Locus (genetics)
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
|
WikiDoc Resources for Locus (genetics) |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Locus (genetics) Most cited articles on Locus (genetics) |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Locus (genetics) |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Locus (genetics) at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Locus (genetics) Clinical Trials on Locus (genetics) at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Locus (genetics) NICE Guidance on Locus (genetics)
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Locus (genetics) Discussion groups on Locus (genetics) Patient Handouts on Locus (genetics) Directions to Hospitals Treating Locus (genetics) Risk calculators and risk factors for Locus (genetics)
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Locus (genetics) |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
[edit | edit source]In biology and evolutionary computation, a locus (plural loci) is a fixed position on a chromosome, such as the position of a gene or a biomarker (genetic marker). A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the locus for a particular biological trait.
Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at some locus are called homozygous, while those that have different alleles at a locus, heterozygous.
Nomenclature
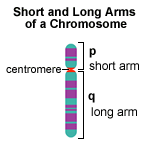
[edit | edit source]The chromosomal locus of a gene might be written "6p21.3".
| Component | Explanation |
| 6 | The chromosome number. |
| p | The position is on the chromosome's short arm (p for petit in French); q indicates the long arm. |
| 21.3 | The numbers following the letter represent the position on the arm: band 21, sub-band 3. The bands are visible under a microscope when the chromosome is suitably stained. Each of the bands is numbered, beginning with 1 for the band nearest the centromere. Sub-bands and sub-sub-bands are visible at higher resolution. |
A range of locations is specified in a similar way. For example, the locus of gene OCA1 may be written "11q1.4-q2.1", meaning it is on the long arm of chromosome 11, somewhere in the range of sub-band 4 of band 1, and sub-band 1 of band 2.
The ends of a chromosome are labeled "ptel" and "qtel", and so "2qtel" refers to the telomere of the long arm of chromosome 2.
External links
[edit | edit source]
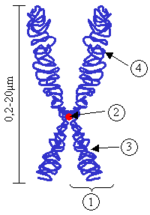
(1) Chromatid. One of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase.
(2) Centromere. The point where the two chromatids touch, and where the microtubules attach.
(3) Short arm
(4) Long arm.
de:Genlocus fa:لوکوس gl:Locus hu:Lókusz id:lokus it:Locus lv:Lokuss nl:Locus (biologie)
 KSF
KSF