RNA splicing
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 7 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 7 min
In molecular biology, splicing is a modification of an RNA after transcription, in which introns are removed and exons are joined. This is needed for the typical eukaryotic messenger RNA before it can be used to produce a correct protein through translation. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing is done in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), but there are also self-splicing introns.
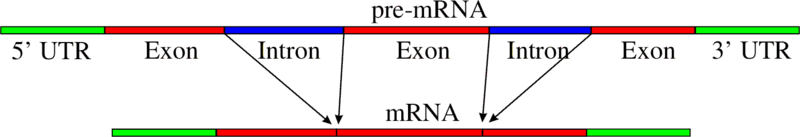
Splicing pathways
[edit | edit source]Several methods of RNA splicing occur in nature: the type of splicing depends on the structure of the spliced intron and the catalysts required for splicing to occur.
Spliceosomal introns
[edit | edit source]Spliceosomal introns often reside in eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Within the intron, a 3' splice site, 5' splice site, and branch site are required for splicing. Splicing is catalyzed by the spliceosome which is a large RNA-protein complex composed of five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs, pronounced 'snurps' ). The RNA components of snRNPs interact with the intron and may be involved in catalysis. Two types of spliceosomes have been identified (the major and minor) which contain different snRNPs.
- Major
- The major spliceosome splices introns containing GU at the 5' splice site and AG at the 3' splice site. It is composed of the U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 snRNPs and is active in the nucleus.
- E Complex-U1 binds to the GU sequence at the 5' splice site, along with accessory proteins/enzymes ASF/SF2, U2AF (binds at the Py-AG site), SF1/BBP (BBP=Branch Binding Protein);
- A Complex-U2 binds to the branch site, and ATP is hydrolyzed;
- B1 Complex-U5/U4/U6 trimer binds, and the U5 binds exons at the 5' site, with U6 binding to U2;
- B2 Complex-U1 is released, U5 shifts from exon to intron and the U6 binds at the 5' splice site;
- C1 Complex-U4 is released, U6/U2 catalyzes transesterification, U5 binds exon at 3' splice site, and the 5' site is cleaved, resulting in the formation of the lariat;
- C2 Complex-U2/U5/U6 remain bound to the lariat, and the 3' site is cleaved and exons are ligated using ATP hydrolysis. The spliced RNA is released and the lariat debranches.
- E Complex-U1 binds to the GU sequence at the 5' splice site, along with accessory proteins/enzymes ASF/SF2, U2AF (binds at the Py-AG site), SF1/BBP (BBP=Branch Binding Protein);
- This type of splicing is termed canonical splicing or termed the lariat pathway, which accounts for more than 99% of splicing. By contrast, when the intronic flanking sequences do not follow the GU-AG rule, noncanonical splicing is said to occur (see "minor spliceosome" below). [1]
- Minor
- The minor spliceosome is very similar to the major spliceosome, however it splices out rare introns with different splice site sequences and is active in the cytosol [2]. While the minor and major spliceosomes contain the same U5 snRNP, the minor spliceosome has different, but functionally analogous snRNPs for U1, U2, U4, and U6, which are respectively called U11, U12, U4atac, and U6atac. [3]
- Trans-splicing
- Trans-splicing is a form of splicing that joins two exons that are not within the same RNA transcript.
Self-splicing
[edit | edit source]Self-splicing occurs for rare introns that form a ribozyme, performing the functions of the spliceosome by RNA alone. There are three kinds of self-splicing introns, Group I, Group II and Group III. Group I and II introns perform splicing similar to the spliceosome without requiring any protein. This similarity suggests that Group I and II introns may be evolutionarily related to the spliceosome. Self-splicing may also be very ancient, and may have existed in an RNA world that was present before protein. Although the two splicing mechanisms described below do not require any proteins to occur, 5 additional RNA molecules and over 50 proteins are used and hydrolyzes many ATP molecules. The splicing mechanisms use ATP in order to accurately splice mRNA's. If the cell were to not use any ATP's, the process would be highly inaccurate and many mistakes would occur. Two transesterifications characterize the mechanism in which group I introns are sliced: 1) 3'OH of a free guanine nucleoside (or one located in the intron) or a nucleotide cofactor (GMP, GDP, GTP) attacks phosphate at the 5' splice site. 2) 3'OH of the 5'exon becomes a nucleophile and the second transesterification results in the joining of the two exons. The mechanism in which group II introns are spliced (two transesterification reaction like group I introns) is as follows: 1)The 2'OH of a specific adenosine in the intron attacks the 5' splice site, thereby forming the lariat 2) The 3'OH of the 5' exon triggers the second transesterification at the 3' splice site thereby joining the exons together.
tRNA splicing
[edit | edit source]tRNA (also tRNA-like) splicing is another rare form of splicing that usually occurs in tRNA. The splicing reaction involves a different biochemistry than the spliceomsomal and self-splicing pathways. Ribonucleases cleave the RNA and ligases join the exons together.
