measured | 2004 | [55] |
| Madrid, Spain | 177.0 cm (5' 9.7") | 164 cm (5' 4.6") | 18 | Measured | 2004 | [55] |
| Galicia, Spain | 177.0 cm (5' 9.7") | 164 cm (5' 4.6") | 18 | Measured | 2004 | [55] |
| Zaragoza, Spain | 177.0 cm (5' 9.7") | 162 cm (5' 4.6") | 18 | Measured | 2004 | [55] |
| Sweden | 181.3 cm (5' 11.3") | 166.8 cm (5' 5.7") | 25-34 | Measured.[56] | 2005 | [57] |
| Switzerland | 175.5 cm (5' 9") | 164.0 cm (5' 3.8") | [16] | |||
| Taiwan | 172.04 cm (5' 7.73") | 159.68 cm (5' 3") | 18.5 | [58] | ||
| Thailand | 167.5 cm (5' 5.9") | 157.3 cm (5' 1.9") | STOU university student | Self-reported | 1991-1995 | [59] |
| Turkey, Province of Edirne | 173.8 cm (5' 8.5") | 161.4 cm (5' 3.5") | 17 | 2001 | [60] | |
| United Kingdom | 175.2 cm (5' 8.9") | 161.6 cm (5' 3.6") | 16+ | 2006 | [61] | |
| United Kingdom | 176.7 cm (5' 9.6") | 163.7 cm (5' 4.4") | 16-24 | 2006 | [61] | |
| USA | 175.8 cm (5' 9.3") | 162.0 cm (5' 3.8") | 20+ | Measured | 1999-2002 | [62] |
| USA | 178.2 cm (5' 10.2") | 164.1 cm (5' 4.6") | White Americans, 20-39 | Measured | 1999-2002 | [62] |
| USA | 177.8 cm (5' 10") | 164.0 cm (5' 4.6") | African-Americans, 20-39 | Measured | 1999-2002 | [62] |
| USA | 169.7 cm (5' 6.8") | 158.1 cm (5' 2.2") | Mexican-Americans, 20-39 | Measured | 1999-2002 | [62] |
| USA (South Texas) | 172.5 cm (5' 7.9") | 159.6 cm (5' 2.8") | Mexican-Americans, 17 | Measured | 1998-1999 | [63] |
| Vietnam | 162.1 cm (5' 4") | 152.2 cm (5' 00") | 25-29 | Measured | 1992-1993 | [64] |
Determinants of growth and height
[edit | edit source]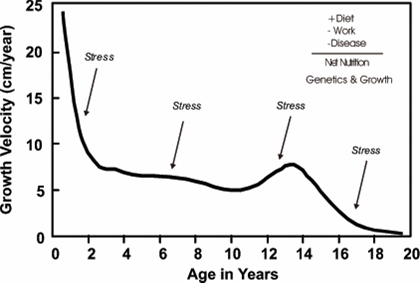
The study of human growth is known as auxology. Growth and height have long been recognized as a measure of the health and wellness of individuals, hence part of the reasoning for the use of growth charts. For individuals, as indicators of health problems, growth trends are tracked for significant deviations and growth is also monitored for significant deficiency from genetic expectations. Genetics is a major factor in determining the height of individuals, though it is far less influential in regard to populations. Average height is increasingly used as a measure of the health and wellness (standard of living and quality of life) of populations. Attributed as a significant reason for the trend of increasing height in parts of Europe is the egalitarian populations where proper medical care and adequate nutrition are relatively equally distributed. Changes in diet (nutrition) and a general rise in quality of health care and standard of living are the cited factors in the Asian populations. Average height in the United States has remained essentially stagnant since the 1950s even as the racial and ethnic background of residents has shifted. Severe malnutrition is known to cause stunted growth in North Korean, portions of African, certain historical European, and other populations. Diet (in addition to needed nutrients; such things as junk food and attendant health problems such as obesity), exercise, fitness, pollution exposure, sleep patterns, climate (see Allen's rule and Bergmann's Rule for example), and even happiness (psychological well-being) are other factors that can affect growth and final height.
