Psychedelic plants
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 13 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 13 min
Psychedelic Plants are plants that contain psychedelic drugs. Some of them have been used for thousands of years for religious purposes.
Cannabis[edit | edit source]
Main article: Cannabis
Cannabis (Marijuana) is a popular and unique psychedelic plant. Cannabis is also unique because it contains a psychedelic substance, THC, that contains no nitrogen and is not an indole, phenethylamine, anticholinergics (deliriant), or a disassociative drug. It is the weakest of the psychedelics but can produce hallucinations at higher doses. Currently, certain universities and research firms are studying the medicinal effects of cannabis. Many US states such as California and many countries have created a Medical Cannabis law to allow patients to use cannabis as (among other things) a pain killer, appetite suppressant and appetite stimulant.
Plants containing psychedelic tryptamines[edit | edit source]
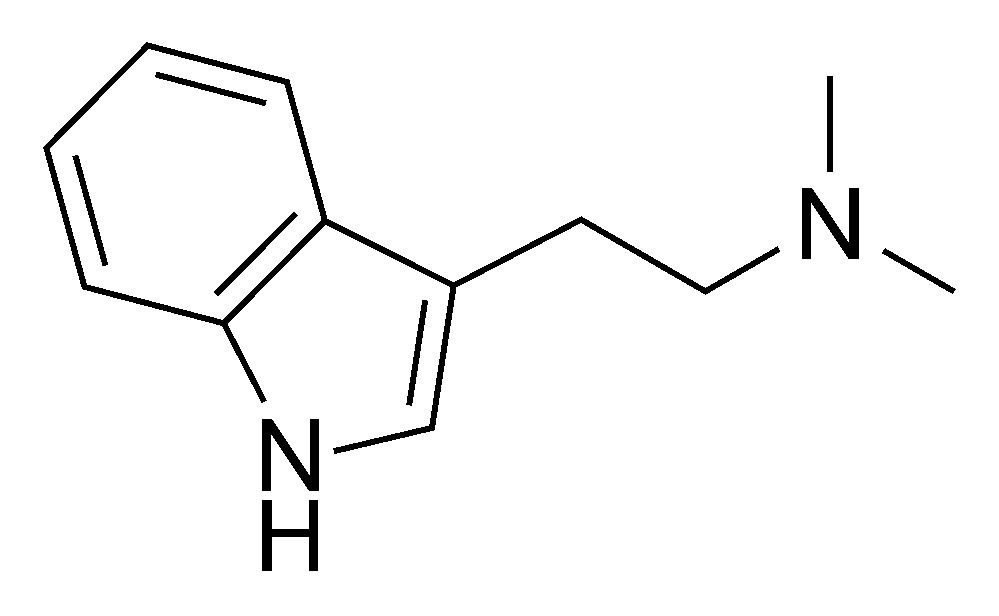
Many of the psychedelic plants contain DMT, which is either snorted (Virola, Yopo snuffs), smoked, or drunk with MAOIs (Ayahuasca). It can not simply be eaten, and it needs to be extremely concentrated to be smokable, since the user needs to smoke all of it in a minute or else tolerance builds rapidly.
- Justicia pectoralis, DMT in leaves[1]
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| DMT[2] | |
| DMT[2] | |
| 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
Shibam |
DMT[2] |
| DMT[2] | |
aff. litorale | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2] | |
| Traces of DMT[2] | |
| DMT[2] |
Fabaceae family (Leguminosae):
Caesalpinioideae (subfamily of Fabaceae) :
- Petalostylis cassioides: 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[3]
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tryptamines in leaves and stems, MAO's up to 0.5%[4]
| Up to 1.5% alkaloids, mainly consisting of tryptamine in leaf[5] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine, 2.4% in leaves[6] | |
| Active principles in leaf[7] | |
| Psychoactive.[8][9] Ash used in Pituri.[10] Ether extracts about 2-6% of the dried leaf mass.[11] | |
| Psychoactive,[8] Tryptamines | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine[12], NMT and DMT in leaf (1.1-10.2 ppm)[13] | |
| Tryptamine alkaloids.[14] Significant amount of tryptamine in the seeds.[15] | |
| 5-MeO-DMT in stem bark[16] | |
| 0.02% tryptamine and β-carbolines, in the leaf, Tetrahydroharman[7][17][18] | |
| Psychoactive[19] Ash used in Pituri.[10] | |
| DMT, amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine[20] | |
| DMT[2] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark | |
| DMT[21] | |
| 0.3% alkaloids in leaf and stem, almost all N-methyl-tetrahydroharman, with traces of tetrahydroharman, some of tryptamine[22][23][24] | |
| Nicotine[25] | |
| DMT & NMT in leaf, stem & bark 0.04% NMT and 0.02% DMT in stem.[7] Also N,N-dimethyltryptamine N-oxide[26] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine[12] | |
| Psychoactive[8][9] Ash used in Pituri.[10] | |
| Psychoactive,[8] Tryptamines[27] | |
| Tryptamine, in the leaf, stem[7] and seeds.[15] Phenethylamine in leaf and seeds[15] | |
| Psychoactive[19] | |
| Psychoactive,[8] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[18] | |
| Psychoactive[19] | |
| Psychoactive,[19] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[18] | |
| Traces of 5-MeO-DMT[28] in fruit. β-methyl-phenethylamine, flower.[29] Ether extracts about 2-6% of the dried leaf mass.[30] Alkaloids are present in the bark[31] and leaves.[32] Amphetamines and mescaline also found in tree.[27] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| Tryptamine, phenethylamine,[33] in flowers[15] other tryptamines,[34] phenethylamines[35] | |
| Psychoactive,[8] plus deadly toxins | |
| N-methyl-β-phenethylamine,[12] phenethylamine[36] | |
| Phenethylamine, hordenine at a ratio of 2:3 in dried leaves, 0.6% total[6] | |
| Hordenine, 1.2% in bark[6] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| Psychoactive[37] | |
| DMT, NMT | |
| Psychoactive | |
| Psychoactive[8][9] | |
| 1.5[6]-1.88%[38] alkaloids, 92% consisting of phenylethylamine.[6] 0.9% N-methyl-2-
phenylethylamine found a different time.[6] | |
| DMT, in the leaf[7] | |
| Psychoactive[8][9] | |
| 0.2% tryptamine in bark, leaves, some in flowers, phenylethylamine in flowers,[33] 0.2% DMT in plant.[39] Histamine alkaloids.[18] | |
| Tryptamine in leaves, bark[15] | |
| Tryptamine[15] | |
| 0.6% NMT and DMT in about a 2:3 ratio in the stem bark, both present in leaves[7] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| DMT, in the bark and leaf,[40] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[18] | |
| DMT, in the leaf[7] | |
| DMT, in the leaf[7] | |
| Psychoactive, DMT in the leaf | |
| Tryptamine,[34] DMT, NMT, other tryptamines,[37] 0.4-0.5% in dried bark, 0.07% in branch tips.[41] | |
| Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[42][17] NMT | |
| Psychoactive[19] | |
| 0.3% DMT in leaf, NMT[7] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| Tryptamine in the leaf,[7] 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark, phenethylamine, trace amounts[33] | |
| DMT in leaf[7] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark | |
| Less than 0.2% DMT in leaf, NMT; DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark[43] | |
| phenylethylamine, β-methyl-phenethylamine[33][6] | |
| Psychoactive[8][9] Ash used in Pituri.[10] | |
| Psychoactive,[8] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[18] | |
| DMT, NMT,[44] nicotine,[27] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids found[18] | |
| DMT, NMT, tryptamine, amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine and others[45] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine[12] | |
| Psychoactive[8][9] Ash used in Pituri.[10] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine, Phenethylamine[36] Amphetamines and mescaline also found.[27] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine[12] | |
Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[7] NMT, other tryptamines. DMT in plant,[29] DMT in bark.Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
| |
| DMT, in the leaf[7] | |
| DMT and NMT, in the leaf, stem and trunk bark, 0.81% DMT in bark, MMT[46][7] | |
