1998 in paleontology
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 19 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 19 min
| List of years in paleontology |
|---|
| (table) |
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils.[1] This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1998.
Flora
[edit]Lycophytes
[edit]Lycophyte research
[edit]- Wehr (1998) reports, without description, Selaginella species spikemoss fossils occurring in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands Klondike Mountain Formation.[2]
Angiosperms
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp nov |
Valid |
Manchester & Chen |
A betulaceous fruit |
Fungi
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen et sp nov |
valid |
Currah, Stockey, & LePage |
A hyperparasitic pleosporalean fungus of uncertain family affinity. |
|||||
|
Gen et sp nov |
valid |
Currah, Stockey, & LePage |
A parasitic phyllachoralean fungus of uncertain family affinity. |
Fungal research
[edit]- Currah, Stockey, & LePage (1998) describe the a phyllachoralean "tar spot" parasitizing Uhlia palm leaves, and host for a hyperparasitic pleosporalean fungus. They note them to be one of the first occurrences of hyperparasitic relationships in the fossil record.[4]
Arthropods
[edit]Newly named crustaceans
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen nov |
Valid |
Hof |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
A mantis shrimp, type species is U. yehoachi (originally named as Eryon yehoachi in 1955). | ||||
|
Sp nov |
Jr synonym |
Jenner, Hof & Schram |
A mantis shrimp, moved to the genus Daidal (2007)[7] |
Newly named insects
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Andrade |
 | |||||
|
Comb nov. |
valid |
(Lin) Andersen |
A water strider |
|||||
|
Sp nov. |
valid |
Deuve |
A ground beetle |
 | ||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Andrade |
 | |||||
|
Gen et sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
A macroveliid water strider |
|||||
|
Gen et sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
A riffle bug |
|||||
|
Sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
||||||
|
Gen et sp nov. |
valid |
Deuve |
A ground beetle |
 | ||||
|
Sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
||||||
|
Gen et 3 sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
A water strider |
|||||
|
Gen et sp nov. |
valid |
Andersen |
A limnobatodine water strider |
|||||
|
Comb nov. |
valid |
(Handlirsch) Andersen |
A water strider |
Brachiopods
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp nov |
valid |
Herrera, Salas & Giolitti |
A species of Iridistrophia |
|||||
|
Sp nov |
valid |
Herrera, Salas & Giolitti |
A species of Iridistrophia |
|||||
|
Sp nov |
valid |
Herrera, Salas & Giolitti |
A species of Iridistrophia |
|||||
|
Sp nov |
valid |
Herrera, Salas & Giolitti |
A species of Iridistrophia |
|||||
|
Sp nov |
valid |
Herrera, Salas & Giolitti |
A species of Eoschuchertella |
Molluscs
[edit]Bivalves
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sp nov |
Valid |
Geyer & Streng |
Early Cambrian Fordillidae bivalve |
Echinoderms
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaidia[14] |
Gen et sp nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is A. sumralli. |
|||
| Altairia[14] |
Gen et comb nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is A. wintoni, originally named as Comptonia wintoni in 1920. |
|||
| Betelgeusia[14] |
Gen et sp nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is B. reidi. |
|||
| Capellia[14] |
Gen et sp nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is C. mauricei. |
|||
| Crateraster texensis[14] |
Comb nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, originally named as Pentagonaster texensis in 1920. |
|||
| Denebia[14] |
Gen et comb nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is D. americana, originally named as Pentaceros americanus in 1920. |
|||
| Fomalhautia[14] |
Gen et comb nov |
Valid |
Blake & Reid |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A starfish, type species is F. hortensae, originally named as Metopaster hortensae in 1920. |
Amphibians
[edit]newly named anurans
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen et sp nov |
Valid |
Henrici |
A possible Rhinophrynidae frog |
Archosauromorpha
[edit]Dinosaurs
[edit]- A paper in the journal Nature is published by Karen Chin and others announcing the earlier discovery of a "king-sized coprolite" attributed to Tyrannosaurus rex.