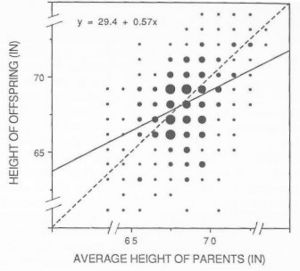
Height is, like other phenotypic traits, determined by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Genetic potential plus nutrition minus stressors is a basic formula. Genetically speaking, the heights of mother and son and of father and daughter correlate, suggesting that a short mother will more likely bear a shorter son, and tall fathers will have tall daughters.[65] Humans grow fastest (other than in the womb) as infants and toddlers (birth to roughly age 2) and then during the pubertal growth spurt. A slower steady growth velocity occurs throughout childhood between these periods; and some slow, steady, declining growth after the pubertal growth spurt levels off is common. These are also critical periods where stressors such as malnutrition (or even severe child neglect) have the greatest effect. Conversely, if conditions are optimal then growth potential is maximized; and also there is catch-up growth — which can be significant — for those experiencing poor conditions when those conditions improve.
Moreover, the health of a mother throughout her life, especially during her critical periods, and of course during pregnancy, has a role. A healthier child and adult develops a body that is better able to provide optimal prenatal conditions. The pregnant mother's health is important as gestation is itself a critical period for an embryo/fetus, though some problems affecting height during this period are resolved by catch-up growth assuming childhood conditions are good. Thus, there is an accumulative generation effect such that nutrition and health over generations influences the height of descendants to varying degrees.
The age of the mother also has some influence on the her child's height. Although 2 Esdras recorded that "Those born in the strength of youth" were taller than "those born during the time of old age, when the womb is failing"[66], studies in modern times have observed a gradual increase in height with maternal age.[67][68][69]
The precise relationship between genetics and environment is complex and uncertain. Human height is 90% heritable[70] and has been considered polygenic since the Mendelian-biometrician debate a hundred years ago.[71] The only gene so far attributed with normal height variation is HMGA2. This is only one of many, as each copy of the allele concerned confers an additional 0.4 cm, accounting for just 0.3% of population variance.[70]
Race and height
[edit | edit source]The Nilotic peoples of Sudan such as the Dinka have been described as the tallest in the world, with the males in some communities having average heights of 1.9 m (6 ft 3 in) and females at 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in)[72]. A notable example is Manute Bol, who, at 2.31m(7ft 7in), was the tallest basketball player in the NBA. The Dinka are characterized as having long legs, narrow bodies and short trunks, an adaptation to hot weather[73]. However, a 1995 study casts doubt on the claim of extraordinary height in Dinka, which after studying the average height of Dinka males in one location, listed the actual number as 1.76 m (5 ft 9.45 in.) [74] Adults of the Pygmy peoples have an approximate average height of 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in).
Process of growth
[edit | edit source]Growth in stature, determined by its various factors, results from the lengthening of bones via cellular divisions chiefly regulated by somatotropin (human growth hormone (hGH)) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. Somatotropin also stimulates the release of another growth inducing hormone insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) mainly by the liver. Both hormones operate on most tissues of the body, have many other functions, and continue to be secreted throughout life; with peak levels coinciding with peak growth velocity, and gradually subsiding with age after adolescence. The bulk of secretion occurs in bursts (especially for adolescents) with the largest during sleep. Exercise promotes secretion. Adolescents who take steroids can experience stunted growth. A positive net nutrition is also important, with proteins and various other nutrients especially important.
The majority of linear growth occurs as growth of cartilage at the epiphysis (ends) of the long bones which gradually ossify to form hard bone. The legs compose approximately half of adult human height, and leg length is a somewhat sexually dimorphic trait. Height is also attained from growth of the spine, and contrary to popular belief, men are the "leggier" sex with a longer leg to torso ratio, conversely to women's longer torso to leg ratio. (The illusion of the proportion being the other way around is caused by fatty deposits placed high on women's hips.) Some of this growth occurs after the growth spurt of the long bones has ceased or slowed. The majority of growth during growth spurts is of the long bones. Additionally, the variation in height between populations and across time is largely due to changes in leg length. The remainder of height consists of the cranium. Height is sexually dimorphic and statistically it is more or less normally distributed, but with heavy tails.
