2021 Kuomintang chairmanship election
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 12 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 12 min
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 50.71% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
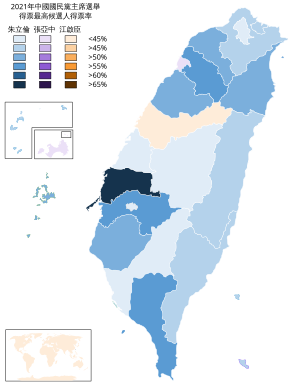 County level units won by Eric Chu. County level units won by Chang Ya-chung. County level units won by Johnny Chiang. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2021 Kuomintang chairmanship election (Chinese: 2021年中國國民黨主席選舉) was scheduled to be held in July 2021. It was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and eventually rescheduled for 25 September 2021. It was the tenth direct election of the party leader in Kuomintang (KMT) history. All registered, due-paying KMT party members were eligible to vote.
Candidates
[edit]Jaw Shaw-kong applied to renew his Kuomintang party membership in February 2021, and expressed interest in contesting the party leadership.[1] In response, the National Communications Commission noted that the Broadcasting Corporation of China could be fined under Article 5-1 of the Radio and Television Act if Jaw simultaneously held leadership positions in a political party and a radio or television media enterprise.[2] After formally attaining party membership, Jaw reiterated that he would run for the chairmanship.[3] As candidates for the party chairmanship must have served on the Kuomintang's Central Committee or Central Advisory Committee, the KMT announced that a proposal to appoint Jaw to the Central Advisory Committee would be considered during the 21st National Congress.[4] Jaw decided not to run for the party leadership on 28 April 2021.[5][6]
On 20 February 2021, incumbent chair Johnny Chiang stated that he would run for a full term as party leader.[7][8]
Cho Po-yuan announced his campaign for the party leadership on 11 July 2021.[9]
On 2 August 2021, Eric Chu stated that he would seek the Kuomintang chairmanship, a position he had previously held from 2015 to 2016.[10][11] Chu promised to reestablish a polling department within the party if he were reelected chairman.[12]
Election scheduling and candidate registration
[edit]The chairmanship election was scheduled for 24 July 2021, and was to be held alongside delegate elections for the Kuomintang's 21st National Congress. Registration of eligible candidates was to take place on 3 or 4 June, and completed registration forms were to be received on either 7 or 8 June.[13] Candidacy processing fees were charged for the first time during the 2021 leadership election; each campaign was expected to pay a total of NT$13.2 million.[14] Following a meeting of the KMT's Central Standing Committee on 26 May 2021, committee members decided to postpone the leadership election due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.[15] During an in-person meeting on 28 July 2021, the Central Standing Committee decided to reschedule the chairmanship election for 25 September 2021. Registration forms were available to eligible candidates on 12 and 13 August. The two-day period to accept completed forms was extended to 16 or 17 August.[16][17]
Eric Chu registered his candidacy on 16 August, and afterwards, outlined several goals for the party leader: empower the Kuomintang legislative caucus, expand international and Cross-Strait outreach, focus on younger party members, and win both the 2022 local and 2024 presidential elections.[18][19] Johnny Chiang, Chang Ya-chung, and Cho Po-yuan registered their candidacies the next day.[20] Chiang described a number of his objectives and vowed to step down if any one was not met. Chiang promised to build intraparty consensus and improve communication between its members. He sought passage of the questions proposed by the Kuomintang in the 2021 Taiwanese referendum, to win a total of fifteen mayoral or magisterial seats in the 2022 local elections, and claim a legislative majority in the 2024 Taiwanese legislative election, led by the selection of "star" candidates on the Kuomintang party list. As a "kingmaker," Chiang committed to helping the party choose its presidential candidate.[21] Regarding Cross-Strait relations, Chiang suggested convening a committee to advise the party on the topic,[22] as well as naming a representative of the party to promote relations.[23]