- Lourinhasaurus gastroliths documented.[16]
- Cedarosaurus gastroliths documented.[17]
- Caudipteryx gastroliths documented.[18]
- Volunteers from the Denver Museum of Natural History discovered Tony's Bone Bed in the Cedar Mountain Formation's Poison Strip Member.[19]
Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list.[20]
| Name | Status | Authors | Location | Notes | Images | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
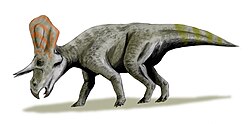
| Altirhinus[21] | Valid taxon |
             | ||||
| ''Augustia'' |
Preoccupied |
|
||||
| Camposaurus[22] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Caseosaurus[22] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Caudipteryx[23] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Cristatusaurus[24] | Valid taxon | |||||
| Eobrontosaurus[25] | Valid taxon. Now Synonym of Brontosaurus | |||||
| Eolambia[26] | Valid taxon | |||||
| Gargoyleosaurus[27] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Gastonia[28] | Valid taxon | |||||
| Gongxianosaurus[29] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Histriasaurus[30] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Lourinhanosaurus[31] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Lourinhasaurus[32] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Megaraptor[33] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Nedcolbertia[34] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Notohypsilophodon[35] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Ozraptor[36] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Protohadros[37] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| ''Rahona''[38] | Preoccupied |
|
|
|||
| Rahonavis[39] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Scipionyx[40] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Shanxia[41] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Shuvuuia[42] | Valid taxon |
|
||||
| Sonorasaurus[43] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Suchomimus | Valid taxon | An African spinosaurs | Sereno et al. 1998 | |||
| Tianzhenosaurus[44] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Variraptor[45] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
| Zuniceratops[46] | Valid taxon |
|
|
|||
Newly named birds
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
An Alexornithidae Brodkorb, 1976, this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid ? |
Late Pliocene |
MN 17 |
A Scolopacidae?, the holotypical tarsometatarsus looks more like a Charadriidae. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
Late Blancan |
|
A Cathartidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Pliocene |
Late-Early Irvingtonian |
|
An Anhingidae. |
|||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
MN 2-3 |
A Gruidae, transferred to the genus Balearica by Mourer-Chauviré in 2001,[51] this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pleistocene |
Cave Deposits |
An Accipitridae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Miocene |
MN 11-12 |
An Accipitridae. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
An Enantiornithes Walker, 1981, Euenantiornithes Incertae Sedis, this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle-Late Pliocene |
An Anatidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
A Fringillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
A Fringillidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Middle Miocene |
A Struthionidae, eggshells. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
An Alexornithidae Brodkorb, 1976, this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Campanian-Early Maastrichtian, |
An Ornithothoraces, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Miocene |
A Gaviidae. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene, |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
|
A Strigidae. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Piciformes, Gracilitarsidae G. Mayr, 2001, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
An Apodiformes, ?Archaeotrogonidae Mourer-Chauviré, 1980, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
An Alexornithidae Brodkorb, 1976, this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Strigidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Coliidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
An Upupiformes, Laurillardiidae Harrison, 1979. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
An Upupiformes, Laurillardiidae Harrison, 1979, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Strigidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Miocene |
A Miopiconidae G. Mayr, 1998, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A Phoenicopteriformes, Palaelodidae Stejneger, 1885. |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
A Phoenicopteriformes, Palaelodidae Stejneger, 1885. |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Zygodactylidae Brodkorb, 1971, not surely a Primozygodactylus. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Zygodactylidae Brodkorb, 1971, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Zygodactylidae Brodkorb, 1971. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
A Halcyornithidae Harrison et Walker, 1972. The genus Pseudastur is preoccupied and replaced by Pseudasturides Mayr, 2004, this is the type species of both genera.[66] |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
ppMichael Daniels |
Middle Eocene |
A stem Psittaciformes, this is the type species of the new genus. |
||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Middle Eocene |
An Alcediniformes Incertae Sedis, this is the type species of the new genus. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
||||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Late Pliocene |
|
A Scolopacidae. |
||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Struthionidae, eggshells. |
|||||
|
Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Pliocene |
A Phasianidae. |
|||||
|
Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. |
Valid |
Early Miocene |
A Psittacidae, this is the type species of the new genus. |
Pterosaurs
[edit]New taxa
[edit]
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
References
[edit]- ^ Gini-Newman, Garfield; Graham, Elizabeth (2001). Echoes from the past: world history to the 16th century. Toronto: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Ltd. ISBN 9780070887398. OCLC 46769716.
- ^ Wehr, W. "Middle Eocene insects and plants of the Okanogan Highlands". In Martin, J. (ed.). Contributions to the Paleontology and Geology of the West Coast. Seattle, Washington: University of Washington Press. pp. 99–109.
- ^ Akhmet'ev, M.A.; Golovneva, L.B. (1998). "New data on composition and age of Malomikhailovka flora from the Upper Cretaceous of the Amur River lower courses". Stratigraphy and Geological Correlation. 6 (3): 249–261.
