Renal circulation
 From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
From Wikidoc - Reading time: 2 min
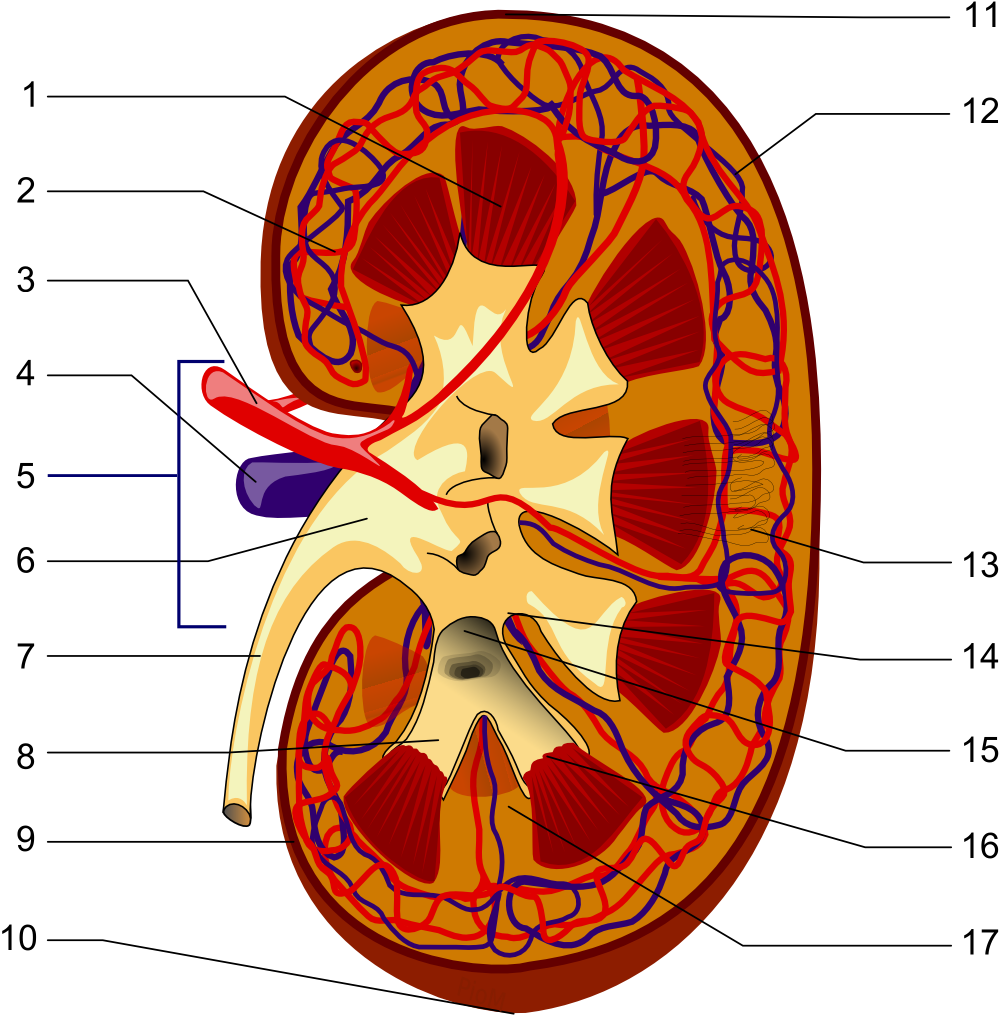
2. Efferent artery
3. Renal artery
4. Renal vein
5. Renal hilum
6. Renal pelvis
7. Ureter
8. Minor calyx
9. Renal capsule
10. Inferior renal capsule
11. Superior renal capsule
12. Afferent vein
13. Nephron
14. Minor calyx
15. Major calyx
16. Renal papilla
17. Renal column
|
WikiDoc Resources for Renal circulation |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Renal circulation Most cited articles on Renal circulation |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Renal circulation |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Cochrane Collaboration on Renal circulation |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Renal circulation at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Renal circulation Clinical Trials on Renal circulation at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Renal circulation NICE Guidance on Renal circulation
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Renal circulation Discussion groups on Renal circulation Patient Handouts on Renal circulation Directions to Hospitals Treating Renal circulation Risk calculators and risk factors for Renal circulation
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Renal circulation |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
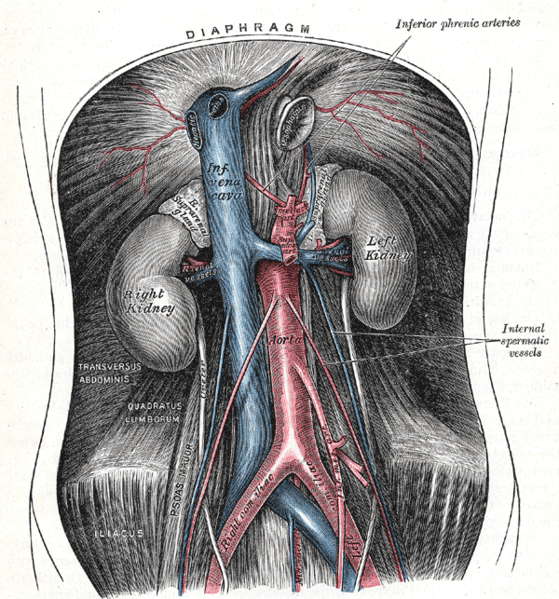
The renal circulation receives around 20% of the cardiac output. It branches from the abdominal aorta and returns blood to the ascending vena cava. It is the blood supply to the kidney, and contains many specialized blood vessels.
Circulation
[edit | edit source]The table below shows the path that blood takes when it travels through the glomerulus, traveling "down" the arteries, and "up" the veins. However, this model is greatly simplified for clarity and symmetry. Some of the other paths and complications are described at the bottom of the table.
| Arteries (down) | Veins (up) |
| Abdominal aorta | Vena cava |
| Renal artery (Note 1) | Renal vein |
| Segmental arteries | - |
| Lobar arteries | - |
| Interlobar artery | Interlobar vein |
| Arcuate arteries (Note 2) | Arcuate vein |
| Interlobular artery (Note 3) | Interlobular vein |
| Afferent arterioles | Efferent arterioles (Note 4) |
| Glomerulus | Glomerulus |
- Note 1: The renal artery also provides a branch to the inferior suprarenal artery to supply the adrenal gland.
- Note 2: The arcuate arterioles also supply blood to the vasa recta. The vasa recta supplies blood to the arcuate veins, thus bypassing the glomerulus.
- Note 3: The interlobular artery also supplies to the stellate veins.
- Note 4: The efferent arterioles don't directly drain into the interlobular vein, but rather they go to the peritubular capillaries first. The efferent arterioles also drain into the vasa recta.
 KSF
KSF