Evolution
[edit | edit source]Splicing occurs in all the kingdoms or domains of life, however, the extent and types of splicing can be very different between the major divisions. Eukaryotes splice many protein-coding messenger RNAs and some non-coding RNAs. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, splice rarely, but mostly non-coding RNAs. Another important difference between these two groups of organisms is that prokaryotes completely lack the spliceosomal pathway.
Because spliceosomal introns are not conserved in all species, there is debate concerning when spliceosomal splicing evolved. Two models have been proposed: the intron late and intron early models (see intron evolution).
| Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes | |
|---|---|---|
| Spliceosomal | + | - |
| Self-splicing | + | + |
| tRNA | + | + |
Biochemical mechanism
[edit | edit source]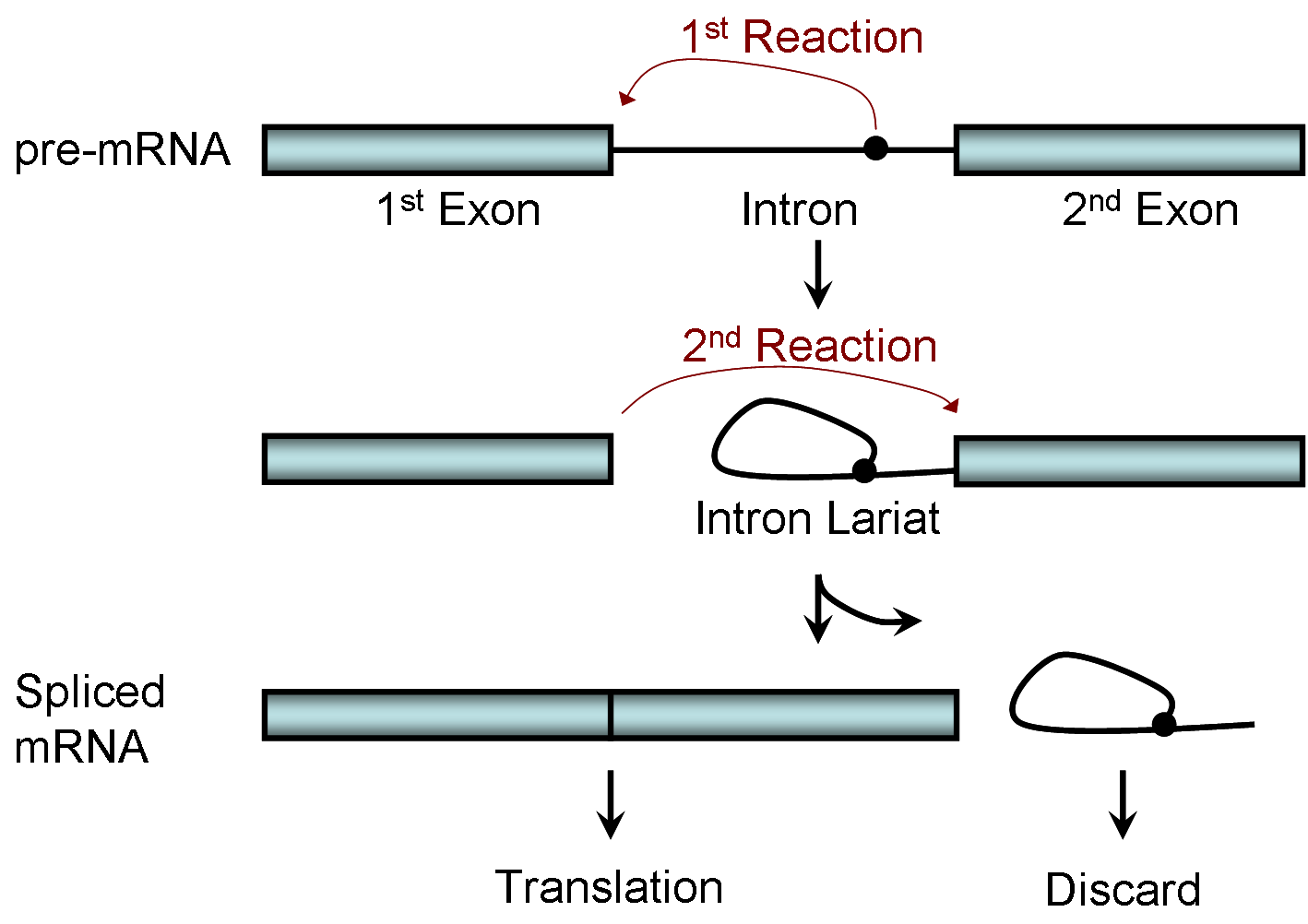
Spliceosomal splicing and self-splicing involves a two-step biochemical process. Both steps involve transesterification reactions that occur between RNA nucleotides. tRNA splicing, however, is an exception and does not occur by transesterification.
