Lidocaine description
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
| Lidocaine |
|---|
| XYLOCAINE® FDA Package Insert |
| Indications and Usage |
| Dosage and Administration |
| Contraindications |
| Warnings and Precautions |
| Adverse Reactions |
| Drug Interactions |
| Overdosage |
| Description |
| Clinical Pharmacology |
| Nonclinical Toxicology |
| How Supplied/Storage and Handling |
| Labels and Packages |
| Clinical Trials on Lidocaine |
| ClinicalTrials.gov |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Zaghw, M.D. [2]
Description[edit | edit source]
Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl Injection, USP) is a sterile non-pyrogenic solution of an antiarrhythmic agent administered intravenously by direct injection.
Xylocaine Injection is composed of an aqueous solution of lidocaine hydrochloride. Lidocaine HCl (C14H22N2O•HCl) is chemically designated acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2, 6 dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride and is represented by the following structural formula:
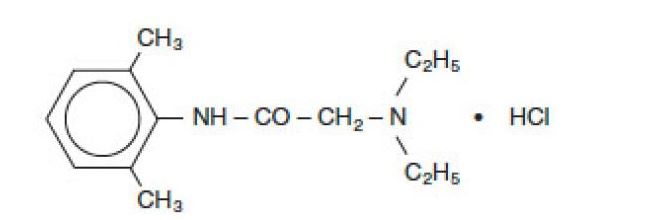 |
pH adjusted to 5.0−7.0 with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid. Single use container. Solution does not contain preservatives.[1]
References[edit | edit source]
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Lidocaine_description4 views | Status: cached on November 09 2024 19:39:03↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF