Caribbean
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 49 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 49 min
 Map of the Caribbean region of the Americas | |
| Area | 239,681 km2 (92,541 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 44,182,048[1][2] |
| Population density | 151.5/km2 (392/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Afro-Caribbean Latin-Caribbean Indo-Caribbean White-Caribbean Mixed-Caribbean Asian-Caribbean Indigenous |
| Religions |
|
| Demonym | Caribbean, West Indian |
| Countries | |
| Dependencies | List |
| Languages | |
| Time zones | UTC−05:00 to UTC−04:00 |
| Internet TLD | Multiple |
| Calling code | Multiple |
| Largest cities | |
| UN M49 code | 029 – Caribbean419 – Latin America and the Caribbean019 – Americas001 – World |
The Caribbean[a] is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks.
It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo islands and Belizean islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the continental mainland of the Americas bordering the region from the Yucatán Peninsula in North America through Central America to the Guianas in South America.[5][6]
Overview
[edit]
Situated largely on the Caribbean plate, the region has thousands of islands, islets, reefs, and cays.[7] Island arcs delineate the northern and eastern edges of the Caribbean Sea:[7] the Greater Antilles in the north and the Lesser Antilles, which includes the Leeward Islands, Windward Islands, and the Leeward Antilles, to the east and south. The nearby northwestern Lucayan Archipelago, comprising The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, and the island of Barbados in the Lesser Antilles, are considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. All the islands in the Antilles, including the Lucayan Archipelago, form the West Indies, a term often interchangeable with the Caribbean. The archipelago of Bermuda is not part of the Caribbean, as it lies in the Sargasso Sea to the north, but it is an associate member of the Caribbean Community.[8][9]

On the continental mainland of the Americas, the Caribbean coasts of Mexico, Central America, and South America, including the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, Bay Islands Department of Honduras, the Mosquitia region, Cartagena and Barranquilla in Colombia, Maracaibo and Cumaná in Venezuela, are considered part of the Caribbean.[10] As with the coastal areas of the mainland, Belize, Panama, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana are often completely included within the Caribbean due to their strong political and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America, or regarded as its own subregion as the Caribbean.[11][12] The Caribbean is sometimes considered alongside Latin America as a region.[13]

Generally, the Caribbean region is organized into 33 political entities, including 13 sovereign states, 12 dependencies, 7 overseas territories, and various disputed territories. From 15 December 1954 to 10 October 2010, there was a territory known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five islands, all of which were Dutch dependencies.[14] From 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the British West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies.
The modern Caribbean is one of the most ethnically diverse regions on the planet, as a result of colonization by the Spanish, English, Dutch, and French; the Atlantic slave trade from Sub-Saharan Africa; indentured servitude from the Indian subcontinent and Asia; as well as modern immigration from around the world.
Etymology and pronunciation
[edit]The region takes its name from the Caribs, an indigenous ethnic group present in the Lesser Antilles and parts of adjacent South America at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Americas.[15]
The two most prevalent pronunciations of "Caribbean" outside the Caribbean are /ˌkærɪˈbiːən/ (KARR-ə-BEE-ən), with the primary stress on the third syllable, and /kəˈrɪbiən/ (kə-RIB-ee-ən), with the stress on the second. Most authorities of the last century preferred the stress on the third syllable.[16] This is the older of the two pronunciations, but the stressed-second-syllable variant has been established for over 75 years.[17][when?] It has been suggested that speakers of British English prefer /ˌkærɪˈbiːən/ (KARR-ə-BEE-ən) while North American speakers more typically use /kəˈrɪbiən/ (kə-RIB-ee-ən),[18] but major American dictionaries and other sources list the stress on the third syllable as more common in American English too.[19][20][21][22] According to the American version of Oxford Online Dictionaries, the stress on the second syllable is becoming more common in UK English and is increasingly considered "by some" to be more up to date and more "correct".[23]
The Oxford Online Dictionaries claim the stress on the second syllable is the most common pronunciation in the Caribbean itself, but according to the Dictionary of Caribbean English Usage, the most common pronunciation in Caribbean English stresses the first syllable instead, /ˈkærɪbiæn/ (KARR-ih-bee-an).[4][23]
Definition
[edit]
The word Caribbean has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to Africa, slavery, European colonisation and the plantation system.
- The United Nations geoscheme for the Americas presents the Caribbean as a distinct region within the Americas.
- Physiographically, the Caribbean region is mainly a chain of islands surrounding the Caribbean Sea. To the north, the region is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico, the Straits of Florida and the Northern Atlantic Ocean, which lies to the east and northeast. To the south lies the coastline of the continent of South America.
History
[edit]
The oldest evidence of humans in the Caribbean is in southern Trinidad at Banwari Trace, where remains have been found from 7,000 years ago. These pre-ceramic sites, which belong to the Archaic (pre-ceramic) age, have been termed Ortoiroid. The earliest archaeological evidence of human settlement in Hispaniola dates to about 3600 BC, but the reliability of these finds is questioned. Consistent dates of 3100 BC appear in Cuba. The earliest dates in the Lesser Antilles are from 2000 BC in Antigua. A lack of pre-ceramic sites in the Windward Islands and differences in technology suggest that these Archaic settlers may have Central American origins. Whether an Ortoiroid colonization of the islands took place is uncertain, but there is little evidence of one.
DNA studies changed some of the traditional beliefs about pre-Columbian indigenous history. According to National Geographic, "studies confirm that a wave of pottery-making farmers—known as Ceramic Age people—set out in canoes from the northeastern coast of South America starting some 2,500 years ago and island-hopped across the Caribbean. They were not, however, the first colonizers. On many islands they encountered a foraging people who arrived some 6,000 or 7,000 years ago ... The ceramicists, who are related to today's Arawak-speaking peoples, supplanted the earlier foraging inhabitants—presumably through disease or violence—as they settled new islands."[24]
Between 400 BC and 200 BC, the first ceramic-using agriculturalists, the Saladoid culture, entered Trinidad from South America. They expanded up the Orinoco River to Trinidad, and then spread rapidly up the islands of the Caribbean. Some time after 250 AD another group, the Barancoid, entered Trinidad. The Barancoid society collapsed along the Orinoco around 650 AD and another group, the Arauquinoid, expanded into these areas and up the Caribbean chain. Around 1300 AD a new group, the Mayoid, entered Trinidad and remained the dominant culture until Spanish settlement.
At the time of the European discovery of most of the islands of the Caribbean, three major Amerindian indigenous peoples lived on the islands: the Taíno in the Greater Antilles, the Bahamas and the Leeward Islands; the Island Caribs and Galibi in the Windward Islands; and the Ciboney in western Cuba. The Taínos are subdivided into Classic Taínos, who occupied Puerto Rico and part of Hispaniola; Western Taínos, who occupied the Bahamian archipelago, Cuba, Jamaica, and part of Hispaniola; and the Eastern Taínos, who occupied the northern Lesser Antilles. The southern Lesser Antilles, including Martinique and Trinidad, were inhabited by both Carib-speaking and Arawak-speaking groups.
European contact
[edit]Soon after Christopher Columbus came to the Caribbean including Hispaniola and Martinica, both Portuguese and Spanish explorers began claiming territories in Central and South America. These early colonies brought gold to Europe; most specifically England, the Netherlands, and France. These nations hoped to establish profitable colonies in the Caribbean. Colonial rivalries made the Caribbean a cockpit for European wars for centuries.
Columbus, and the early colonists of Hispaniola, treated the indigenous peoples brutally, even enslaving children.[25] In 1512, after pressure from Dominican friars, the Laws of Burgos were introduced by the Spanish Crown to better protect the rights of the New World natives. The Spanish used a form of slavery called the Encomienda, where slaves would be awarded to the conquistadors, who were charged with protecting and converting their slaves. This had a devastating impact on the population,[26] so starting in 1503, slaves from Africa were imported to the colony. Jamaica was ceded to England by Spain while both Martinica and the western third of Hispaniola were ceded to France.
While early slave traders were Portuguese and Spanish, known as the First Atlantic System, by the 17th century the trade became dominated by British, French, and Dutch merchants. This was known as the Second Atlantic System. 5 million African slaves would be taken to the Caribbean, and around half would be traded to the British Caribbean islands. Slavery was abolished first in the Dutch Empire in 1814. Spain abolished slavery in its empire in 1811, with the exceptions of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Santo Domingo. Slavery was not abolished in Cuba until 1886.[27] Britain abolished the slave trade in 1807, and slavery proper in 1833. France abolished slavery in its colonies in 1848.

The Caribbean was known for pirates, especially between 1640 and 1680. The term "buccaneer" is often used to describe a pirate operating in this region. The Caribbean region was war-torn throughout much of its colonial history, but the wars were often based in Europe, with only minor battles fought in the Caribbean. Some wars, however, were born of political turmoil in the Caribbean itself.
In 1791, a slave rebellion in the French colony of Saint-Domingue led to the establishment in 1804 of Haiti, the first republic in the Caribbean. Neighboring Santo Domingo (now Dominican Republic) would attain its independence on three separate occasions in 1821, 1844 and 1865. Cuba became independent in 1898 following American intervention in the War of Independence during the Spanish-American war. Following the war, Spain's last colony in the Americas, Puerto Rico, became an unincorporated territory of the United States.
Decolonisation and modern period
[edit]Between the 1960s and '80s, most of the British holdings in the Caribbean achieved political independence, starting with Jamaica in 1962, then Trinidad and Tobago (1962), British Guiana (1966), Barbados (1966), the Bahamas (1973), Grenada (1974), Dominica (1978), St. Lucia (1979), St. Vincent (1979), Antigua and Barbuda (1981), and St. Kitts and Nevis (1983). Presently, the United States, Britain, France and the Netherlands still have some Caribbean possessions.
The decline of the export industries meant a need to diversify the economies of the Caribbean territories. The tourism industry started developing in the early 20th century, rapidly developing in the 1960s when regular international flights made vacations affordable and is now a $50 billion industry. Another industry that developed in the early 20th century was offshore banking and financial services, particularly in The Bahamas and the Cayman Islands, as the proximity of the Caribbean islands to North America made them an attractive location for branches of foreign banks seeking to avail themselves of less complicated regulations and lower tax rates.
US interventions
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (November 2024) |
The United States has conducted military operations in the Caribbean for at least 100 years.[28]
Since the Monroe Doctrine, the United States gained a major influence on most Caribbean nations. In the early part of the 20th century this influence was extended by participation in the Banana Wars. Victory in the Spanish–American War and the signing of the Platt Amendment in 1901 ensured that the United States would have the right to interfere in Cuban political and economic affairs, militarily if necessary. After the Cuban Revolution of 1959, relations deteriorated rapidly leading to the Bay of Pigs Invasion, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and successive US attempts to destabilize the island, based upon Cold War fears of the Soviet threat. The US invaded and occupied Hispaniola for 19 years (1915–34), subsequently dominating the Haitian economy through aid and loan repayments. The US invaded Haiti again in 1994. After the 2004 Haitian coup d'état, the US were accused by CARICOM of arranging it to remove elected Haitian leader Jean-Bertrand Aristide. In 1965, 23,000 US troops were sent to the Dominican Republic to quash a local uprising against military rule (see Dominican Civil War). President Lyndon Johnson had ordered the invasion to stem what he deemed to be a "Communist threat". However, the mission appeared ambiguous and was roundly condemned throughout the hemisphere as a return to gunboat diplomacy. In 1983, the US invaded Grenada to remove populist left-wing leader Maurice Bishop. The US maintains a naval military base in Cuba at Guantanamo Bay. The base is one of five unified commands whose "area of responsibility" is Latin America and the Caribbean. The command is headquartered in Miami, Florida.
-
Counter-attack by Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces supported by T-34 tanks near Playa Giron during the Bay of Pigs Invasion, 19 April 1961.
-
A Marine heavy machine gunner monitors a position along the international neutral corridor in Santo Domingo, 1965.
-
A Soviet-made BTR-60 armored personnel carrier seized by US forces during Operation Urgent Fury (1983)
-
US Army Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk, Bell AH-1 Cobra and Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopters on deck of the US Navy aircraft carrier USS Dwight D. Eisenhower off Haiti, 1994.
Geography
[edit]
The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (which has minor volcanic features), Curaçao, Barbados, Bonaire, the Cayman Islands, Saint Croix, the Bahamas, and Antigua. Others possess rugged towering mountain-ranges like the islands of Saint Martin, Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, Dominica, Montserrat, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Saint Kitts, Saint Lucia, Saint Thomas, Saint John, Tortola, Grenada, Saint Vincent, Guadeloupe, Martinique and Trinidad and Tobago.
Definitions of the terms Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles often vary. As part of the Puerto Rico Bank and the Puerto Rico-Virgin Islands microplate, the Virgin Islands are sometimes included with the Greater Antilles. The term Lesser Antilles is often used to define an island arc that includes Grenada but excludes Trinidad and Tobago and the Leeward Antilles.

The waters of the Caribbean Sea host large, migratory schools of fish, turtles, and coral reef formations. The Puerto Rico Trench, located on the fringe of the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea just to the north of the island of Puerto Rico, is the deepest point in all of the Atlantic Ocean.[31]
The region sits in the line of several major shipping routes with the Panama Canal connecting the western Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean.
Climate
[edit]

The climate of the area is tropical, varying from tropical rainforest in some areas to tropical monsoon and tropical savanna in others. There are also some locations that are arid climates with considerable drought in some years, and the peaks of mountains tend to have cooler temperate climates.
Rainfall varies with elevation, size and water currents, such as the cool upwellings that keep the ABC islands arid. Warm, moist trade winds blow consistently from the east, creating both rain forest and semi arid climates across the region. The tropical rainforest climates include lowland areas near the Caribbean Sea from Costa Rica north to Belize, as well as the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico, while the more seasonal dry tropical savanna climates are found in Cuba, northern Colombia and Venezuela, and southern Yucatán, Mexico. Arid climates are found along the extreme northern coast of Venezuela out to the islands including Aruba and Curaçao, as well as the northwestern tip of Yucatán.
While the region generally is sunny much of the year, the wet season from May through November sees more frequent cloud cover (both broken and overcast), while the dry season from December through April is more often clear to mostly sunny. Seasonal rainfall is divided into 'dry' and 'wet' seasons, with the latter six months of the year being wetter than the first half. The air temperature is hot much of the year, varying from 25 to 33 C (77 F to 90 F) between the wet and dry seasons. Seasonally, monthly mean temperatures vary from only about 5 C (7 F) in the northern most regions, to less than 3 C in the southernmost areas of the Caribbean.
Hurricane season is from June to November, but they occur more frequently in August and September and more common in the northern islands of the Caribbean. Hurricanes that sometimes batter the region usually strike northwards of Grenada and to the west of Barbados. The principal hurricane belt arcs to northwest of the island of Barbados in the Eastern Caribbean. A great example being recent events of Hurricane Irma devastating the island of Saint Martin during the 2017 hurricane season.
Sea surface temperatures change little annually, normally running from 30 °C (87 °F) in the warmest months to 26 °C (76 °F) in the coolest months. The air temperature is warm year round, in the 70s, 80s and 90s, and only varies from winter to summer about 2–5 degrees on the southern islands and about a 10–20 degrees difference on the northern islands of the Caribbean. The northern islands, like the Bahamas, Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, may be influenced by continental masses during winter months, such as cold fronts.
Aruba: Latitude 12°N
| Climate data for Oranjestad, Aruba (1981–2010, extremes 1951–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
33.0 (91.4) |
33.9 (93.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.9 (94.8) |
35.2 (95.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
36.1 (97.0) |
36.5 (97.7) |
35.4 (95.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
34.8 (94.6) |
36.5 (97.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.0 (86.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
31.5 (88.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.7 (80.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.7 (83.7) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.1 (84.4) |
29.2 (84.6) |
28.7 (83.7) |
28.1 (82.6) |
27.2 (81.0) |
28.1 (82.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24.5 (76.1) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.9 (78.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 21.3 (70.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.8 (71.2) |
22.7 (72.9) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39.3 (1.55) |
20.6 (0.81) |
8.7 (0.34) |
11.6 (0.46) |
16.3 (0.64) |
18.7 (0.74) |
31.7 (1.25) |
25.8 (1.02) |
45.5 (1.79) |
77.8 (3.06) |
94.0 (3.70) |
81.8 (3.22) |
471.8 (18.58) |
| Source: DEPARTAMENTO METEOROLOGICO ARUBA,[32] (extremes)[33] | |||||||||||||
Puerto Rico: Latitude 18°N
| Climate data for San Juan, Puerto Rico | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33 (92) |
36 (96) |
36 (96) |
36 (97) |
36 (96) |
36 (97) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
36 (97) |
36 (97) |
37 (98) |
36 (96) |
34 (94) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 28 (83) |
29 (84) |
29 (85) |
30 (86) |
31 (87) |
32 (89) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
32 (89) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
