Nicotine (inhalant)
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 16 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 16 min
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Nicotine (inhalant) is a Dependency Agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of Reducing the withdrawal symptoms, including nicotine craving, associated with quitting smoking. Common adverse reactions include skin irritation, nasal irritation, nasal spray, oral irritation, dizziness, headache, insomnia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Nicotine Inhaler is indicated as an aid to smoking cessation for the relief of nicotine withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine Inhaler therapy is recommended for use as part of a comprehensive behavioral smoking cessation program.
- Patients must desire to stop smoking and should be instructed to stop smoking completely as they begin using Nicotine Inhaler. It is important that patients understand the instructions, and have their questions answered. They should clearly understand the directions for using the Nicotine Inhaler and safely disposing of the used cartridges.
- The initial dosage of Nicotine Inhaler is individualized. Patients may selftitrate to the level of nicotine they require. Most successful patients in the clinical trials used between 6 and 16 cartridges a day. Best effect was achieved by frequent continuous puffing (20 minutes). The recommended duration of treatment is 3 months, after which patients may be weaned from the Nicotine Inhaler by gradual reduction of the daily dose over the following 6 to 12 weeks. The safety and efficacy of the continued use of Nicotine Inhaler for periods longer than 6 months have not been studied and such use is not recommended.
- Dosing recommendations are summarized in the table below.
Directions to use
- Initial Treatment (Up to 12 Weeks)
- For best results, patients should be encouraged to use at least 6 cartridges per day at least for the first 3 to 6 weeks of treatment. In clinical trials, the average daily dose was >6 (range 3 to 18) cartridges for patients who successfully quit smoking. Additional doses may be needed to control the urge to smoke with a maximum of 16 cartridges daily for up to 12 weeks. Regular use of Nicotine Inhaler during the first week of treatment may help patients adapt to the irritant effects of the product. Some patients may exhibit signs or symptoms of nicotine withdrawal or excess which will require an adjustment of the dosage
- Gradual Reduction of Dose (Up to 12 Weeks)
- Most patients will need to gradually discontinue the use of Nicotine Inhaler after the initial treatment period. Gradual reduction of dose may begin after twelve weeks of initial treatment and may last for up to twelve weeks. Recommended strategies for discontinuing use include suggesting to patients that they use the product less frequently, keep a tally of daily usage, try to meet a steadily reducing target or set a planned quit date for stopping use of the product.
- Individualization of Dosage
- The success or failure of smoking cessation is influenced by the quality, intensity and frequency of supportive care. Patients are more likely to quit smoking if they are seen frequently and participate in formal smoking cessation programs.
- The goal of Nicotine Inhaler therapy is complete abstinence. If a patient is unable to stop smoking by the fourth week of therapy, treatment should probably be discontinued.
- Patients who fail to quit on any attempt may benefit from interventions to improve their chances for success on subsequent attempts. Patients who were unsuccessful should be counseled and should then probably be given a therapeutic holiday before the next attempt. A new quit attempt should be encouraged when conditions are more favorable.
- Based on the clinical trials, a reasonable approach to assisting patients in their attempt to quit smoking is to begin initial treatment, using the recommended dosage . Dosage can then be adjusted in those patients with signs or symptoms of nicotine withdrawal or excess. Patients who are successfully abstinent on Nicotine Inhaler should be treated at the selected dosage for up to 12 weeks, after which use of the Inhaler should be gradually reduced over the next 6 to 12 weeks. Some patients may not require gradual reduction of dosage and may abruptly stop treatment successfully. The safe use of this product for longer than 6 months has not been established.
- The symptoms of nicotine withdrawal overlap those of nicotine excess . Since patients using Nicotine Inhaler may also smoke intermittently, it is sometimes difficult to determine if they are experiencing nicotine withdrawal or nicotine excess. Controlled clinical trials of nicotine products suggest that palpitations, nausea and sweating are more often symptoms of nicotine excess, whereas anxiety, nervousness and irritability are more often symptoms of nicotine withdrawal.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nicotine (inhalant) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nicotine (inhalant) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Nicotine (inhalant) in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Nicotine (inhalant) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Nicotine (inhalant) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Use of Nicotine Inhaler therapy is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity or allergy to nicotine or to menthol.
