Alderney Airport
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 11 min
Alderney Airport | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | States of Guernsey | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Alderney | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | St Anne | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 290 ft / 88 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 49°42′24″N 002°12′52″W / 49.70667°N 2.21444°W | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | alderney | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2022) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Alderney Airport (IATA: ACI, ICAO: EGJA) is the only airport on the island of Alderney, Guernsey. Built in 1935, Alderney Airport was the first airport in the Channel Islands. Located on the Blaye (1 NM (1.9 km; 1.2 mi) southwest of St Anne), it is the closest Channel Island airport to the south coast of England and the coast of France. Its facilities include a hangar, the Airport Fire Station, and avgas refuelling.
Alderney Airport is the base and on-record hub of Air Alderney, an airline that, as of 2022, has had problems commencing flights since 2017.
Runways
[edit]Alderney is unique amongst Channel Islands airports in having three operational runways. The main runway, 08/26 is 880 m (2,887 ft) long and is mainly asphalt. The two secondary runways are both grass, 13/31 being 733 m (2,405 ft) long, with 03/21 having a length of 497 m (1,631 ft). The main runway is equipped with low-intensity lighting, with portable lighting being available on runway 13/31. The approach and runway lights were replaced in 2006.
Operations
[edit]The terminal building, erected in 1968, contains an arrivals room and a departure lounge, with a check-in desk for the airport's only scheduled airline, Aurigny.[3] Alderney is not a 24-hour airport; during winter, it is open Monday to Saturday from 0740 until 1830 and on Sunday from 0840 until 1830. During summer, it is open Monday - Thursday from 0740 until 1830 and Friday - Sunday from 0740 until 1920.
The airport also has its own non-directional beacon, with runways 08 and 26 utilizing this for instrument approaches during Instrument meteorological conditions. Both runways also have an approved GPS (satellite) approach.[4] This means that aircraft can land in lower visibility.
Alderney has self-manoeuvring stands. Formal stands are not required due to the lack of space to accommodate nose-in-configured aircraft.
Airline and destinations
[edit]| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aurigny | Guernsey, Southampton |
Currently the only direct scheduled links from the island are Southampton and Guernsey. Routes to other destinations such as Brighton, Bournemouth, Cherbourg, Exeter, Plymouth and Jersey were abandoned over the years due to what Blue Islands, for example, claimed was 'lack of interest'. These routes had been operated on and off by Aurigny and Blue Islands but also Alderney Air Ferries, Air Sarnia, and Air Camelot during the 1970s and 1980s. The number of air routes to the island is at its lowest since the Second World War except for a brief intermission during the 1967-8 period, when another airline (Glos Air, later to be Aurigny Air Services) was found to fill the void (see below right).[citation needed]
From September 2013, airline Aurigny operated direct flights to Jersey on a trial basis for a period of six weeks.[5]
In April 2015, it was announced that the States of Alderney had asked airline Citywing to operate a seasonal Summer service between Alderney and Jersey using Let L-410 aircraft.[6] However this service has not materialised.[citation needed]
In January 2017, a new airline Air Alderney was set up with the intention of commencing direct flights using Britten-Norman Islander aircraft from Alderney to destinations including Jersey, Cherbourg, Lee-on–Solent, and Brighton. Despite considerable progress being made in acquiring aircraft and obtaining an Air Operator's Certificate, to date operations have not yet commenced due to complications regarding ground operations at the intended destination airports.[citation needed]
Future
[edit]The States of Alderney put aside £400,000 from the £1m paid for a £12 million expansion of the airport proposed in 2019. This was to be used to pay for redevelopment of the terminal, which is over 50 years old. During the 2020 covid lockdown, while aircraft movements were low, airport staff refurbished the buildings, including repairs to a leaky flat roof on the 1960s terminal, and patch repaired the runway.[7][8]
The runway was previously resurfaced in 1999 with a surface material having a design life of between 12 and 15 years. A major patch and repair was undertaken on the eastern end of the runway in the Autumn of 2016, to provide a short term improvement, but by 2018 it was reported that major work would soon be required for continued safe operations. In 2020 the runway was patched and repaired during covid lockdown by airport staff.[7][9]