- ^ a b c Currah, R.S.; Stockey, R.A.; LePage, B.A. (1998). "An Eocene tar spot on a fossil palm and its fungal hyperparasite". Mycologia. 90 (4): 667–673. doi:10.1080/00275514.1998.12026955.
- ^ Hof, Cees H.J. (1998). "Late Cretaceous stomatopods (Crustacea, Malacostraca) from Israel and Jordan". Contributions to Zoology. 67 (4): 257–266. doi:10.1163/18759866-06704003. ISSN 1383-4517.
- ^ Jenner, Ronald A.; Hof, Cees H. J.; Schram, Frederick R. (1998). "Palaeo- and archaeostomatopods (Hoplocarida, Crustacea) from the Bear Gulch Limestone, Mississippian (Namurian), of central Montana". Contributions to Zoology. 67 (3): 155. ISSN 1383-4517.
- ^ Schram, Frederick R. (2007). "Paleozoic Proto-Mantis Shrimp Revisited". Journal of Paleontology. 81 (5): 895–916. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ De Andrade, M. L. (1998). "First description of fossil Acanthostichus from Dominican amber (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)". Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft. 71: 269–274.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Andersen, N.M. (1998). "Water striders from the Paleogene of Denmark and review of fossil record and evolution of semi aquatic bugs (Hemiptera Gerromorpha)". Biologiske Skrifter. 50: 1–157.
- ^ a b Deuve, T. (1998). "Trois fossiles remarquablement conservés du Miocène de France, appartenant aux genres Carabus L. et Ledouxnebria nov. (Coleoptera, Carabidae et Nebriidae)". Bulletin de la Société Entomologique de France. 103 (3): 229–236. doi:10.3406/bsef.1998.17421. S2CID 133246271.
- ^ de Andrade., M. L. (1998). "Fossil and extant species of Cylindromyrmex (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)". Revue suisse de Zoologie. 105: 581–664. doi:10.5962/bhl.part.80052.
- ^ a b c d e Herrera, Zarela Angelica; Salas, María José; Giolitti, Javier A. (January 1998). "Chilidiopsoidea (Brachiopoda) del Devónico Inferior de la Precordillera Argentina". Spanish Journal of Palaeontology. 13 (2): 149–166. doi:10.7203/sjp.24049. ISSN 2660-9568.
- ^ Elicki, O.; Gürsu, S. (2009). "First record of Pojetaia runnegari Jell, 1980 and Fordilla Barrande, 1881 from the Middle East (Taurus Mountains, Turkey) and critical review of Cambrian bivalves" (PDF). Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 83 (2): 267–291. doi:10.1007/s12542-009-0021-9. S2CID 49380913. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
- ^ a b c d e f g Blake, Daniel B.; Reid, Robert (May 1998). "Some Albian (Cretaceous) asteroids (Echinodermata) from Texas and their paleobiological implications". Journal of Paleontology. 72 (3): 512–532. doi:10.1017/S002233600002429X. ISSN 0022-3360.
- ^ Henrici, A. C. (1998). "A new pipoid anuran from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation at Dinosaur National Monument, Utah". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 18 (2): 321–332. doi:10.1080/02724634.1998.10011060.
- ^ Dantas et al. (1998). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167.
- ^ Sanders and Carpenter (1998). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167.
- ^ Qiang et al. (1998). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167.
- ^ "Introduction," DiCroce and Carpenter (2001). Page 185.
- ^ Olshevsky, George. "Dinogeorge's Dinosaur Genera List". Archived from the original on 2011-07-15. Retrieved 2008-08-07.
- ^ Norman, D.B. 1998. On Asian ornithopods (Dinosauria: Ornithischia). 3. A new species of Iguanodontid dinosaur. Zool. Journal Linn. Soc. 122: pp. 291-348.
- ^ a b Hunt, A.P., Lucas, S.G., Heckert, A.B., R.M. Sullivan, and M.G. Lockley. 1998. Late Triassic Dinosaurs from the Western United States. Geobios 31 (4): pp. 511-531.
- ^ Ji, Q.., P.J. Currie, M.A. Norell, and S.-A. Ji. 1998. Two feathered dinosaurs from northeastern China. Nature 393: pp. 753-761.
- ^ Taquet, P. and D.A. Russell. 1998. New data on spinosaurid dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous of the Sahara. Comptes rendus de l'Academie des Sciences, Sciences de la Terre et des Planetes 327: pp. 347-353.