Warnings
- Nicotine from any source can be toxic and addictive. Smoking causes lung disease, cancer and heart disease, and may adversely affect pregnant women or the fetus. For any smoker, with or without concomitant disease or pregnancy, the risk of nicotine replacement in a smoking cessation program should be weighed against the hazard of continued smoking, and the likelihood of achieving cessation of smoking without nicotine replacement.
- Pregnancy, Warning
- Tobacco smoke, which has been shown to be harmful to the fetus, contains nicotine, hydrogen cyanide, and carbon monoxide. The Nicotine Inhaler does not deliver hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide. However, nicotine has been shown in animal studies to cause fetal harm. It is therefore presumed that Nicotine Inhaler can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. The effect of nicotine delivery by Nicotine Inhaler has not been examined in pregnancy . Therefore, pregnant smokers should be encouraged to attempt cessation using educational and behavioral interventions before using pharmacological approaches. If Nicotine Inhaler is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while using it, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
- Safety Note Concerning Children
- This product contains nicotine and should be kept out of the reach of children and pets. The amounts of nicotine that are tolerated by adult smokers can produce symptoms of poisoning and could prove fatal if the nicotine from the Nicotine Inhaler is inhaled, ingested, or buccally absorbed by children or pets. A cartridge contains about 60% of its initial drug content when it is discarded, which is about 6 mg. Patients should be cautioned to keep both the used and unused cartridges of Nicotine Inhaler out of the reach of children and pets.
- All components of the Nicotine Inhaler system should also be kept out of the reach of children and pets to avoid accidental swallowing and choking.
Precautions
- General
- The patient should be urged to stop smoking completely when initiating Nicotine Inhaler therapy . Patients should be informed that if they continue to smoke while using the product, they may experience adverse effects due to peak nicotine levels higher than those experienced from smoking alone. If there is a clinically significant increase in cardiovascular or other effects attributable to nicotine, the treatment should be discontinued . Physicians should anticipate that concomitant medications may need dosage adjustment. Sustained use (beyond 6 months) of Nicotine Inhaler by patients who stop smoking has not been studied and is not recommended.
- Bronchospastic Disease
- Nicotine Inhaler has not been specifically studied in asthma or chronic pulmonary disease. Nicotine is an airway irritant and might cause bronchospasm. Nicotine Inhaler should be used with caution in patients with bronchospastic disease. Other forms of nicotine replacement might be preferable in patients with severe bronchospastic airway disease.
- Cardiovascular or Peripheral Vascular Diseases
- The risks of nicotine replacement in patients with cardiovascular and peripheral vascular diseases should be weighed against the benefits of including nicotine replacement in a smoking cessation program for them. Specifically, patients with coronary heart disease (history of myocardial infarction and/or angina pectoris), serious cardiac arrhythmias, or vasospastic diseases (Buerger's disease, Prinzmetal's variant angina and Raynaud's phenomena) should be evaluated carefully before nicotine replacement is prescribed.
- Tachycardia and palpitations have been reported occasionally with the use of Nicotine Inhaler as well as with other nicotine replacement therapies. No serious cardiovascular events were reported in clinical studies with Nicotine Inhaler, but if such symptoms occur, its use should be discontinued.
- Nicotine Inhaler generally should not be used in patients during the immediate post-myocardial infarction period, nor in patients with serious arrhythmias, or with severe or worsening angina.
- Renal or Hepatic Insufficiency
- The pharmacokinetics of nicotine have not been studied in the elderly or in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. However, given that nicotine is extensively metabolized and that its total system clearance is dependent on liver blood flow, some influence of hepatic impairment on drug kinetics (reduced clearance) should be anticipated. Only severe renal impairment would be expected to affect the clearance of nicotine or its metabolites from the circulation .