On the 4th of July 2022 the States of Alderney backed plans to extend the runway from 2,877 ft (877m) to about 3,444 ft (1,050m) so that larger aircraft such as the ATR 72 plane can serve the island giving an additional 20,000 seats per year to help tourism. The terminal building and fire station would also be improved as part of the scheme. Aurigny Air Services Ltd also stated that the expansion would reduce their operating costs as they could remove the Dornier 228 from their fleet.[10]
In December 2022 the States of Guernsey agreed to spend £24m on extending, widening and strengthening the runway, construction of a new terminal building and refurbishment of the fire service facilities. £3.5 million will be contributed towards the costs by the States of Alderney.[11][12]
It was reported in January 2023 that land acquisition to allow the runway extension and repositioning of the track to the west had already started. It was also reported that tenders would be issued in the next few months, but work to secure Civil Aviation Authority and European Union Aviation Safety Agency approval for designs for the work would be needed, before issuing construction tenders. However, it is expected that Work will begin in 2024 and will be completed in the second quarter of 2025.[13] Plans were approved in May 2024.[14]
Statistics
[edit]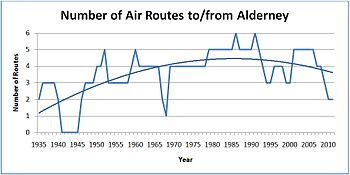
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
| Year | Passenger Numbers |
Year | Passenger Numbers |
Year | Passenger Numbers |
Year | Passenger Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 102,649 | 1999 | 77,198 | 2009 | 74,835 | 2019 | 50,562 [17] |
| 1990 | 105,458 | 2000 | 75,199 | 2010 | 70,012 | 2020 | 27,211 |
| 1991 | 80,684 | 2001 | 72,111 | 2011 | 69,546 | 2021 | 42,261 |
| 1992 | 78,365 | 2002 | 72,861 | 2012 | 64,165 | 2022 | 51,646 [18] |
| 1993 | 77,313 | 2003 | 72,248 | 2013 | 62,855 | ||
| 1994 | 83,681 | 2004 | 74,292 | 2014 | 61,317 | ||
| 1995 | 84,834 | 2005 | 76,205 | 2015 | 59,843 | ||
| 1996 | 84,012 | 2006 | 76,806 | 2016 | 57,595 | ||
| 1997 | 81,048 | 2007 | 79,087 | 2017 | 54,760 | ||
| 1998 | 73,099 | 2008 | 77,104 | 2018 | 53,343 |
References
[edit]- ^ "Alderney - EGJA". Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 9 December 2008.
- ^ "UK airport data 2020: Tables 3, 9 and 13.pdf". UK Civil Aviation Authority. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- ^ Alderney Airport website (see external links)
- ^ Jeppesen Airport Charts
- ^ "BBC News: Alderney to Jersey air route back in new trial". 27 July 2013.
- ^ "BBC News: Citywing airline asked to run Alderney-Jersey route". 16 April 2015.
- ^ a b Annual Report 2020 Guernsey and Alderney Airports (PDF) (Report). 31 August 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ Pinnegar, Edward (2010). A History of Aviation in Alderney. Stroud: Amberley Publishing. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-84868-981-7.
- ^ Ferbrache (President STSB), P T R; Smithies (Vice President STSB), J C S F; Kuttelwascher (Member STSB), J; Falla (MBE Non-States Member STSB), S J; Hollis (Non-States Member STSB), J C (19 November 2018). "3.6". THE STATES OF DELIBERATION of the ISLAND OF GUERNSEY: STATES TRADING SUPERVISORY BOARD: ALDERNEY AIRPORT RUNWAY REHABILITATION (Report). p. 6. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ "Alderney runway expansion plans could be scaled back". 16 November 2022. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ Simon De La Rue (16 December 2022). "States agrees to redevelop Alderney Airport at cost of £24m". Guernsey Press. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ "Alderney's £24 million runway extension and new terminal building approved". Retrieved 16 December 2022.
- ^ "Alderney airport and runway tenders 'issued in the next few months'". GuernseyPress. 3 January 2023. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ "Major £24 million plans to extend runway and upgrade terminal at Alderney Airport approved". ITV News Channel. 30 May 2024. Retrieved 30 May 2024.
- ^ "Alderney Airport Master Plan". States of Guernsey. Archived from the original on 4 October 2006. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ "United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority". Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- ^ "Annual Report 2019" (PDF). Guernsey Airport.
- ^ "Annual Report 2022" (PDF). 22 September 2023.
Further reading
[edit]- Pinnegar, Edward (5 August 2010). A History of Aviation in Alderney. Amberley Publishing, Stroud. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-84868-981-7.
External links
[edit] Media related to Alderney Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Alderney Airport at Wikimedia Commons- Official website
- Live Alderney Arrivals / Departures (provided by FlightStats)
- NATS AIS (NATS Aeronautical Information Service)
 KSF
KSF