| β-methyl-phenethylamine[12] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| Psychoactive[8] | |
| DMT, NMT, and other tryptamines[37] | |
| Psychoactive.[8] Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf, NMT, other tryptamines | |
| Tryptamine, in the leaf and stem,[7] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[18] | |
| Tryptamines[34], 5-MeO-alkyltryptamine[15] | |
| Psychoactive[8] |
List of Acacia Species Having Little or No Alkaloids in the Material Sampled:[18]
0% <math>\le</math> C <math>\le</math> 0.02%, C...Concentration of Alkaloids [%]
Other Plants Containing DMT:
| |
Bufotenin and Dimethyltryptamine have been isolated from the seeds and seed pods, 5-MeO-DMT from the bark of the stems.[49]
The seeds were found to contain 12.4% bufotenine, 0.06% 5-MeO-DMT and 0.06% DMT.[50] | |
| |
|
Bufotenine is in the seeds.[52] | |
| Dried root 0.200% DMT and dried root bark 0.340% DMT[53] | |
| DMT in root bark[54] | |
| Roots: 0.087% DMT,[55] Bufotenine-N-oxide 0.03% | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, whole plant, roots, stems, leaves[1] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, leaves, roots[1] | |
| DMT (dominates in seedlings and young plants), 5-MEO-DMT (dominates in mature plant), whole plant, roots, stems, leaves, flowers[1] | |
| 5-MEO-DMT[1] | |
| DMT-N-oxide, roots[1] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and roots[56] | |
| DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and root bark[1] | |
| DMT[57] | |
| DMT in bark[1] | |
| 1% DMT in dry root bark.[58] | |
| DMT[59] | |
| "The leaves, seeds, stems and roots contain L-Dopa, Serotonin, 5-HTP, and Nicotine, as well as N,N-DMT, Bufotenine, and 5-MeO-DMT."[60] | |
| 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[56] | |
| DMT in leaves and stems[1] | |
| 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT[56] |
Malpighiaceae family:
- Diplopterys cabrerana: DMT 0.17-1.74%, average of 0.47% DMT[61]
Myristicaceae (Nutmeg family):
- Horsfieldia superba: 5-MeO-DMT[56] and beta-carbolines[3]
- Iryanthera macrophylla: 5-MeO-DMT in bark[56]
- Iryanthera ulei: 5-MEO-DMT in bark[1]
- Osteophloem platyspermum: DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark[1]
- Virola genus; for example:
| Virola calophylla | Leaves 0.149% DMT, 0.006% MMT[1] |
| Virola calophylloidea | DMT[59] |
| Virola carinata | DMT in leaves[1] |
| Virola cuspidata | DMT[4] |
| Virola divergens | DMT in leaves[1] |
| Virola elongata | DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark and leaves[1] |
| Virola melinonii | DMT in bark[1] |
| Virola multinervia | DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark and leaves[1] |
| Virola pavonis | DMT in leaves[1] |
| Virola peruviana | DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark[1] |
| Virola rufula | Alkaloids in bark and root, 95% of which is MeO-DMT [62] |
| Virola sebifera | DMT in bark[1] |
| Virola surinamensis | DMT[4] |
| Virola theiodora | DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark, roots, leaves and flowers[1] DMT |
| Virola venosa | DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in roots, leaves[1] DMT |
- Testulea gabonensis: 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT,[56] DMT in bark and root bark[1], NMT
Genus Pandanus (Screw Pine): DMT in nuts[56]
Poaceae family (Gramineae)
| Species | |
None of the above alkaloids are said to have been found in Phalaris californica, Phalaris canariensis, Phalaris minor and hybrids of P. arundinacea together with P. aquatica.[64]
- Punica granatum "DMT in root cortex"[4]
Rubiaceae family:
Rutaceae family:
- Dictyoloma incanescens DC.: 5-MeO-DMT in leaves,[1][62] 0.04% 5-MeO-DMT in bark[56]
- Dutaillyea drupacea: > 0.4 % 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[1][37]
- Dutaillyea oreophila: 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[1]
- Evodia rutaecarpa: 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[1], fruit and roots
- Limonia acidissima: 5-MeO-DMT in stems[1]
- Melicope leptococca: 0.2% total alkaloids, 0.07% 5-MeO-DMT; 5-MeO-DMT in leaves and stems,[1] also "5-MeO-DMT-Oxide and a beta-carboline"[3]
- Pilocarpus organensis: 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[1]
- Vepris ampody: Up to 0.2% DMT in leaves and branches[1]Closing
</ref>missing for<ref>tag - Zanthoxylum procerum: DMT in leaves[1]
- Urtica pilulifera: Bufotenin[4]
Other Indoles[edit | edit source]
Mescaline[edit | edit source]
</ref> missing for <ref> tag |
|||
-dimethoxyphenethylamine[70] |
|||
Plants containing beta-carbolines[edit | edit source]
Beta-carbolines are "reversible" MAO-A inhibitors. They are found in some plants used to make Ayahuasca. In high doses the harmala alkaloids are somewhat hallucinogenic on their own.
| Harmine | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Harmalol | |
| Harman | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] |
- Newbouldia laevis, Harman
| Harmine |
- Hammada leptoclada, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Kochia scoparia, Harmine, etc.