Spliceosomal and self-splicing transesterification reactions occur via two sequential transesterification reactions. First, the 2'OH of a specific branch-point nucleotide within the intron that is defined during spliceosome assembly performs a nucleophilic attack on the first nucleotide of the intron at the 5' splice site forming the lariat intermediate. Second, the 3'OH of the released 5' exon then performs a nucleophilic attack at the last nucleotide of the intron at the 3' splice site thus joining the exons and releasing the intron lariat.
Alternative splicing
[edit | edit source]In many cases, the splicing process can create a range of unique proteins by varying the exon composition of the same messenger RNA. This phenomenon is then called alternative splicing.
Experimental manipulation of splicing
[edit | edit source]Splicing events can be experimentally altered[4] by binding steric-blocking antisense oligos such as Morpholinos or Peptide nucleic acids to snRNP binding sites, to the branchpoint nucleotide that closes the lariat,[5] or to splice-regulatory element binding sites.[6]
Splicing errors
[edit | edit source]Common errors:
- Mutation of a splice site resulting in loss of function of that site. Results in exposure of a premature stop codon, loss of an exon, or inclusion of an intron.
- Mutation of a splice site reducing specificity. May result in variation in the splice location, causing insertion or deletion of amino acids, or most likely, a loss of the reading frame.
- Transposition of a splice site, leading to inclusion or exclusion of more RNA than expected, resulting in longer or shorter exons.
Protein splicing
[edit | edit source]Not only pre-mRNA but also proteins can undergo splicing. Although the biomolecular mechanisms are different, the principle is the same, that parts of the protein, called inteins instead of introns, are removed. The remaining parts, called exteins instead of exons, are fused together. Protein splicing has been observed in lower organisms, yeast, plants and animals, including in humans.[7]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Ng B, Yang F, Huston DP; et al. (2004). "Increased noncanonical splicing of autoantigen transcripts provides the structural basis for expression of untolerized epitopes". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 114 (6): 1463–70. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.09.006. PMID 15577853. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ König H, Matter N, Bader R, Thiele W, Müller F (2007). "Splicing segregation: the minor spliceosome acts outside the nucleus and controls cell proliferation". Cell. 131 (4): 1718–29. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.043. PMID 18022366. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Patel AA, Steitz JA (2003). "Splicing double: insights from the second spliceosome". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4 (12): 960–70. doi:10.1038/nrm1259. PMID 14685174.
- ↑ Draper BW, Morcos PA, Kimmel CB (2001). "Inhibition of zebrafish fgf8 pre-mRNA splicing with morpholino oligos: a quantifiable method for gene knockdown". Genesis. 30 (3): 154–6. doi:10.1002/gene.1053. PMID 11477696.
Sazani P, Kang SH, Maier MA; et al. (2001). "Nuclear antisense effects of neutral, anionic and cationic oligonucleotide analogs". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (19): 3965–74. PMID 11574678. Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Morcos, PA (2007). "Achieving targeted and quantifiable alteration of mRNA splicing with Morpholino oligos". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 358 (2): 521–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.172. PMID 17493584.
- ↑ Bruno IG, Jin W, Cote GJ (2004 Oct 15). "Correction of aberrant FGFR1 alternative RNA splicing through targeting of intronic regulatory elements". Hum. Mol. Genet. 13 (20): 2409–20. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh272. PMID 15333583. Check date values in:
|date=(help)(Epub August 27, 2004) - ↑ Ken-ichi Hanada, James C. Yang (2005). "Increased Novel biochemistry: post-translational protein splicing and other lessons from the school of antigen processing" (PDF). J Mol Med. 83 (6): 420–428. doi:10.1007/s00109-005-0652-6.
- Lodish, Harvey (1999). Molecular Cell Biology. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co. ISBN 0-7167-3706-X. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - Hartl, Daniel L. (2005). Genetics: Analysis of Genes and Genomes. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 0763715115. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help)
See also
[edit | edit source]| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Splicing. |
cs:Splicing de:Spleißen (Biologie) et:Splaising eo:Splisado it:Splicing he:שחבור (ביולוגיה) nl:Splicing fi:Silmukointi uk:Сплайсинг
 KSF
KSF