Height abnormalities
[edit | edit source]Most intra-population variance of height is genetic. Short stature and tall stature are usually not a health concern. If the degree of deviation from normal is significant, hereditary short stature is known as familial short stature and tall stature is known as familial tall stature. Confirmation that exceptional height is normal for a respective person can be ascertained from comparing stature of family members and analyzing growth trends for abrupt changes, among others. There are, however, various diseases and disorders that cause growth abnormalities. Most notably, extreme height may be pathological, such as gigantism (very rare) resulting from childhood hyperpituitarism, and dwarfism which has various causes. Rarely, no cause can be found for extreme height; very short persons may be termed as having idiopathic short stature. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2003 approved hGH treatment for those 2.25 standard deviations below the population mean (approximately the lowest 1.2% of the population). An even rarer occurrence, or at least less used term and recognized "problem", is idiopathic tall stature.
If not enough growth hormone is produced and/or secreted by the pituitary gland, then a patient with growth hormone deficiency can undergo treatment. This treatment involves the injection of pure growth hormone into thick tissue to jump-start the growth process.
Role of an individual's height
[edit | edit source]Tallness has been suggested to be associated with better cardio-vascular health and overall better-than-average health and longevity (Njolstad et al. 1996,[75] McCarron et al 2002[76]). However, height may not be causative of better health and longevity (Miura et al. 2002). Other studies have found no association, or suggest that shorter stature is associated with better health (Samaras & Elrick, 1999[77]). On the other hand, being excessively tall can cause various medical problems, including cardiovascular issues, due to the increased load on the heart to supply the body with blood, and issues resulting from the increased time it takes the brain to communicate with the extremities. For example, Robert Wadlow, the tallest man known to verifiable history, developed walking difficulties as his height continued to increase throughout his life. In many of the pictures of the later portion of his life, Wadlow can be seen gripping something for support. Late in his life he was forced to wear braces on his legs and to walk with a cane, and he died after developing an infection in his legs because he was unable to feel the irritation and cutting caused by his leg braces (it is important to note that he died in 1940, before the widespread use of modern antibiotics). Height extremes of either excessive tallness or shortness can cause social exclusion and discrimination for both men and women (heightism).
Epidemiological studies have also demonstrated a positive correlation between height and intelligence. The reasons for this association appear to include that height serves as a biomarker of nutritional status or general mental and physical health during development, that common genetic factors may influence both height and intelligence, and that both height and intelligence are affected by adverse early environmental exposures.
In addition, an individual's height can be largely a part of what social clique, or group that they fall in to, though this is usually associated with pre-teens and teenagers. For example, in some schools, students on the basketball team might be "cool," and those with short stature wouldn't likely make the team. Therefore, in some cases, this could contribute to them being classified as "uncool," which can be detrimental to that particular individual's self-esteem. A study done on men in Sweden has shown that there is a strong correlation between subnormal stature and suicide. [78]
This can also sometimes be translated over into the corporate world. Individuals with short stature can sometimes appear to not have any leadership ability or power, since some people might not take them seriously due to their short stature. However, this is not always the case with most employers. Historically this assumption has not always reflected reality; for instance Napoleon was not much taller than 5ft according to sources (though Napoleon's height is subject to great debate, and he may have been as tall as 5' 7", see Napoleon's height for further information). Ignatius Loyola, founder of the Jesuit order was 5'. Both Lenin and Stalin were of below average height. A modern example would be Deng Xiaoping of China who undertook massive reforms to the Chinese economy in the 1980s and was reported to have only been 5' 2".
The role of height in sports
[edit | edit source]Height often plays a crucial role in sports. For most sports, height is useful as it affects the leverage between muscle volume and bones towards greater speed of movement. It is most valuable in sports like basketball and volleyball, where the "short" players are almost always well above average in height compared to the general population. In men's professional basketball, the guards, the smallest players, are usually around 6'2" to 6'6" (1.88 to 1.98 m), and the centers, the tallest players, are generally from 6'10" to 7'2" (2.08 to 2.18 m). Famous basketball player Shaquille O'Neal is listed at 7'1"[79] (2.16 m). In some sports, such as horse racing, auto racing, figure skating, diving, and gymnastics, a smaller frame is more valuable. In other sports, the role of height is specific to particular positions (i.e . In American Football, running backs have an advantage if they are shorter than the defenders due to lower centers of gravity and decreased visibility.) In Rugby Union Height is Vital for key positions such as Second Row who catch the ball while being hoisted up in lineouts. In weightlifting shorter levers are advantageous and taller than average competitors usually compete in the 105 kg + group.