- Endocrine Diseases
- Nicotine Inhaler therapy should be used with caution in patients with hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma or insulin-dependent diabetes, since nicotine causes the release of catecholamines by the adrenal medulla.
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Nicotine delays healing in peptic ulcer disease; therefore, Nicotine Inhaler therapy should be used with caution in patients with active peptic ulcers and only when the benefits of including nicotine replacement in a smoking cessation program outweigh the risks.
- Accelerated Hypertension
- Nicotine therapy constitutes a risk factor for development of malignant hypertension in patients with accelerated hypertension; therefore, Nicotine Inhaler therapy should be used with caution in these patients and only when the benefits of including nicotine replacement in a smoking cessation program outweigh the risks.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Assessment of adverse events in the 1,439 patients (730 on active drug) who participated in controlled clinical trials (including three dose finding studies) is complicated by the occurrence of signs and symptoms of nicotine withdrawal in some patients and nicotine excess in others. The incidence of adverse events is confounded by: (1) the many minor complaints that smokers commonly have, (2) continued smoking by many patients and (3) the local irritation from both the active drug and the placebo.
- Local Irritation
- Nicotine Inhaler and the placebo were both associated with local irritant side effects. Local irritation in mouth and throat was reported by 40% of patients on active drug as compared to 18% of patients on placebo. Irritant effects were higher in the two pivotal trials with higher doses being 66% on active drug and 42% on placebo. Coughing (32% active versus 12% placebo) and rhinitis (23% active versus 16% placebo) were also higher on active drug. The majority of patients rated these symptoms as mild. The frequency of cough, and mouth and throat irritation declined with continued use of Nicotine Inhaler. Other adverse events that occurred in over 3% of patients on active drug in placebo controlled pivotal trials considered possibly related to the local irritant effects of the Nicotine Inhaler are taste comments, pain in jaw and neck, tooth disorders and sinusitis.
- Withdrawal
- Symptoms of withdrawal were common in both active and placebo groups. Common withdrawal symptoms seen in over 3% of patients on active drug included: dizziness, anxiety, sleep disorder, depression, withdrawal syndrome, drug dependence, fatigue and myalgia.
- Nicotine-Related Adverse Events
- Smoking Related Adverse Events
- Smoking related adverse events present in greater than 3% of patients on active drug include chest discomfort, bronchitis, and hypertension.
- Other Adverse Events
- Adverse events of unknown relationship to nicotine occurring in greater than 3% of patients on active drug include headache (26% of patients on active and 15% of patients on placebo), influenza-like symptoms, pain, back-pain, allergy, paresthesias, flatulence and fever.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Nicotine (inhalant) in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Physiological changes resulting from smoking cessation, with or without nicotine replacement, may alter the pharmacokinetics of certain concomitant medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants and theophylline. Doses of these and perhaps other medications may need to be adjusted in patients who successfully quit smoking.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): D
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Nicotine (inhalant) in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Nicotine (inhalant) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
- Nicotine Inhaler is not recommended for use during labor and delivery. The effect of nicotine on a mother or the fetus during labor is unknown.