- ^ Bakker, RT. 1998. Dinosaur Mid-Life Crisis: The Jurassic-Cretaceous Transition in Wyoming and Colorado: In: Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial Ecosystems (S.G.Lucas, J.I. Kirkland and J.W. Estep, eds.). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 14: pp. 67- 77.
- ^ Kirkland, J.I. 1998. A new hadrosaurid from the Upper Cedar Mountain Formation (Albian- Cenomanian: Cretaceous) of Eastern Utah - the oldest known hadrosaurid (Lambeosaurine?). Pp. 283-295 in: Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial Ecosystems (S.G. Lucas, J.I. Kirkland, and J.W. Estep, eds.). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 14.
- ^ Carpenter, K., C. Miles, and K. Cloward. 1998. Skull of a Jurassic ankylosaur (Dinosauria). Nature. 393: pp. 782-783.
- ^ Kirkland, J.I. 1998. A Polacanthinae Ankylosaur (Ornithischia: Dinosauria) from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian) of Eastern Utah. In: Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial Ecosystems (S.G. Lucas, J.I. Kirkland, and J.W. Estep, eds.). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 14: pp. 271-281.
- ^ He X., C. Wang, S. Liu, F. Zhou, T. Liu, K. Cai, and B. Dai. 1998. A new sauropod dinosaur during Early Jurassic in Gongxian County, Sichuan China. Sichuan Dizhi Xuebao Acta Geologica Sichuan 18 (1), pp. 1-6.
- ^ Dalla Vecchia, F.M. 1998. Remains of Sauropoda (Reptilia, Saurischia) in the Lower Cretaceous (Upper Hauterivian/Lower Barremian) Limestones of SW Istria (Croatia). Geol. Croat 51 (2): pp. 105-134.
- ^ Mateus, O. 1998. Lourinhanosaurus antunesi, a New Upper Jurassic Allosauroid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from Lourinhã (Portugal). Memórias da Academia de Ciências de Lisboa. 37: pp. 111- 124.
- ^ Dantas, P.M., J.L. Sanz, C.M. Silva, F. Ortega, V.F. Santos, and M. Cachão. 1998. Lourinhasaurus n. gen. Novo dinossáurio saurópode do Jurássico superior (Kimmeridgiano superior-Titoniano inferior) de Portugal. Actas do V Congresso de Geologia. 84 (1): A-91-A-94.
- ^ Novas, F.E. 1998. Megaraptor namunhuaiquii, gen. et sp. nov., a large-clawed, Late Cretaceous theropod from Patagonia. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 18 (1): pp. 4-9.
- ^ Kirkland, J.I., B.B. Britt, C.H. Whittle, S.K. Madsen, and D.L. Burge. 1998. A small coelurosaurian theropod from the Yellow Cat Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation (Lower Cretaceous, Barremian) of eastern Utah. In: Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial ecosystems (S.G. Lucas, J.I. Kirkland, and J.W. Estep, eds.). Bull. New Mexico Mus. Nat. Hist. Sci.14: pp. 239-248.
- ^ Tapia, A. 1919. Una mandibula de dinosaurio procedente de Patagonia. Rev. Soc. Arg. Cienc. Nat. Vil. 4: pp. 369-370.
- ^ Long, J.A. and R.E. Molnar. 1998. A new Jurassic theropod dinosaur from Western Australia. Records of the Western Australian Museum. 19: pp. 121-129.
- ^ Head, J.J. 1998. A new species of basal hadrosaurid (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) from the Cenomanian of Texas. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 18 (4):pp. 718-738.
- ^ Forster, C.A., S.D. Sampson, L.M. Chiappe, and D.W. Krause. 1998. The theropod ancestry of birds: new evidence from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. Science. 279: pp. 1915-1919.
- ^ Forster, C.A., S.D. Sampson, L.M. Chiappe, and D.W. Krause. 1998. The theropod ancestry of birds: new evidence from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. Science. 279: pp. 1915-1919.
- ^ Dal Sasso C. and M. Signore. 1998. Scipionyx samniticus (Saurischia, Theropoda): the first Italian dinosaur. Third European Workshop on Vertebrate Paleontology (abstract): p. 23.
- ^ Barrett, P. M., Y. Hailu, R. Upchurch, and A.C. Burton. 1998. A new ankylosaurian Dinosaur (Ornithischia: Ankylosauria) from the Upper Cretaceous of Shanxi Province, People’s Republic of China. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 18 (2): pp. 376-384.