Association football (Soccer)
[edit | edit source]For example, in Association football, tall goalkeepers have an advantage because they have greater armspans and can jump higher easily, so one will rarely, if ever, see a short goalkeeper at the professional level. However, shorter goalkeepers will have an easier time reaching low shots as they can reach the ground fractionally sooner than taller keepers. In wide positions and certain attacking ones, height is not always important with some of the best players in the world (e.g. Garrincha, Edgar Davids, Romário and Maradona) being shorter than average and in many cases gaining an advantage with their low center of gravity. However, height is generally considered advantageous for central defenders and for target men forwards who usually aim to score with their head for instance Jan Koller, Ruud van Nistelrooy, Niall Quinn and Peter Crouch.
Cricket
[edit | edit source]Similarly, in cricket, some great batsmen like Donald Bradman 5'7", Sachin Tendulkar 5'5", Brian Lara 5'6", Sunil Gavaskar 5'4" and Aravinda De Silva 5'2" are/were short. On the other hand, many successful fast bowlers are/were well over 6'; for example past greats Joel Garner, Courtney Walsh, and Curtly Ambrose were all 6'6"(198 cm) or taller. Glenn McGrath is also 6'5½" (197 cm). In general, taller bowlers have a higher point of release in their bowling action, making it easier for them to make the ball rear-up from a length. Also, they can generate more pace with longer arms and the sling action associated with bowling. But, taller batsmen also have greater ease of hitting the ball compared to short-heighted. Some greats like Clive Lloyd are above 6'. England's star batsman Kevin Pietersen is 6'4" tall, while New Zealand all-rounder Jacob Oram measures 6'7".
Rowing
[edit | edit source]In rowing, being tall is a big advantage, because the taller you are the longer your stroke can potentially be, thus moving the boat more effectively. The average male Olympic rower is 6'3.5", and the average female Olympic rower is 5'8",[80] well over the average height.
Rugby Union
[edit | edit source]In rugby union, lineout jumpers, generally Template:Locks, are usually the tallest players on the pitch, as this increases their chance of winning clean ball, whereas Template:Scrum-half are usually relatively short. As examples, current world-class locks Victor Matfield, Chris Jack, and Paul O'Connell are all at least 6'6"/1.98 m, and Simon Shaw even gets up to roughly 6'9", while the sport's all-time leader in international appearances, scrum-half George Gregan, is 5'8"/1.73m. Currently the tallest professional players are Devin Toner and Andries Bekker, who are both 6'10". The tallest man ever to have played was 7'0" tall Richard Metcalfe.
Rugby League
[edit | edit source]Unlike rugby union, height was not seen as important in Rugby League, due to the absence of line-outs. However, recent tactics of cross-field kicking has resulted in the success of taller outside backs. Israel Folau (194cm) and Krisnan Inu (185cm) are examples of the trend in taller wingers and centres, and are both known for their remarkable jumping skills in defense or attack.[81][82]
American Football (Gridiron)
[edit | edit source]In American Football, a tall quarterback is at an advantage because it is easier for him to see over the heads of large offensive and defensive linemen while he is in the pocket in a passing situation. At 5'9", Doug Flutie was initially considered to be too short to become a NFL quarterback despite his Heisman Trophy-winning success at the college level.
Tall wide receivers have an advantage of being able to outjump shorter defensive backs to catch highly thrown passes. By contrast, shorter defensive backs are utilized because of their typically greater agility, as the ability to change directions instantly is a prerequisite for the position. Short running backs are at an advantage because their shorter stature and lower center of gravity generally makes them harder to tackle effectively. In addition, they can easily "hide" behind large offensive linemen, making it harder for defenders to react at the beginning of a play. Thus, in the NFL and in NCAA Division I football, running backs under 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m) are more common than running backs over 6 ft 3 in (1.91 m). Former Heisman Trophy winner and Pro Football Hall of Famer Barry Sanders, thought by some to be the greatest running back in history, is a classic example of a running back with an extraordinarily low center of gravity, as he stood only 5 ft 7 1/2 in (1.71 m). However, Jim Brown, another player often considered the greatest running back of all time, was more than 6 ft 2 in (1.88 m) tall, demonstrating benefits conferred by the greater power and leverage which height provides.
Kickers are generally short, they are shorter because this allows them to get under the ball easier. Punters are generally very tall because of longer legs achieving greater leg swing and this translates into more power on the ball.
