Probucol
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 3 min
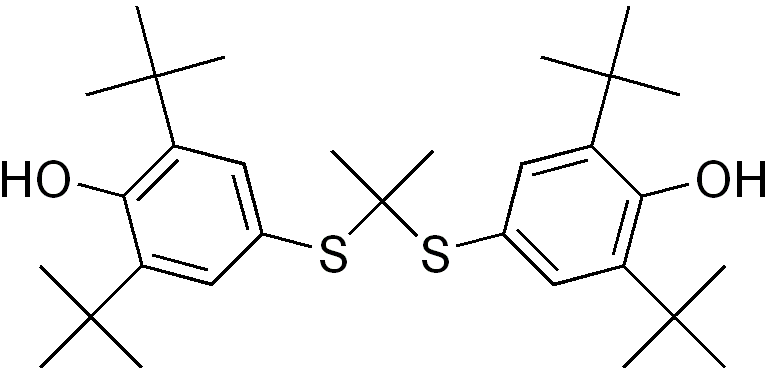 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H48O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 516.844 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Probucol |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Probucol |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Probucol at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Probucol at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Probucol
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Probucol Risk calculators and risk factors for Probucol
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Probucol |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]
Overview
[edit | edit source]Probucol is an anti-hyperlipidemic drug[1] initially developed in the treatment of coronary artery disease.
However, clinical trials were stopped after it was found that it may lower HDL in patients with a previous history of heart disease.
Probucol was initially developed in the 1970s by a chemical company to maximize airplane tire longevity.
Probucol is associated with QT interval prolongation.
Mechanism
[edit | edit source]Probucol lowers the level of cholesterol in the bloodstream by increasing the rate of LDL catabolism. Additionally, probucol may inhibit cholesterol synthesis and delay cholesterol absorption.[2] Probucol is a powerful antioxidant which inhibits the oxidation of cholesterol in LDLs; this slows the formation of foam cells, which contribute to atherosclerotic plaques.
It is believed to act at ABCA1.[3]
It also lowers levels of HDL.[4]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Yamamoto A (December 2008). "A Uniqe Antilipidemic Drug - Probucol". J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 15 (6): 304–5. doi:10.5551/jat.E621. PMID 19075491.
- ↑ "Probucol. Drugs.com web site. [1]
- ↑ Favari E, Zanotti I, Zimetti F, Ronda N, Bernini F, Rothblat GH (December 2004). "Probucol inhibits ABCA1-mediated cellular lipid efflux". Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24 (12): 2345–50. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000148706.15947.8a. PMID 15514211.
- ↑ Miida T, Seino U, Miyazaki O; et al. (October 2008). "Probucol markedly reduces HDL phospholipids and elevated prebeta1-HDL without delayed conversion into alpha-migrating HDL: putative role of angiopoietin-like protein 3 in probucol-induced HDL remodeling". Atherosclerosis. 200 (2): 329–35. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.12.031. PMID 18279878.
 KSF
KSF