- ^ Chiappe, L.P., M.A. Norell, and J.M. Clark. 1998. The skull of a relative of the stem-group bird Mononykus. Nature. 392: pp. 275-278.
- ^ Ratkevich, R and R. Scarborough. 1998. New Cretaceous brachiosaurid dinosaur, Sonorasaurus thompsoni, gen. et. sp. nov, from Arizona. Journal of the Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science 31 (1): pp. 71-81.
- ^ Pang, Q., and Z. Cheng. 1998. A new ankylosaur of Late Cretaceous from Tianzhen, Shaxi. Progress in Natural Science 8 (3): pp. 326-334.
- ^ Le Loeuff, J., and E. Buffetaut. 1998. A new dromaeosaurid theropod from the Upper Cretaceous of Southern France. Oryctos 1: pp. 105-112.
- ^ Wolfe, D.G., and J.I. Kirkland J I. 1998. Zuniceratops christopheri n. gen. & n. sp., a ceratopsian dinosaur from the Moreno Hill Formation (Cretaceous, Turonian) of West-Central New Mexico. In: Lower and Middle Cretaceous terrestrial ecosystems (S.G. Lucas, J.I. Kirkland, and J.W. Estep, eds.). New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, Bulletin 14: pp. 303- 317.
- ^ a b c d Andrei V. Panteleyev (1998). "New Species of Enantiornithines (Aves: Enantiornithes) from Upper Cretaceous of Central Kyzylkum". Russian Journal of Ornithology, Express-issue. 35: 3–15.
- ^ Zlatozar N. Boev (1998). "Actitis balcanica Sp. N. - A Late Pliocene Sandpiper (Aves: Scolopacidae) from Bulgaria" (PDF). Historia Naturalis Bulgarica. 9: 71–77. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-08. Retrieved 2014-08-06.
- ^ a b c d Steven D. Emslie (1998). "Avian Community, Climate, and Sea-level Changes in the Plio-Pleistocene of the Florida Peninsula" (PDF). Ornithological Monographs. 50 (50): 1–113. doi:10.2307/40166707. JSTOR 40166707.
- ^ Jiří Mlíkovský (1998). "A New Barn Owl (Aves: Strigidae) from the Early Miocene of Germany, with Comments on the Fossil History of the Tytoninae" (PDF). Journal für Ornithologie. 139 (3): 247–261. doi:10.1007/bf01653335. S2CID 46731635. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2014-08-06.
- ^ Cécile Mourer-Chauviré (2001). "The Systematic Position of the Genus Basityto Mlikovsky 1998 (Aves: Gruiformes: Gruidae)" (PDF). Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 114 (4): 964–971. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-08. Retrieved 2014-08-06.
- ^ Hou Lianhai in S. Hao & H. Wanbo (1998). "Luobidang Cave Site". South Press: 40–47.
- ^ Zlatozar N. Boev in Zlatozar N. Boev & Dimitar Kovachev (1998). "Buteo spassovi sp. n. - a Late Miocene Buzzard (Accipitridae, Aves) from SW Bulgaria". Geologica Balcanica. 29 (1–2): 125–129.
- ^ Claudia P. Tambussi (1998). "Nuevo Anatidae (Aves: Anseriformes) del Plioceno de la Region Pampeana, Argentina". Bolletí de la Societat d'Història Natural de les Balears. 41: 19–25.
- ^ a b Zlatozar N. Boev (1998). "Late Pliocene Hawfinches (Coccothraustes Brisson 1760) (Aves: Fringillidae) from Bulgaria" (PDF). Historia Naturalis Bulgarica. 9: 87–99. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-08. Retrieved 2014-08-06.
- ^ a b Brigitte Senut, Yannicke Dauphin & Martin Pickford (1998). "Nouveaux Restes Aviens du Néogène de la Sperrgebiet (Namibie): Complément à la Biostratigraphie Avienne des Éolianites du Désert de Namib". Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série II. 327 (9): 639–644. Bibcode:1998CRASE.327..639S. doi:10.1016/s1251-8050(99)80119-0.
- ^ Eric Buffetaut & Jean Le Loeuff (1998). "A New Giant Ground Bird from the Upper Cretaceous of Southern France". Journal of the Geological Society, London. 155 (1): 1–4. Bibcode:1998JGSoc.155....1B. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.155.1.0001. S2CID 128496095.
- ^ Jiří Mlíkovský (1998). "A New Loon (Aves: Gaviidae) from the Middle Miocene of Austria" (PDF). Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien. Ser. A. 99: 331–339. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2014-08-06.