Debates
[edit]A televised debate between the four candidates took place on 4 September.[24] Chiang again stressed his role as a kingmaker during the presidential election, stating that he would not run for the post himself. He regarded the maintenance of peace and safety as vital to Cross-Strait relations, and said that the Kuomintang needed to offer more opportunities to its younger members. In his remarks, Chu expressed the belief that the elected chairman must focus on consolidation of party strengths against the Democratic Progressive Party. To Chu, the kingmaker role would be served by a stronger KMT. Chu commented that the party must participate in Cross-Strait interactions, and focus on social exchanges with China, to show the public the party's commitment to peace, prosperity and safety. He also vowed to create opportunities for younger party members. Chang criticized Chiang and Chu for making intangible and empty promises. Chang's main goal was to sign a peace treaty with Beijing, if the Kuomintang won a legislative majority in 2024. Chang also advocated for a China-based office to be established, in order to help Taiwanese expatriates in China. Cho felt that young Kuomintang members deserved attention and respect from a selfless and professional party leader, and stated that, if elected, he would invite Chinese Communist Party general secretary Xi Jinping to Taiwan for a summit on Cross-Strait relations.[25][26] A group of Taiwan independence activists led by the Taiwan Republic Office gathered outside the TVBS Media building, where the debate was held, in protest, shouting slogans at each of the four chairperson candidates. Chang responded to the protesters by giving a thumbs-down sign.[27]
On 13 September, the Kuomintang's Central Election Supervision Committee referred Chang to the party's Central Evaluation and Disciplinary Committee, reasoning that Chang had made multiple verbal attacks on Chu during the campaign. Both Chiang and Chu opposed the election committee's decision, and a proposal to rescind the action, initiated by Chang's committee representative Chen Ming-yi, was passed two days later.[28]
A livestreamed debate on party policy was held at China Television studios on 17 September, during which the 1992 Consensus was a primary topic. Chiang stated that the "original definition of the consensus" should be restored, and that objections to the consensus itself had been reduced because the Democratic Progressive Party was unable to manage Cross-Strait relations. Cho was also critical of the DPP, believing that strained relations were due to the DPP abandonment of the consensus. In turn, Chu said that, during a 2015 meeting with Xi Jinping, he had emphasized his position that the consensus allowed Taiwan and China to have different interpretations of the term "One-China." Chu backed the "creative ambiguity" of the consensus. Chang opined that the consensus was one of the Kuomintang's guiding principles, but that he would seek to negotiate a memorandum of understanding for peace with the Chinese Communist Party. Chu objected to Chang, expressing concern that Chang's actions would rapidly unify China and Taiwan.[29][30]
Election
[edit]Polls were open from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. on 25 September 2021.[31] Eric Chu received 85,164 of 187,999 votes cast, finishing ahead of Chang Ya-chung (60,632 votes), Johnny Chiang (35,090 votes), and Cho Po-yuan (5,133 votes). Voter turnout was 50.71 percent.[32][33] The election results were confirmed by the Kuomintang's Central Standing Committee on 29 September.[34][35] Although Central Standing Committee member Lin Chin-chieh suggested that Chu take office as soon as possible, the committee voted for Chu to assume the chairmanship on 5 October 2021.[35] Chu was duly inaugurated as chairman on that date.[36][37]
Reactions
[edit]In his capacity as General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party, Xi Jinping wrote a letter congratulating Eric Chu on winning the Kuomintang chairmanship. The message referred to the 1992 Consensus, and expressed hope for Cross-Strait peace, unification, and rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.[38] Chu's response to Xi acknowledged that peace had been kept due to recognition of the consensus between the Kuomintang and Chinese Communist Party in the past, unlike the Democratic Progressive Party's "anti-China" policies and actions promoting "desinicization."[39] Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Council described Chu's reply to Xi as "cater[ing] to the CCP while ignoring the facts." The Democratic Progressive Party criticized Chu's acknowledgement of Xi, stating that no party leader in a democracy would expect commendation from autocratic government leaders elsewhere.[40]
Opinion polling
[edit]| Date | Pollster | Sample size | Chang Ya-chung | Johnny Chiang | Cho Po-yuan | Eric Chu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9–13 September 2021 | TVBS[41][42] | 1,257 | 30.6 | 12.8 | 0.9 | 27.5 |
| 22–23 September 2021 | Trend Survey[43] | 818 | 28.4 | 18.0 | 1.8 | 29.3 |
Results
[edit]| No. | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Johnny Chiang | 35,093 | 18.87% | |
| 2 | Cho Po-yuan | 5,133 | 2.76% | |
| 3 | Chang Ya-chung | 60,631 | 32.59% | |
| 4 | Eric Chu | 85,163 | 45.78% | |
| Eligible voters | 370,711 | |||
| Total votes | 188,000 | |||
| Valid votes | 186,020 | |||
| Invalid votes | 1,980 | |||
| Turnout | 50.71% | |||
| Subdivision | Eligible Voters | Total Votes | Turnout | Valid Votes | Invalid Votes | Johnny Chiang | Cho Po-yuan | Chang Ya-chung | Eric Chu | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | Votes | % | Votes | % | ||||||
| Taipei City | 45,202 | 17,386 | 38.46% | 17,254 | 132 | 2,054 | 11.90% | 234 | 1.36% | 7,355 | 42.63% | 7,611 | 44.11% |
| New Taipei City | 41,483 | 19,693 | 47.47% | 19,522 | 171 | 2,712 | 13.89% | 239 | 1.22% | 6,987 | 35.79% | 9,584 | 49.09% |
| Keelung City | 6,305 | 2,427 | 38.49% | 2,402 | 25 | 363 | 15.11% | 27 | 1.12% | 872 | 36.30% | 1,140 | 47.46% |
| Yilan County | 6,897 | 3,594 | 52.11% | 3,567 | 27 | 533 | 14.94% | 54 | 1.51% | 1,055 | 29.58% | 1,925 | 53.97% |
| Taoyuan City | 26,266 | 12,625 | 48.07% | 12,522 | 103 | 1,229 | 9.81% | 143 | 1.14% | 4,801 | 38.34% | 6,349 | 50.70% |
| Hsinchu County | 9,085 | 5,771 | 63.52% | 5,712 | 59 | 749 | 13.11% | 82 | 1.44% | 1,730 | 30.29% | 3,151 | 55.16% |
| Hsinchu City | 8,561 | 3,636 | 42.47% | 3,600 | 36 | 623 | 17.31% | 58 | 1.61% | 1,548 | 43.00% | 1,371 | 38.08% |
| Miaoli County | 11,185 | 7,231 | 64.65% | 7,140 | 91 | 1,365 | 19.12% | 102 | 1.43% | 2,044 | 28.63% | 3,629 | 50.83% |
| Taichung City | 31,814 | 18,592 | 58.44% | 18,377 | 215 | 8,162 | 44.41% | 332 | 1.81% | 5,230 | 28.46% | 4,653 | 25.32% |
| Changhua County | 20,802 | 13,060 | 62.78% | 12,902 | 158 | 2,664 | 20.65% | 2,387 | 18.50% | 2,656 | 20.59% | 5,195 | 40.27% |
| Nantou County | 9,322 | 5,018 | 53.83% | 4,970 | 48 | 1,144 | 23.02% | 145 | 2.92% | 1,468 | 29.54% | 2,213 | 44.53% |
| Yunlin County | 9,970 | 6,493 | 65.13% | 6,420 | 73 | 801 | 12.48% | 113 | 1.76% | 1,185 | 18.46% | 4,321 | 67.31% |
| Chiayi County | 7,619 | 3,428 | 44.99% | 3,401 | 27 | 550 | 16.17% | 86 | 2.53% | 843 | 24.79% | 1,922 | 56.51% |
| Chiayi City | 6,224 | 2,361 | 37.93% | 2,331 | 30 | 390 | 16.73% | 48 | 2.06% | 888 | 38.10% | 1,005 | 43.11% |
| Tainan City | 25,471 | 12,543 | 49.24% | 12,409 | 134 | 1,965 | 15.84% | 245 | 1.97% | 3,593 | 28.95% | 6,607 | 53.24% |
| Kaohsiung City | 45,799 | 24,260 | 52.97% | 23,963 | 297 | 4,345 | 18.13% | 405 | 1.69% | 9,221 | 38.48% | 9,992 | 41.70% |