Nursing Mothers
- Caution should be exercised when the Nicotine Inhaler is administered to nursing mothers. The safety of Nicotine Inhaler therapy in nursing infants has not been examined. Nicotine passes freely into breast milk; the milk to plasma ratio averages 2.9. Nicotine is absorbed orally. An infant has the ability to clear nicotine by hepatic first-pass clearance; however, the efficiency of removal is probably lowest at birth. Nicotine concentrations in milk can be expected to be lower with Nicotine Inhaler when used as recommended than with cigarette smoking, as maternal plasma nicotine concentrations are generally reduced with nicotine replacement. The risk of exposure of the infant to nicotine from Nicotine Inhaler therapy should be weighed against the risks associated with the infant's exposure to nicotine from continued smoking by the mother (passive smoke exposure and contamination of breast milk with other components of tobacco smoke) and from the Nicotine Inhaler alone, or in combination with continued smoking.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric and adolescent patients below the age of 18 years have not been established for any nicotine replacement product. However, no specific medical risk is known or expected in nicotine dependent adolescents. Nicotine Inhaler should be used for the treatment of tobacco dependence in the older adolescent only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of Nicotine Inhaler did not include sufficient numbers of subjects age 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reports on clinical experience have not identified differences between older and younger patients. In general, dosage selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosage range reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nicotine (inhalant) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nicotine (inhalant) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nicotine (inhalant) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nicotine (inhalant) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Nicotine (inhalant) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Nicotine (inhalant) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Inhalant
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Nicotine (inhalant) in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Nicotine (inhalant) in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Signs and Symptoms of Nicotine Toxicity
- Signs and symptoms of an overdose of the Nicotine Inhaler would be expected to be the same as those of acute nicotine poisoning including: pallor, cold sweat, nausea, salivation, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, disturbed hearing and vision, tremor, mental confusion, and weakness. Prostration, hypotension, and respiratory failure may ensue with large overdoses. Lethal doses produce convulsions quickly and death follows as a result of peripheral or central respiratory paralysis or, less frequently, cardiac failure.
- Overdose from Inhalation
- The oral LD50 for nicotine is >5 mg/kg in dogs and >24 mg/kg in rodents. Death is due to respiratory paralysis. The oral minimum acute lethal dose for nicotine in adult humans is reported to be 40 to 60 mg (<1 mg/kg). The effects of using several cartridges in rapid succession are unknown .
- One cartridge of Nicotine Inhaler contains 10 mg nicotine, of which, approximately 4 mg is delivered nicotine. It is unlikely that an excessive nicotine overdose will occur via inhalation. Should such an overdose occur, however, with signs of nicotine poisoning, the patient should be instructed to contact his/her physician immediately. For additional emergency information, call your regional poison center or call the National Capital Poison Center toll free (1-800-222-1222).
- Overdose from Ingestion
- Persons ingesting Nicotine Inhaler cartridges should be referred to a health care facility for management. In unconscious patients with a secure airway, instill activated charcoal via a nasogastric tube. A saline cathartic or sorbitol may be added to the first dose of activated charcoal. Repeated doses of activated charcoal should be administered as long as the cartridge remains in the gastrointestinal tract since it will continue to release nicotine for many hours. The Nicotine Inhaler cartridges can be identified with a radiogram.
- Management of Nicotine Poisoning
- Other supportive measures include diazepam or barbiturates for seizures, atropine for excessive bronchial secretions or diarrhea, respiratory support for respiratory failure, and vigorous fluid support for hypotension and cardiovascular collapse.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Nicotine (inhalant) Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Nicotine, the chief alkaloid in tobacco products, binds stereo-selectively to nicotinic-cholinergic receptors at the autonomic ganglia, in the adrenal medulla, at neuromuscular junctions, and in the brain. Two types of central nervous system effects are believed to be the basis of nicotine's positively reinforcing properties. A stimulating effect is exerted mainly in the cortex via the locus ceruleus and a reward effect is exerted in the limbic system. At low doses the stimulant effects predominate while at high doses the reward effects predominate. Intermittent intravenous administration of nicotine activates neurohormonal pathways, releasing acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, vasopressin, beta-endorphin, growth hormone, and ACTH.
Structure
- Nicotine® Inhaler (nicotine inhalation system) consists of a mouthpiece and a plastic cartridge delivering 4 mg of nicotine from a porous plug containing 10 mg nicotine. The cartridge is inserted into the mouthpiece prior to use. Nicotine is a tertiary amine composed of a pyridine and a pyrrolidine ring. It is a colorless to pale yellow, freely water-soluble, strongly alkaline, oily, volatile, hygroscopic liquid obtained from the tobacco plant. Nicotine has a characteristic pungent odor and turns brown on exposure to air or light. Of its two stereoisomers, S(-)nicotine is the more active. It is the prevalent form in tobacco, and is the form in the Nicotine Inhaler. The free alkaloid is absorbed rapidly through skin, mucous membranes, and the respiratory tract.