Baseball
[edit | edit source]In baseball, pitchers tend to be taller than position players. Being taller means longer legs, which power pitches use to generate velocity and a release point closer to the plate, which means the ball reaches the batter more quickly. While taller position players have a larger strike zone, most position players are at least of average height because the larger frame allows them to generate more power. Most successful modern pitchers are safely over 6 feet/1.83 m, some to extremes (e.g., the 6'10"/2.08 m Randy Johnson), with the 5'11"/1.80 m Pedro Martínez a notable exception.
Ice Hockey
[edit | edit source]While the history of the NHL is filled with diminutive players who achieved greatness (Theo Fleury, Martin St. Louis,) the game's physical style has put a premium on imposing players, particular over 6 feet tall and over 200 pounds (Mario Lemieux, Chris Pronger). Taller, bigger players have a longer reach, are able to give out and sustain punishing body checks, and are generally seen as indispensable for a team looking to go deep into the playoffs. Zdeno Chára, at 6 ft 9 in (2.06 m), is the tallest player ever to play in the NHL.
Wrestling
[edit | edit source]Height can be both helpful and detrimental in wrestling. Since taller people have more bone mass, they will generally be slightly weaker than shorter people in the same weight class. This difference is made up in part by their longer arms, which allow them a longer reach and make cradles easier. Also, taller peoples' legs are longer and harder to defend from shorter wrestlers.
Sumo
[edit | edit source]Professional sumo wrestlers are required to be at least 173 cm tall. Some aspiring sumo athletes have silicon implants added to the tops of their heads to reach the necessary height.[83] The average height for a sumo wrestler is 180 cm, far above the national average in Japan.
History of human height
[edit | edit source]Average Height of Troops Born in the Mid-Nineteenth Century, by Country or Place
| Country | Height |
|---|---|
| Australia | 172 cm |
| U.S. | 171 cm |
| Norway | 169 cm |
| Ireland | 168 cm |
| Scotland | 168 cm |
| Sweden | 168 cm |
| Bohemia | 167 cm |
| Lower Austria | 167 cm |
| Moravia | 166 cm |
| U.K. | 166 cm |
| France | 165 cm |
| Russia | 165 cm |
| Germany | 164 cm |
| Netherlands | 164 cm |
| Spain | 162 cm |
| Italy | 161 cm |
Source
- Tallest in the World: Native Americans of the Great Plains in the Nineteenth Century
- European Heights in the Early 18th Century
In the 18th and 19th centuries, Europeans in North America were far taller than those in Europe and were the tallest in the world.[84] The original indigenous population of Plains Native Americans was also among the tallest populations of the world at the time.[85] Several nations, including many nations in Europe, have now surpassed the US, particularly the Netherlands, and the Scandinavian nations.
In the late nineteenth century, the Netherlands was a land renowned for its short population, but today it has the 2nd tallest average in the world, with young men averaging 185 cm (6'1 ft) tall and only shorter than the peoples of the Dinaric Alps (a section largely within the former Yugoslavia which encompasses: all of present-day Montenegro, a sovereign republic; Herzegovina, its entire region within another republic; hinterland and coastal Croatia, Serbia), where males average 185.6 cm (6 ft 1.1 in) tall. The Dinarians and Dutch are now well known in Europe for extreme tallness. In Africa, the Maasai, Dinka and Tutsi populations are known for their tallness.
Average male height in impoverished Vietnam and North Korea[86] remains comparatively small at 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) and 165 cm (5 ft 5 in), respectively. Currently, young adult North Korean males are actually significantly shorter. This contrasts greatly with the extreme growth occurring in surrounding Asian populations with correlated increasing standards of living. Young South Koreans are about 12 cm (5.5 inches) taller than their North Korean counterparts, on average. There is also an extreme difference between older North Koreans and young North Koreans who grew up during the famines of the 1990s-2000s. North Korean and South Korean adults older than 40, who were raised when the North and South's economies were about equal, are generally of the same average height.