23 (74) |
24 (76) |
26 (78) |
26 (78) |
26 (78) |
26 (78) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 16 (61) |
17 (62) |
16 (60) |
18 (64) |
18 (64) |
19 (66) |
21 (69) |
20 (68) |
21 (69) |
19 (67) |
18 (65) |
17 (62) |
16 (61) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 95 (3.7) |
60 (2.4) |
49 (1.9) |
118 (4.6) |
150 (5.9) |
112 (4.4) |
128 (5.0) |
138 (5.4) |
146 (5.7) |
142 (5.6) |
161 (6.3) |
126 (5.0) |
1,431 (56.3) |
| Source: The National Weather Service[34] | |||||||||||||
Cuba: at Latitude 22°N
| Climate data for Havana | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
33.0 (91.4) |
35.9 (96.6) |
36.4 (97.5) |
36.9 (98.4) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.0 (100.4) |
36.1 (97.0) |
37.5 (99.5) |
35.4 (95.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
34.8 (94.6) |
38.0 (100.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.8 (78.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.5 (86.9) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
29.2 (84.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 22.2 (72.0) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.1 (79.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
25.2 (77.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.0 (73.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 5.1 (41.2) |
5.6 (42.1) |
5.4 (41.7) |
11.5 (52.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
18.2 (64.8) |
19.3 (66.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 64.4 (2.54) |
68.6 (2.70) |
46.2 (1.82) |
53.7 (2.11) |
98.0 (3.86) |
182.3 (7.18) |
105.6 (4.16) |
99.6 (3.92) |
144.4 (5.69) |
180.5 (7.11) |
88.3 (3.48) |
57.6 (2.27) |
1,189.2 (46.84) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organisation (UN),[35] Climate-Charts.com[36] | |||||||||||||





Island groups
[edit] The Bahamas
The Bahamas Turks and Caicos Islands (United Kingdom)
Turks and Caicos Islands (United Kingdom)
 Cayman Islands (United Kingdom)
Cayman Islands (United Kingdom) Cuba
Cuba- Hispaniola
 Jamaica
Jamaica Puerto Rico (U.S. Commonwealth)
Puerto Rico (U.S. Commonwealth)
 Navassa Island
Navassa Island
- Leeward Islands
 United States Virgin Islands (U.S.)
United States Virgin Islands (U.S.)
 British Virgin Islands (United Kingdom)
British Virgin Islands (United Kingdom)
 Anguilla (United Kingdom)
Anguilla (United Kingdom) Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
- Saint Martin, politically divided between
 Saint Martin (France)
Saint Martin (France) Sint Maarten (Kingdom of the Netherlands)
Sint Maarten (Kingdom of the Netherlands)
 Saba (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands)
Saba (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands) Sint Eustatius (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands)
Sint Eustatius (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands) Saint Barthélemy (French Antilles, France)
Saint Barthélemy (French Antilles, France) Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 Montserrat (United Kingdom)
Montserrat (United Kingdom) Guadeloupe (French Antilles, France) including
Guadeloupe (French Antilles, France) including
- Windward Islands
- Leeward Antilles
 Aruba (Kingdom of the Netherlands)
Aruba (Kingdom of the Netherlands) Curaçao (Kingdom of the Netherlands)
Curaçao (Kingdom of the Netherlands) Bonaire (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands)
Bonaire (Caribbean Netherlands, Netherlands)
Historical groupings
[edit]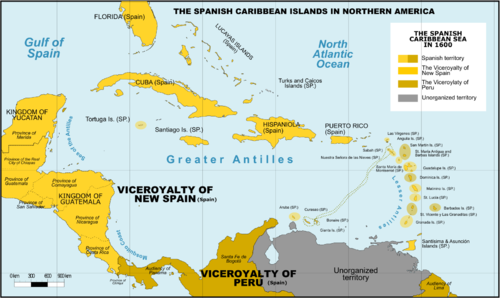



All islands at some point were, and a few still are, colonies of European nations; a few are overseas or dependent territories:
- British West Indies/Anglophone Caribbean – Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Bay Islands, Guyana, Belize, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Croix (briefly), Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago (from 1797) and the Turks and Caicos Islands
- Danish West Indies – Possession of Denmark-Norway before 1814, then Denmark, present-day United States Virgin Islands
- Dutch West Indies – Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten, Bay Islands (briefly), Saint Croix (briefly), Tobago, Surinam and Virgin Islands
- French West Indies – Anguilla (briefly), Antigua and Barbuda (briefly), Dominica, Dominican Republic (briefly), Grenada, Haiti (formerly Saint-Domingue), Montserrat (briefly), Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Sint Eustatius (briefly), Sint Maarten, St. Kitts (briefly), Tobago (briefly), Saint Croix, the current French overseas départements of French Guiana, Martinique and Guadeloupe (including Marie-Galante, La Désirade and Les Saintes), the current French overseas collectivities of Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin
- Portuguese West Indies – present-day Barbados, known as Os Barbados in the 16th century when the Portuguese claimed the island en route to Brazil. The Portuguese left Barbados abandoned years before the British arrived.
