Mucous membrane
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 1 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 1 min
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
The mucous membranes (or mucosae; singular: mucosa) are linings of mostly endodermal origin, covered in epithelium, which are involved in absorption and secretion. They line various body cavities that are exposed to the external environment and internal organs. It is at several places continuous with skin: at the nostrils, the lips, the ears, the genital area, and the anus. The sticky, thick fluid secreted by the mucous membranes and gland is termed mucus. The term mucous membrane refers to where they are found in the body and not every mucous membrane secretes mucus.
Body cavities featuring mucous membrane include most of the respiratory system. The glans penis (head of the penis) and glans clitoridis and the inside of the prepuce (foreskin) and clitoral hood are mucous membranes, not skin.
Components
[edit | edit source]- Epithelium
- Lamina propria
- Smooth muscle/Muscularis mucosa/ (GI tract)
Types of mucosa (incomplete)
[edit | edit source]- Buccal mucosa
- Gastric mucosa
- Intestinal mucosa
- Olfactory mucosa
- Oral mucosa
- bronchial mucosa
- Uterine mucosa
- Endometrium is the mucosa of the uterus
Additional images
[edit | edit source]-
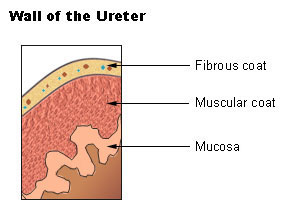
Wall of the ureter.
-
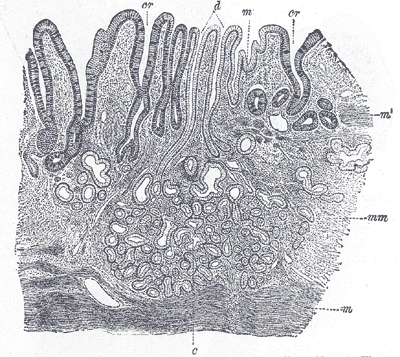
Section of mucous membrane of human stomach, near the cardiac orifice.
-
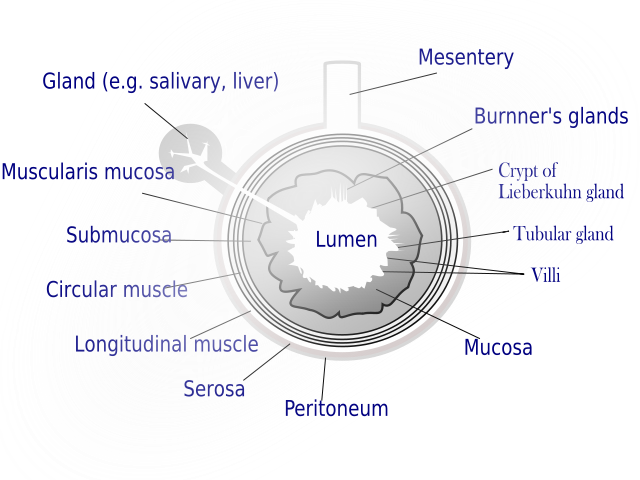
General structure of the gut wall showing the Mucosa.
See also
[edit | edit source]External links
[edit | edit source]- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Template:UCDavisOrganology - "Mammal, whole system (LM, Low)"
- Mucous+Membrane at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
ca:Mucosa cs:Sliznice da:Slimhinde de:Schleimhaut eo:Mukozo fa:غشاء مخاطی id:Membran mukosa it:Mucosa la:Mucosa lt:Gleivinė nl:Slijmvlies no:Slimhinne fi:Limakalvo sv:Slemhinna uk:Слизова оболонка
 KSF
KSF