- Guiera senegalensis, Harman, etc.
- Carex brevicollis, Harmine, etc.
- Carex parva, Beta-carbolines[73]
| Harman, etc. | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Tetrahydroharman, etc. | |
| Tetrahydroharman | |
| Tetrahydroharman | |
| Harman, etc. | |
| Tetrahydroharmol | |
| Tetrahydroharmol |
| Tetrahydroharman | |
| Harman, etc. | |
(Perennial Ryegrass) |
Harman, etc. |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] |
- Nectandra megapotamica, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Acacia baileyana, Tetrahydroharman
- Acacia complanata, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Burkea africana, Harman, etc.
- Desmodium gangeticum, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Desmodium gyrans, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Desmodium pulchellum, Harman, etc.
- Mucuna pruriens, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tetrahydroharman; MAO's up to 0.5%[4]
- Prosopis nigra, Harman, etc.
- S. puchellum, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Strychnos melinoniana, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Strychnos usambarensis, Harman[73]
| 5-methoxytetrahydroharman, (-)-N(6)-methoxytetrahydroharman, dimethyltryptamine-N(6)-oxide[12] | |
| Harmine 0.31-8.43%,[74] tetrahydroharmine, telepathine, dihydroshihunine[75] | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Harmine, telepathine[12] | |
| Harmine, telepathine[12] | |
| Harmine | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Beta-carbolines[73] | |
| Harmine |
- Gymnacranthera paniculata, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Horsfieldia superba: Beta-carbolines[3]
- Virola cuspidata, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Virola rufula, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Virola theidora, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Testulea gabonensis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Plectocomiopsis geminiflorus, Beta-carbolines[73]
Passifloraceae:[edit | edit source]
| Harmine, Harmaline, Harman, etc. 0.03%.[76] Alkaloids in rind of fruit 0.25%[76] | |
- Calligonum minimum, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Leptaflorine, etc.
- Nauclea diderrichii, Harman etc.
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Harman
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Harman
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Harman
- Pauridiantha lyalli, Harman
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Harman
- Simira klugii, Harman
- Simira rubra, Harman
- Uncaria attenuata, Harman
- Uncaria canescens, Harman
- Uncaria orientalis, Harman
- Borreria verticillata, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Nauclea diderrichii, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Pauridiantha yalli, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Pavetta lanceolata, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Psychotria carthagenensis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Psychotria viridis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Simira klugii, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Simira rubra, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Uncaria attenuata, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Uncaria canescens, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Uncaria orientalis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Araliopsis tabouensis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Findersia laevicarpa, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Xanthoxylum rhetsa, Beta-carbolines[73]
Rutaceae family:
- Evodia species: Some contain carbolines
- Melicope leptococca: Beta-carboline[3]
- Chrysophyllum lacouritianum, Norharman etc.
- Ailanthus malabarica, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Perriera madagascariensis, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Picrasma ailanthoides, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Picrasma crenata, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Picrasma excelsa, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Picrasma javanica, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Vestia lycioides, Beta-carbolines[73]
- Symplocos racemosa, Harman
- Grewia mollis, Beta-carbolines[73]
(Syrian Rue) |
The seeds contain about 2-6% alkaloids, most of which is harmaline.[77] Peganum harmala is also an abortifacient. |
Other psychedelic plants[edit | edit source]
| File:Salvia divinorum - Herba de Maria.jpg | Salvinorin A, 0.89-3.87 mg/g, also Salvinorin B and Salvinorin C[78] | |
|
File:Argyreia nervosa.jpg Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) |
Seeds contain high amounts of LSA (also known as d-lysergic acid amide, d-lysergamide, ergine, and LA-111), often 50-150X the amounts found in Ipomoea violacea. | |
| File:Iboga.jpg | Ibogaine in root bark[79] | |
| Ibogaine in root leaves[79] | ||
| Ibogaine and similar alkaloids[79] | ||
|
Tabernaemontana sp. |
Ibogaine[79] | |
| File:Nymphaea caerulea.jpg | Recent studies have shown Nympaea caerulea to have psychedelic properties, and may have been used as a sacrament in ancient Egypt and certain ancient South American cultures. Dosages of 5 to 10 grams of flowers induces slight stimulation, a shift in thought processes, and mild closed-eye visuals. Nymphaea caerulea is very often confused with Nelumbo nucifera (Sacred Lotus), which contains the alkaloid nuciferine, which has sedative and muscle-relaxing properties. The active principal alkaloid in N. caerulea is currently unknown. | |
| File:Kratomtree.jpg | Leaves contain mitragynine (thought to be primary psychoactive), mitraphylline, and 7-hydroxymitragynine. (An unusual stimulant and narcotic-like effect reminiscent of caffeine and opium) | |
| File:Leonotis leonurus flower.jpg | Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana) | |
| File:Leonotis nepetifolia1.jpg | Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana) | |
| File:Calea zacatechichi cutting.jpg | Produces vivid dreams after smoking. It is also employed by the Chontal people as a medicinal herb against gastrointestinal disorders, and is used as an appetizer, cathartic anti-dysentery remedy, and as a fever-reducing agent. |
| D-lysergic acid amide, lysergol, and turbicoryn | |
Apocynaceae family:
- Catharanthus roseus is (perhaps unpleasantly) "hallucinogenic."[80]
- Vinca minor
Aquifoliaceae family:
- Ilex guayusa, which is used as an additive to some versions of Ayahuasca.[81] According to the Ecuadorian indigenous, it is also slightly hallucinogenic on its own, when drunk in high enough quantities.
