Calone
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 3 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 3 min
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
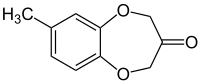
7-Methyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,5-benzodioxepin-3-one | |
| Other names
Calone 1951; Watermelon ketone; Methylbenzodioxepinone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.823 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 178.187 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystals, flakes or clumps |
| Odor | distinctive |
| Melting point | 35–41 °C (95–106 °F; 308–314 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calone or methylbenzodioxepinone, trade-named Calone 1951, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OCH2)2CO. A white solid, it is a derivative of 4-methylcatechol. In the fragrance industry it is known as "watermelon ketone".[1]
It was discovered by Pfizer in 1966. It is used to give the olfactory impression of a fresh seashore through the marine and ozone nuances. Calone is similar in structure to brown algae pheromones like ectocarpene and is also distantly related in structure to the benzodiazepine class of sedatives.[2]
Calone is an unusual chemical compound which has an intense "sea-breeze" note with slight floral and fruit overtones. It has been used as a scent component since the 1980s for its watery, fresh, ozone accords, and as a more dominant note in several perfumes of the marine trend, beginning in the 1990s. In 2014, Plummer et al. reported the synthesis and fragrance properties of several related aliphatic analogues.[3] Swiss company Firmenich later released CASCALONE®, a sweet, watery version of calone with a transparent floral signature.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Panten, Johannes; Surburg, Horst (2016). "Flavors and Fragrances, 3. Aromatic and Heterocyclic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. pp. 1–45. doi:10.1002/14356007.t11_t02. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- ^ Yudov, Matvey. "Calone: The Air of the 1990s ~ Raw Materials ~ Fragrantica". fragrantica.com. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- ^ C. M. Plummer, R. Gericke, P. Kraft, A. Raynor, J. Froese, T. Hudlicky, T. J. Rook, O. A. H. Jones and H. M. Hϋgel (4 December 2014). "Synthesis of Saturated Benzodioxepinone Analogues: Insight into the Importance of the Aromatic Ring Binding Motif for Marine Odorants". Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015 (3): 486–495. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201403142.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "CASCALONE®". www.firmenich.com. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
 KSF
KSF