- Chemical Name: S-3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) pyridine
- Molecular Formula: C10H14N2
- Molecular Weight: 162.23
- Ionization Constants: pKa1 = 7.84, pKa2 = 3.04 at 15°C
- Octanol-Water Partition Coefficient: 15:1 at pH 7Nicotine is the active ingredient; inactive components of the product are menthol and a porous plug which are pharmacologically inactive. *Nicotine is released when air is inhaled through the Inhaler.
Pharmacodynamics
- The cardiovascular effects of nicotine include peripheral vasoconstriction, tachycardia, and elevated blood pressure. Acute and chronic tolerance to nicotine develops from smoking tobacco or ingesting nicotine preparations. Acute tolerance (a reduction in response for a given dose) develops rapidly (less than 1 hour), but not at the same rate for different physiologic effects (skin temperature, heart rate, subjective effects). Withdrawal symptoms such as cigarette craving can be reduced in most individuals by plasma nicotine levels lower than those from smoking.
- Withdrawal from nicotine in addicted individuals can be characterized by craving, nervousness, restlessness, irritability, mood lability, anxiety, drowsiness, sleep disturbances, impaired concentration, increased appetite, minor somatic complaints (headache, myalgia, constipation, fatigue), and weight gain. Nicotine toxicity is characterized by nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, diaphoresis, flushing, dizziness, disturbed hearing and vision, confusion, weakness, palpitations, altered respiration and hypotension.
- Both smoking and nicotine can increase circulating cortisol and catecholamines, and tolerance does not develop to the catecholaminereleasing effects of nicotine. Changes in the response to a concomitantly administered adrenergic agonist or antagonist should be watched for when nicotine intake is altered during Nicotine Inhaler therapy and/or smoking cessation
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption
- Most of the nicotine released from the Nicotine Inhaler is deposited in the mouth. Only a fraction of the dose released, less than 5%, reaches the lower respiratory tract. An intensive inhalation regimen (80 deep inhalations over 20 minutes) releases on the average 4 mg of the nicotine content of each cartridge of which about 2 mg is systemically absorbed. Peak plasma concentrations are typically reached within 15 minutes of the end of inhalation.
- Absorption of nicotine through the buccal mucosa is relatively slow and the high and rapid rise followed by the decline in nicotine arterial plasma concentrations seen with cigarette smoking are not achieved with the inhaler. After use of the single inhaler the arterial nicotine concentrations rise slowly to an average of 6 ng/mL in contrast to those of a cigarette, which increase rapidly and reach a mean Cmax of approximately 49 ng/mL within 5 minutes.
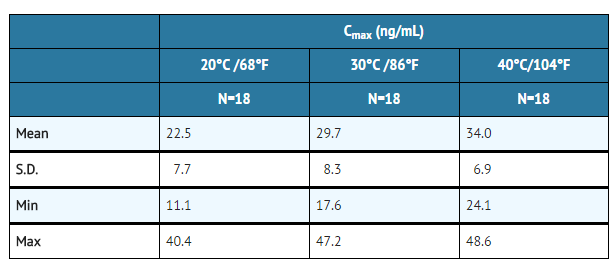
- The temperature dependency of nicotine release from the Nicotine Inhaler was studied between 68°F and 104°F in eighteen patients. Average achievable steady state plasma levels after 20 minutes of an intensive inhalation regimen each hour at ambient room temperature are on the order of 23 ng/mL. The corresponding nicotine plasma levels achievable at 86°F and 104°F are on the order of 30 and 34 ng/mL. Nicotine peak plasma concentration (Cmax) at steady-state, after 20 minutes of an intensive inhalation regimen per hour, for 10 hours.
- Ad libitum use of the Nicotine Inhaler typically produces nicotine plasma levels of 6–8 ng/mL, corresponding to about 1/3 of those achieved with cigarette smoking.
- Distribution
- The volume of distribution following IV administration of nicotine is approximately 2 to 3 L/kg. Plasma protein binding of nicotine is <5%. Therefore, changes in nicotine binding from use of concomitant drugs or alterations of plasma proteins by disease states would not be expected to have significant effects on nicotine kinetics.