Euphorbiaceae family:
Loganaceae family:
- Desfontainia spinosa, causes visions[82]
Lythraceae family:
- Heimia myrtifolia, auditory[83]
- Heimia salicifolia, auditory[83]
See also[edit | edit source]
- Aztec entheogenic complex
- Legal intoxicants
- List of Entheogens
- Louisiana State Act 159
- Psilocybin mushrooms
External links[edit | edit source]
- Descriptions of psychoactive Cacti. Lycaeum Visionary Cactus Guide
- Erowid Tryptamine FAQ -- More Plants Containing Tryptamines
- John Stephen Glasby, Dictionary of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites, Published by CRC Press
- Golden Guide to Hallucinogenic Plants
- Hallucinogens on the Internet: A Vast New Source of Underground Drug Information John H. Halpern, M.D. and Harrison G. Pope, Jr., M.D.
- Peter L. Katavic, Chemical Investigations of the Alkaloids From the Plants Of The Family Elaeocarpaceae, School of Science/Natural Product Discovery (NPD), Faculty of Science, Griffith University
- Alexander T. Shulgin, Psychotomimetic Drugs: Structure-Activity Relationships
- UNODC The plant kingdom and hallucinogens (part II)
- UNODC The plant kingdom and hallucinogens (part III)
- Virola -- Dried Herbarium Specimens
- Virola Species Pictures -- USGS
- Desmanthus illinoensis -- USDA
- A General Introduction to Ayahuasca
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 Ayahuasca Analogues
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Trouts Notes on Sacred Cacti
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Bluezoo Tryptamines
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 .
- ↑ Lycaeum
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Fitzgerald, J.S. Alkaloids of the Australian Legumuminosae -- The Occurence of Phenylethylame Derivatives in Acacia Species, Aust. J . Chem., 1964, 17, 160-2.
- ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 Shaman Australis
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 8.18 8.19 8.20 Index of Rätsch, Christian. Enzyklopädie der psychoaktiven Pflanzen, Botanik, Ethnopharmakologie und Anwendungen, 7. Auflage. AT Verlag, 2004, 941 Seiten. ISBN 3855025703 at [1] Template:Languageicon
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Book Index from Richard Evans Schultes, Albert Hofmann Pflanzen der Götter at DeutschesFachbuch.de Template:Languageicon
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Duboisia hopwoodii - Pituri Bush - Solanaceae - Central America
- ↑ Wattle Seed Workshop Proceedings 12 March 2002, Canberra March 2003 RIRDC Publication No 03/024, RIRDC Project No WS012-06
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 12.8 Glasby, John Stephen (1991). Dictionary of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites. CRC Press. p. 2. ISBN 0850664233.