In the early 1970s, when anthropologist Barry Bogin first visited Guatemala, he observed that Mayan Indian men averaged only 157.5 cm (5 ft 2 in) in height and the women averaged 142.2 cm (4 ft 8 in). Bogin took another series of measurements after the Guatemalan Civil War had erupted, during which up to a million Guatemalans had fled to the United States. He discovered that Mayan refugees, who ranged from six to twelve years old, were significantly taller than their Guatemalan counterparts. By 2000, the American Maya were 10.24 cm (4 in) taller than the Guatemalan Maya of the same age, largely due to better nutrition and access to health care. Bogin also noted that American Maya children had a significantly lower sitting height ratio, (i.e. relatively longer legs, averaging 7.02 cm longer) than the Guatemalan Maya.[87][88]
Bibliography
[edit | edit source]- Fitting the Task to the Man, 1987 (for heights in USA and Japan)
- Eurostats Statistical Yearbook 2004 (for heights in Germany)
- Netherlands Central Bureau for Statistics, 1996 (for average heights)
- Mean Body Weight, Height, and body mass index, United States 1960 - 2002
- UK Department of Health - Health Survey for England
- Statistics Norway, Conscripts, by height, Per cent
- Statistics Sweden (in Swedish)
- Burkhard Bilger. "The Height Gap." The New Yorker
- A collection of data on human height, referred to here as "karube" but originally collected from other sources, was originally available here but is no longer. A copy is available here. (an English translation of this Japanese page would make it easier to evaluate the quality of the data...).
- http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/04news/americans.htm
- Aminorraya, A. et al.: Growth Charts of Heights and Weights of Male Children and Adolescents of Isfahan, Iran. Journal of Health and Population Nutrition, 21(4):2003, p. 341-346
- Blaha, P. et al.: 6. Celostatni antropologicky vyzkum deti a mladeze 2001, Ceska republika [6th Nationwide anthropological research of children and youth 2001, Czech republic], Charles University in Prague 2005
- Bogin, B.A. (1999) Patterns of human growth. 2nd ed Cambridge U Press
- Bogin, B.A. (2001) The growth of humanity Wiley-Liss
- Cavelaars, A.E.J.M.,Kunst, A.E.,Geurts, J.J.M.,Crialesi, R.,Grotvedt, L.,Helmert U. Persistent variations in average height between countries and between socio-economic groups: an overview of 10 European countries. Annals of Human Biology. 27(4),407 - 421.
- Deurenberg P., Kalpana Bhaskaran, Petrina Lim Kim Lian: Singaporean Chinese adolescents have more subcutaneous adipose tissue than Dutch Caucasians of the same age and body mass index. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 12(3):2003, p. 261-265
- Eveleth, P.B. & Tanner, J.M. (1990) Worldwide variation in human growth, 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press.
- Lintsi, M., Kaarma, H.: Growth of Estonian seventeen-year-old boys during the last two centuries. Economics and Human Biology 4 (2006) 89–103.
- Miura, K. Nakagawa, H. & Greenland, P. (2002) Invited commentary: height-cardiovascular disease relation: where to go from here? Am. J. Epidemiol. 155:688–689.
- Ruff, C. (2002) Variation in human body size and shape. Ann. Rev. Anthropol. 31:211-232.
- Average height of adolescents in the Dinaric Alps
- Average height of young Spaniards (in Spanish)
- Differences between height (stature) and recumbent length
- Mandel, MD, E. Zimlichman, MD, F. B. Mimouni, MD, FACN, FAAP, I. Grotto, MD, MPH, and Y. Kreiss, MD Height-Related Changes in Body Mass Index: A Reappraisal
- A. Case, PhD, C. Paxson, PhD, Stature and Status: Height, Ability, and Labor Market Outcomes
- Global Height Trends in Industrial and Developing Countries, 1810-1984: An Overview 2006 10 20
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Mariana del Pino, Luisa Bay, Horacio Lejarraga, Irina Kovalskys, Enrique Berner and Cecile Rausch Herscovic. "Archik;hK:Mvos Argentinos de Pediatría". SciELO Argentina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 ABS How Australians Measure Up 1995 data
- ↑ NATIONAL NUTRITION SURVEY
- ↑ IBGE(2005)
- ↑ Folha de SP
- ↑ http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1579217 Anthropometry measures and prevalence of obesity in the urban adult population of Cameroon: an update from the Cameroon Burden of Diabetes Baseline Survey
- ↑ 2005 Canadian Community Health Survey 3.1
- ↑ Ethnic Differences in the Association between Body Mass Index and Hypertension, American Journal of Epidemiology
- ↑ National Institute for Nutrition and Food Safety
- ↑ National Institute for Nutrition and Food Safety
- ↑ Productive Benefits of Improving Health: Evidence from Low-Income Countries,T. Paul Schultz*
- ↑ Blaha et al. 2005
- ↑ DST Statistical Yearbook 2007
- ↑ [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16168365?dopt=Abstract Average height of adolescents in the Dinaric Alps, Pineau JC, Delamarche P, Bozinovic S.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Cavelaars et al 2000.