- Metabolism
- More than 20 metabolites of nicotine have been identified, all of which are less active than the parent compound. The primary urinary metabolites are cotinine (15% of the dose) and trans-3-hydroxycotinine (45% of the dose). Cotinine has a half-life of 15 to 20 hours and concentrations that exceed nicotine by 10-fold. The major site for the metabolism of nicotine is the liver. The kidney and lung are also sites of nicotine metabolism.
- Elimination
- About 10% of the nicotine absorbed is excreted unchanged in the urine. This may be increased to up to 30% with high urine flow rates and urinary acidification below pH 5. The average plasma clearance is about 1.2 L/min in a healthy adult smoker. The apparent elimination half-life of nicotine is 1 to 2 hours.
- Gender Differences
- Intersubject variability coefficients of variation (C.V.) for the pharmacokinetic parameters (AUC and Cmax) were approximately 40% and 30% respectively, for males and females. There were no medically significant differences between females and males in the kinetics of Nicotine Inhaler.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Nicotine itself does not appear to be a carcinogen in laboratory animals. However, nicotine and its metabolites increased the incidences of tumors in the cheek pouches of hamsters and forestomach of F344 rats, respectively when given in combination with tumor-initiators. One study, which could not be replicated, suggested that cotinine, the primary metabolite of nicotine, may cause lymphoreticular sarcoma in the large intestine of rats. Neither nicotine nor cotinine was mutagenic in the Ames salmonella test. Nicotine induced reparable DNA damage in an E. coli test system. Nicotine was shown to be genotoxic in a test system using Chinese hamster ovary cells. In rats and rabbits, implantation can be delayed or inhibited by a reduction in DNA synthesis that appears to be caused by nicotine. Studies have shown a decrease in litter size in rats treated with nicotine during gestation.
Clinical Studies
- The efficacy of Nicotine Inhaler therapy as an aid to smoking cessation was demonstrated in two single-center, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials with a total of 445 healthy patients. The number of Nicotine Inhaler cartridges used was a minimum dose of 4 cartridges/day and a maximum dose of 20 cartridges/day. In both studies, the recommended duration of treatment was 3 months; however, the patients were permitted to continue to use the product for up to 6 months, if they wished. The quit rates are the percentage of all persons initially enrolled who continuously abstained after week 2. Nicotine Inhaler was more effective than placebo at 6 weeks, 3 months and 6 months. The efficacy is shown in the following table.
How Supplied
- Disposal
- See patient information sheet for instructions on handling and disposal. After using the Nicotine Inhaler, carefully separate the mouthpiece, remove the used cartridge and throw it away, out of the reach of children and pets. Store the mouthpiece in the plastic storage case for further use. The mouthpiece is reusable and should be cleaned regularly with soap and water. The Nicotine Inhaler cartridges can be detected on a radiogram.
How Supplied
- Nicotine INHALER (nicotine inhalation system) is supplied as 168 cartridges each containing 10 mg (4 mg is delivered) nicotine (NDC 0009-5400-01). Each unit consists of 5 mouthpieces, 28 storage trays each containing 6 cartridges and 1 plastic storage case. A patient information leaflet is enclosed with the package.
- Store at room temperature not to exceed 77°F (25°C).
- Protect cartridges from light.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Nicotine (inhalant) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Nicotine (inhalant) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Nicotine (inhalant) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- A patient information sheet is included in the package of Nicotine Inhaler cartridges dispensed to the patient. Patients should be encouraged to read the information sheet carefully and to ask their physician and pharmacist about the proper use of the product (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Patients must be advised to keep both used and unused cartridges out of the reach of children and pets.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Nicotine (inhalant) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Nicotine (inhalant) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Nicotine (inhalant) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nicotine (inhalant) |Label Name=Nicotine (inhalant)04.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Nicotine (inhalant) |Label Name=Nicotine (inhalant)05.png
}}
 KSF
KSF