- ↑ English Title: Nutritive value assessment of the tropical shrub legume Acacia angustissima: anti-nutritional compounds and in vitro digestibility. Personal Authors: McSweeney, C. S., Krause, D. O., Palmer, B., Gough, J., Conlan, L. L., Hegarty, M. P. Author Affiliation: CSIRO Livestock Industries, Long Pocket Laboratories, 120 Meiers Road, Indooroopilly, Qld 4068, Australia. Document Title: Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2005 (Vol. 121) (No. 1/2) 175-190
- ↑ Maya Ethnobotanicals
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 Acacia (Polish)
- ↑ Lycaeum
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 www.serendipity.com
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 18.7 18.8 Chemotaxonomie der Pflanzen By Robert Hegnauer
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 www.bushfood.net
- ↑ Ask Dr. Shulgin Online: Acacias and Natural Amphetamine
- ↑ www.abc.net.au
- ↑ Acacia Complanata Phytochemical Studies
- ↑ Lycaeum -- Acacias and Entheogens
- ↑ Lycaeum
- ↑ SBEPL
- ↑ NMR spectral assignments of a new chlorotryptamine alkaloid and its analogues from Acacia confusa Malcolm S. Buchanan, Anthony R. Carroll, David Pass, Ronald J. Quinn Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry Volume 45, Issue 4 , Pages359 - 361. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 27.3 Naturheilpraxis Fachforum (German)
- ↑ Lycaeum
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- ↑ Wattle Seed Workshop Proceedings 12 March 2002, Canberra March 2003 RIRDC Publication No 03/024, RIRDC Project No WS012-06
- ↑ www.bpi.da.gov.ph
- ↑ Purdue University
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 Hegnauer, Robert (1994). Chemotaxonomie der Pflanzen. Springer. p. 500. ISBN 3764329793.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 www.bluelight.ru
- ↑ Lycaeum (Acacia floribunda)
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 Chemistry of Acacias from South Texas
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 37.3 wiki.magiskamolekyler.org (Swedish)
- ↑ Acacia kettlewelliae
- ↑ Lycaeum Acacia longifolia
- ↑ extentech.sheetster.com
- ↑ Acacia obtusifolia Phytochemical Studies
- ↑ Plants Containing DMT (German)
- ↑ Hortipedia
- ↑ Pflanzentabelle APB (German)
- ↑ Magiska Molekylers wiki
- ↑ Arbeitsstelle für praktische Biologie (APB)
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 47.3 47.4 47.5 47.6 UNO
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 48.4 48.5 48.6 48.7 48.8 Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- ↑ Herbotechnica (Spanish)
- ↑ Erowid
- ↑ Psychedelics Encyclopedia By Peter G. Stafford, p. 313.
- ↑ PubMed
- ↑ Ayahuasca Analogues
- ↑ www.psychonaut.com
- ↑ Trout's Notes on Desmodium
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 56.3 56.4 56.5 56.6 56.7 .
- ↑ Erowid Mimosa Vault
- ↑ Lycaeum -- Mimosa hostilis
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 UNODC Bulletin on Narcotics 1969
- ↑ Erowid entry(2002), [2]
- ↑ DMT Plants List
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 www.tryptamines.com
- ↑ Erowid Arundo Donax Info Page 1
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 64.2 Lycaeum
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 65.2 Erowid Phalaris FAQ
- ↑ Amazing Nature
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ Trichocereus
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 69.3 69.4 Forbidden Fruit Archives
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 70.2 70.3 70.4 70.5 Visionary Cactus Guide
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Erowid
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 Partial List of Alkaloids in Trichocereus Cacti
- ↑ 73.00 73.01 73.02 73.03 73.04 73.05 73.06 73.07 73.08 73.09 73.10 73.11 73.12 73.13 73.14 73.15 73.16 73.17 73.18 73.19 73.20 73.21 73.22 73.23 73.24 73.25 73.26 73.27 73.28 73.29 73.30 73.31 73.32 73.33 73.34 73.35 73.36 73.37 73.38 73.39 73.40 73.41 73.42 73.43 73.44 73.45 73.46 73.47 73.48 73.49 73.50 73.51 73.52 73.53 73.54 73.55 Angiosperm Families Containing Beta-Carbolines
- ↑ Callaway JC, Brito GS & Neves ES (2005). Phytochemical analyses of Banisteriopsis caapi and Psychotria viridis. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs 37(2): 145-150.
- ↑ John Stephen Glasby, Dictionary of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites, Published by CRC Press
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 www.drugs.com
- ↑ www.amazing-nature.com
- ↑ Clones of Salvia divinorum
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 79.2 79.3 Tihkal
- ↑ Catharanthus roseus
- ↑ Ayahuasca Analogues
- ↑ Schultes, Richard Evans, Iconography of New World Plant Hallucinogens. p. 101
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 Sinicuichi FAQ
 KSF
KSF