- ↑ National Public Health Institute (Finland)
- ↑ INSEE 2003
- ↑ INSEE 2003
- ↑ Productive Benefits of Improving Health: Evidence from Low-Income Countries,T. Paul Schultz*
- ↑ Rebecca Sear
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 [2] according to the sociodemographic characteristics
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Committee for determining the eligibility of young men for military service.
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ Icelandic boys, girls
- ↑ Angus Deaton, 2008
- ↑ Venkaiah, 2002
- ↑ Indonesia Family Life Survey,1997
- ↑ Youth Profile in Some Suburban Areas In East Java (Preliminary Survey of The Indonesian Youth Stature at The Fiftieth Anniversary of Indonesia)
- ↑ http://diglib.tums.ac.ir/pub/magmng/pdf/6079.pdf Secular Trend of Height Variations in Iranian Population Born between 1940 and 1984
- ↑ http://www.unu.edu/unupress/food/fnb23-4.pdf Relationship between waist circumference and blood pressure among the population in Baghdad,Iraq,Haifa Tawfeek
- ↑ (a study made between the years 1980-2000)
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Cacciari et al. 2001
- ↑ Excel(Male)(Female)Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology -Japan 2005]
- ↑ ExcelOfficial Statistics by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- ↑ Ministry of Education, Science and Technology -Physical Examination Statistics Annual Report on Student(Korea 1970~2006)
- ↑ (Male)(Female)Korea Institute of Sport Science- Physical Fitness Survey
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Students' Physical Development(Height) by Province Offerer : Ministry of Education and Human Resources Development
- ↑ VISUOMENĖS SVEIKATA Anthropometrical data and physical fitness of Lithuanian soldiers
- ↑ Distribution of Body Weight, Height and Body Mass Index in a National Sample of Malaysian Adults
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 2003 study. A 2007 Eurostat study revealed the same results - the average Maltese person is 164.9cm (5'4.9") compared to the EU average of 169.6 cm (5'6.7").
- ↑ B C Msamati,P S Igbigbi; East Afr Med J. 2000
- ↑ Nutritional status of adults in rural Mali,Katherine A. Dettwyler
- ↑ Salud Publica Mexico
- ↑ DINED 2004 TU Delft
- ↑ (page 60) Size and Shape of New Zealanders: NZ Norms for Anthropometric Data 1993****. Based on British norms and their relations to New Zealand values
- ↑ http://care.diabetesjournals.org/cgi/reprint/21/11/1836.pdf Association of Waist Circumference With Risk of Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes in Nigerians, Jamaicans, and African-Americans,IKE S. OKOSUN, PHD.RICHARD S. COOPER, MD,CHARLES N. ROTIMI, PHD BABATUNDE OSOTIMEHIN, MD,TERRENCE FORRESTER, MD
- ↑ http://www.ssb.no/english/yearbook/tab/tab-106.html Statistics Norway
- ↑ 6th National Nutrition Survey
- ↑ Tendências do Peso em Portugal no Final do Século XX
- ↑ [4]
- ↑ Deurenberg et al. 2003
- ↑ SADHS(1998)
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Sigma Dos Statistics 2003
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 55.2 55.3 Vall d'Hebron Hospital pediatric study about 18-year-old Spaniards, dated in 2004, and other values mentioned in the article below.
- ↑ "Vikt och längd i befolkningen". Statistics Sweden-SCB.
- ↑ Dagens Nyheter (2008-02-29)
- ↑ Ministry of Education, Republic of China (Taiwan)
- ↑ Sukhothai Thammathirat Open University-Health Research Project
- ↑ Prevalence of underweight, overweight and obesity in Turkish adolescents
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Health Survey for England 2006
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 62.2 62.3 Mean Body Weight, Height, and Body Mass Index 1960-2002
- ↑ http://archpedi.ama-assn.org/cgi/reprint/154/8/837.pdf
- ↑ Productive Benefits of Improving Health: Evidence from Low-Income Countries,T. Paul Schultz*
- ↑ Short women more successful with men - 14 August 2002 - New Scientist
- ↑ "Bible, Revised Standard Version 2Esdras 4Ezra5.53".