- ^ Zlatozar N. Boev (1998). "Presence of Bald Ibises (Geronticus Wagler, 1832) (Threskiornithidae - Aves) in the Late Pliocene of Bulgaria". Geologica Balcanica. 28 (1–2): 45–52.
- ^ a b c d e f g Gerald Mayr (1998). ""Coraciiforme" und "Piciforme" Kleinvögel aus dem Mittel-Eozän der Grube Messel (Hessen, Deutschland)". Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg. 205: 1–101.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (1998). "Ein Archaeotrogon (Aves: Archaeotrogonidae) aus dem Mittel-Eozän der Grube Messel (Hessen, Deutschland)?" (PDF). Journal für Ornithologie. 139 (2): 121–129. doi:10.1007/bf01651221. S2CID 22809910.
- ^ a b Jirí Mlíkovský (1998). "Two New Owls (Aves: Strigidae) from the Early Miocene of the Czech Republic, With Comments on the Fossil History of the Subfamily Striginae" (PDF). Buteo. 10: 5–22.
- ^ Gerald Mayr & Dieter S. Peters (1998). "The Mousebirds (Aves: Coliiformes) from the Middle Eocene of Grübe Messel (Hessen, Germany)" (PDF). Senckenbergiana Lethaea. 78 (1–2): 179–197. doi:10.1007/bf03042768. S2CID 82480792.
- ^ a b Robert F. Baird & Patricia Vickers Rich (1998). "Palaelodus (Aves: Palaelodidae) from the Middle to Late Cainozoic of Australia". Alcheringa. 22 (2): 135–151. doi:10.1080/03115519808619196.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (1998). "A New Family of Eocene Zygodactyl Birds" (PDF). Senckenbergiana Lethaea. 78 (1–2): 199–209. doi:10.1007/bf03042769. S2CID 62901085.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2004). "Pseudasturides n. gen., a Replacement Name for the Stam Group Parrot Pseudastur Mayr 1998 (Preoccupied by Pseudastur Blyth, 1850)". Senckenbergiana Lethaea. 83 (1–2): 2.
- ^ Gerald Mayr & Michael Daniels (1998). "Eocene Parrots from Messel (Hessen, Germany) and the London Clay of Walton-on-the-Naze (Essex, England)" (PDF). Senckenbergiana Lethaea. 78 (1–2): 157–177. doi:10.1007/bf03042767. S2CID 128174446.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (1998). ""Coraciiforme" und "Piciforme" Kleinvögel aus dem Mittel-Eozän der Grube Messel (Hessen, Deutschland)". Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg. 205: 1–65.
- ^ Jíří Mlíkovský (1998). "A New Painted Snipe (Aves: Rostratulidae) from the Early Miocene of the Czech Republic" (PDF). Časopis Národniho Muzea, Řada Přírodovědná. 167 (1–4): 99–101. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
- ^ Zlatozar N. Boev (1998). "Fossil Birds of Dorkovo - an Early Pliocene Site in the Rhodope Mts. (Southern Bulgaria)". Geologica Balcanica. 28 (1–2): 53–60.
- ^ Jiří Mlíkovský (1998). "A New Parrot (Aves (Psittacidae) from the Early Miocene of the Czech Republic" (PDF). Acta Societatis Zoologicae Bohemicae. 62: 335–341. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
- Dantas, P.M., Freitas, C., Azevedo, T. Sanz, J.L., Galopim de Carvalho, A.M., Santos, D., Ortega, F., Santos, V., Sanz, J.L., Silva, C.M. & Cachão, M. (1998). Estudo dos Gastrólitos do Dinossáurio Lourinhasaurus do Jurássico Superior Português. Actas do V Congresso Nacional de Geologia. 84 (1): A87-A90.
- DiCroce, K. and K. Carpenter. (2001). "New ornithopod from the Cedar Mountain Formation (Lower Cretaceous) of Eastern Utah". pp. 183–196 in: Tanke, D. & K. Carpenter (eds.) Mesozoic Vertebrate Life. Indiana University Press, Bloomington.
- Qiang, J., .Currie, P.J., Norell., M.A. & Shu-An, J., 1998. Two feathered dinosaurs from northeastern China. Nature 393 753–761.
- Sanders, F.H. & Carpenter, K. (1998). Gastroliths from a camarasaurid in the Cedar Mountain Formation. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. Abstracts with program. 18 (3): 74A.
 KSF
KSF