| Pingtung County | 20,813 | 12,908 | 62.02% | 12,737 | 171 | 1,810 | 14.21% | 179 | 1.41% | 3,408 | 26.76% | 7,340 | 57.63% |
| Hualien County | 10,594 | 6,524 | 61.58% | 6,454 | 70 | 1,420 | 22.00% | 76 | 1.18% | 1,994 | 30.90% | 2,964 | 45.93% |
| Taitung County | 7,897 | 3,875 | 49.07% | 3,839 | 36 | 513 | 13.36% | 70 | 1.82% | 1,343 | 34.98% | 1,913 | 49.83% |
| Penghu County | 3,718 | 1,752 | 47.12% | 1,711 | 41 | 333 | 19.46% | 44 | 2.57% | 457 | 26.71% | 877 | 51.26% |
| Kinmen County | 3,433 | 1,871 | 54.50% | 1,866 | 5 | 276 | 14.79% | 27 | 1.45% | 824 | 44.16% | 739 | 39.60% |
| Lienchiang County | 799 | 458 | 57.32% | 453 | 5 | 83 | 18.32% | 7 | 1.55% | 155 | 34.22% | 208 | 45.92% |
| Overseas | 11,452 | 2,493 | 21.77% | 2,467 | 26 | 1,009 | 40.90% | 30 | 1.22% | 974 | 39.48% | 454 | 18.40% |
References
[edit]- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (2 February 2021). "Jaw asks KMT to restore his party membership". Taipei Times. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Shan, Shelley (2 February 2021). "BCC could face fine if its boss also heads the KMT". Taipei Times. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (4 February 2021). "Jaw Shaw-kong rejoins KMT, eyes chair election". Taipei Times. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Chen, Yun; Chung, Jake (18 February 2021). "KMT to appoint six Central Advisory Committee members, including Jaw". Taipei Times. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Liu, Kuang-ting; Yeh, Joseph (28 April 2021). "TV personality Jaw decides not to run for KMT chairmanship". Retrieved 6 May 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (29 April 2021). "Jaw not running for KMT top job". Taipei Times. Retrieved 6 May 2021.
- ^ Liu, Kuan-ting; Huang, Frances (20 February 2021). "KMT chairman launches re-election bid". Central News Agency. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Hsiao-kuang; Chung, Jake (21 February 2021). "KMT's Chiang throws hat into party chairperson race". Taipei Times. Retrieved 21 February 2021.
- ^ Wang, Cheng-chung; Yeh, Joseph (11 July 2021). "Ex-Changhua County chief throws hat in ring for KMT chairmanship". Central News Agency. Retrieved 11 July 2021.
- ^ Wang, Cheng-chung; Kao, Evelyn (3 August 2021). "Eric Chu to run for party chair, aiming to return KMT to power". Central News Agency. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ Wang, Cheng-chung; Kao, Evelyn (2 August 2021). "Eric Chu runs for chance to lead Taiwan's KMT". Central News Agency. Republished as: "Ex-New Taipei City mayor Eric Chu to run for KMT chair". Taipei Times. 3 August 2021. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (10 August 2021). "Chu pledges poll center if elected as KMT chair". Taipei Times. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (6 May 2021). "KMT sets election date for chairperson, delegates". Taipei Times. Retrieved 6 May 2021.
- ^ Wang, Flor; Liu, Kuan-ting (7 May 2021). "KMT chair election slated for July 24". Central News Agency. Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (27 May 2021). "KMT says chairperson election suspended". Taipei Times. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (28 July 2021). "Chiang denies plans to run for Taoyuan mayor". Taipei Times. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (29 July 2021). "KMT to increase campaign activity to gain support for referendum questions". Taipei Times. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ^ Wang, Cheng-chung; Kao, Evelyn (16 August 2021). "Eric Chu registers for KMT chairmanship election". Central News Agency. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (17 August 2021). "Chu outlines priorities if elected KMT chair". Taipei Times. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- ^ Liu, Kuan-ting; Teng, Pei-ju (17 August 2021). "Incumbent Johnny Chiang registers for KMT chairmanship election". Central News Agency. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (18 August 2021). "Chiang registers for race". Taipei Times. Retrieved 18 August 2021.