- ↑ R J Rona, D Mahabir, B Rocke, S Chinn and M C Gulliford (2003). "Social inequalities and children's height in Trinidad and Tobago".
- ↑ Jane E. Miller (1993). "Birth Outcomes by Mother's Age At First Birth in the Philippines".
- ↑ David J. Pevalin. "Outcomes in Childhood and Adulthood by Mother's Age at Birth: evidence from the 1970 British Cohort Study".
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 M.N. Weedon; et al. (2007). "A common variant of HMGA2 is associated with adult and childhood height in the general population". Nature Genetics: 1245. doi:10.1038/ng2121. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ R.A. Fisher (1918). "The correlation between relatives on the supposition of mendelian inheritance". Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh: 399–433.
- ↑ the tallest people in the world
- ↑ climate sculpts bodies
- ↑ Chali D. (1995) 'Anthropometric measurements of the Nilotic tribes in a refugee camp', Ethiopian Medical Journal, 33, 4, 211-217.
- ↑ Njolstad I, Arnesen E, Lund-Larsen PG. (1996) Body height, cardiovascular risk factors, and risk of stroke in middle-aged men and women: a 14-year follow-up of the Finnmark Study. Circulation 94:2877–2882.
- ↑ McCarron, P., Okasha, M., McEwen, J. et al. (2002) Height in young adulthood and risk of death from cardiorespiratory disease: a prospective study of male former students of Glasgow University, Scotland. Am. J. Epidemiol. 155:683–687
- ↑ Samaras, T.T. & Elrick, H. 1999. Height, body size and longevity. Acta Med Okayama. 53:149-169
- ↑ Strong Inverse Association Between Height and Suicide in a Large Cohort of Swedish Men: Evidence of Early Life Origins of Suicidal Behavior? - Magnusson et al. 162 (7): 1373 - Am J Psychiatry
- ↑ ESPN - Shaquille O'Neal Stats, News, Photos - Phoenix Suns
- ↑ {{cite web|url=http://home.hia.no/~stephens/rowphys.htm%7Ctitle=Physiology of the Elite Rower
- ↑ "Relationship Between Physical Fitness and Playing Ability in Rugby League Players". research journal of the NSCA. 2007-01-01. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ Tim J. Gabbett, Jason Kelly, Troy Pezet: "Relationship Between Physical Fitness and Playing Ability in Rugby League Players", pages 1126-1133. Journal of strength and conditioning research: the research journal of the NSCA, 2007
- ↑ http://www.discoverychannelasia.com/sumo/world_famous_sumos/index.shtml
- ↑ Komlos, J. & Baur, M. From the tallest to (one of) the fattest: the enigmatic fate of the American population in the 20th century. Economics and Human Biology, 2(1), March 2004, p 57-74.
- ↑ Bogin 2001, citing height and distribution data of 8 plains Native Americans tribes collected by Frank Boas during 1888-1903 published by Prince & Steckel 1998, "Tallest in the world: Native Americans of the Great Plains in the nineteenth century". National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series. Historical paper 112 1-35
- ↑ Demick, Barbara. Effects of famine: Short staure evident in North Korean generation. Los Angeles Times. The Seattle Times. 2004-02-14.
- ↑ P.O.V. - Big Enough . The Height Gap | PBS
- ↑ Cat.Inist
See also
[edit | edit source]- Heightism
- Anthropometry
- Height and intelligence
- Human weight
- Human variability
- Human biology
- List of tallest people
- List of shortest people
External links
[edit | edit source]- CDC National Center for Health Statistics: Growth Charts of American Percentiles
- Human Height Around the World
- www.fao.org: Body Weights and Heights by Countries (given in percentiles)
- Height to Weight Charts Height to weight charts according to small, medium and large frame for both men and women.
- Standard to Metric Human Height Converter
- BMI Calculator Calculate a persons Body Mass Index
- The Height Gap, article discussing differences in height around the world
ay:Tansa de:Körpergröße io:Staturo is:Hæð manna it:Statura nl:Lichaamslengte no:Menneskehøyde fi:Ihmisen pituus tg:Қади инсон
 KSF
KSF