- ^ Liu, Kuan-ting; Mazzetta, Matthew; Teng, Pei-ju (11 August 2021). "KMT leader pitches for advisory committee on cross-strait policy". Central News Agency. Retrieved 25 August 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (25 August 2021). "Ma 'ideal' to push cross-strait exchanges: Chiang". Taipei Times. Retrieved 25 August 2021.
- ^ Shih, Hsiao-kuan; Chen, Yun; Chin, Jonathan (3 September 2021). "KMT decries president's use of 'neighbors' in speech". Taipei Times. Retrieved 3 September 2021.
- ^ Lai, Yu-chen; Chung, Yu-chen; Liu, Kay (4 September 2021). "Relationship with China major topic in KMT chair election debate". Central News Agency. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
- ^ Shih, Hsiao-kuang; Chen, Yun; Chung, Jake (5 September 2021). "Aspirant KMT chairs share policies". Taipei Times. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ Pan, Jason (5 September 2021). "Independence advocates protest KMT 'collaborators'". Taipei Times. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (16 September 2021). "KMT committee rescinds decision to refer Chang". Taipei Times. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
- ^ Wang, Cheng-chung; Liu, Kuan-ting; Teng, Pei-ju (18 September 2021). "Eric Chu, Chang Ya-chung exchange fire over China at KMT debate". Central News Agency. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
- ^ Shih, Hsiao-kuang; Chien, Hui-ju; Chung, Jake (19 September 2021). "KMT chair debate focuses on name, '1992 consensus'". Taipei Times. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ^ Low, Y. F. (25 September 2021). "Voting gets underway for KMT chairman, party representative elections". Central News Agency. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ Hsu, Elizabeth; Teng, Pei-ju (25 September 2021). "Former New Taipei Mayor Eric Chu elected KMT chairman". Central News Agency. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ^ Shih, Hsiao-kuang; Hetherington, William (26 September 2021). "Eric Chu wins race for KMT leadership". Taipei Times. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ^ Teng, Pei-ju (25 September 2021). "Newly elected KMT chief Eric Chu calls for unity, aims to open U.S. office". Central News Agency. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ^ a b Liu, Kaun-ting; Chiu, Kuo-chiang; Liu, Kay (29 September 2021). "Eric Chu to take up KMT chairmanship Oct. 5". Central News Agency. Retrieved 29 September 2021. Republished as: "Eric Chu to take KMT helm next week". Taipei Times. 1 October 2021. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ Wang, Flor; Liu, Kuan-ting (5 October 2021). "Eric Chu stresses unity as he takes over leadership of KMT". Central News Agency. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (6 October 2021). "Chiang hands over reins to Chu". Taipei Times. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ Liu, Kuan-ting; Yeh, Su-ping; Kao, Evelyn (26 September 2021). "KMT Chairman-elect Eric Chu reiterates 1992 consensus for ties with China". Central News Agency. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ^ Hsiao, Sherry (27 September 2021). "Chu hopes the KMT, CCP will seek common ground". Taipei Times. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ Chen, Yu-fu; Yang, Chun-hui; Madjar, Kayleigh (27 September 2021). "Pandering to Beijing will make KMT target for 'united front,' MAC tells Chu". Taipei Times. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ "獨家》國民黨主席選舉豬羊變色 最新民調張亞中支持度躍居第一" (in Traditional Chinese). The Storm Media. 16 September 2021. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ "【藍營基層恐慌】黨魁選戰民調大翻盤 張亞中擠下朱立倫、江啟臣躍上第1" (in Traditional Chinese). Up Media. 16 September 2021. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ^ "【完整民調】張亞中28.4%緊咬朱立倫29.3% 江啟臣慘輸10趴遭狠甩" (in Traditional Chinese). Up Media. 24 September 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ "公告110年本黨主席選舉當選名單" (in Chinese). Kuomintang. Retrieved 30 September 2021.
 KSF
KSF