- Spanish West Indies – Cuba, Hispaniola (present-day Dominican Republic), Martinica (until 1635 to France), Haiti (until 1659, lost to France), Puerto Rico, Jamaica (until 1655, lost to Great Britain), the Cayman Islands (until 1670 to Great Britain) Trinidad (until 1797, lost to Great Britain) and Bay Islands (until 1643, lost to Great Britain), coastal islands of Central America (except Belize), and some Caribbean coastal islands of Panama, Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela.
- Swedish West Indies – present-day French Saint-Barthélemy, Guadeloupe (briefly) and Tobago (briefly).
- Courlander West Indies – Tobago (until 1691)
The British West Indies were united by the United Kingdom into a West Indies Federation between 1958 and 1962. The independent countries formerly part of the B.W.I. still have a joint cricket team that competes in Test matches, One Day Internationals and Twenty20 Internationals. The West Indian cricket team includes the South American nation of Guyana, the only former British colony on the mainland of that continent.
In addition, these countries share the University of the West Indies as a regional entity. The university consists of three main campuses in Jamaica, Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago, a smaller campus in the Bahamas and Resident Tutors in other contributing territories such as Trinidad.
Continental countries with Caribbean coastlines and islands
[edit] Belize
Belize
 Colombia
Colombia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Guatemala
Guatemala Honduras
Honduras
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Panama
Panama
- Archipelago off Guna Yala coast (including the San Blas Islands)
- Bocas del Toro Archipelago (approximately 300 islands)
- Galeta Island (Panama)
- Isla Grande
- Soledad Miria
 Mexico
Mexico
 Venezuela
Venezuela



Biodiversity
[edit]The Caribbean islands have one of the most diverse eco systems in the world. The animals, fungi and plants, and have been classified as one of Conservation International's biodiversity hotspots because of their exceptionally diverse terrestrial and marine ecosystems, ranging from montane cloud forests, to tropical rainforest, to cactus scrublands. The region also contains about 8% (by surface area) of the world's coral reefs[37] along with extensive seagrass meadows,[38] both of which are frequently found in the shallow marine waters bordering the island and continental coasts of the region.
For the fungi, there is a modern checklist based on nearly 90,000 records derived from specimens in reference collections, published accounts and field observations.[39] That checklist includes more than 11,250 species of fungi recorded from the region. As its authors note, the work is far from exhaustive, and it is likely that the true total number of fungal species already known from the Caribbean is higher. The true total number of fungal species occurring in the Caribbean, including species not yet recorded, is likely far higher given the generally accepted estimate that only about 7% of all fungi worldwide have been discovered.[40] Though the amount of available information is still small, a first effort has been made to estimate the number of fungal species endemic to some Caribbean islands. For Cuba, 2200 species of fungi have been tentatively identified as possible endemics of the island;[41] for Puerto Rico, the number is 789 species;[42] for the Dominican Republic, the number is 699 species;[43] for Trinidad and Tobago, the number is 407 species.[44]
Many of the ecosystems of the Caribbean islands have been devastated by deforestation, pollution, and human encroachment. The arrival of the first humans is correlated with extinction of giant owls and dwarf ground sloths.[45] The hotspot contains dozens of highly threatened animals (ranging from birds, to mammals and reptiles), fungi and plants. Examples of threatened animals include the Puerto Rican amazon, two species of solenodon (giant shrews) in Cuba and the Hispaniola island, and the Cuban crocodile.
The region's coral reefs, which contain about 70 species of hard corals and from 500 to 700 species of reef-associated fishes[46] have undergone rapid decline in ecosystem integrity in recent years, and are considered particularly vulnerable to global warming and ocean acidification.[47] According to a UNEP report, the Caribbean coral reefs might go extinct in next 20 years due to human population explosion along the coast lines, overfishing, the pollution of coastal areas and global warming.[48]
Some Caribbean islands have terrain that Europeans found suitable for cultivation for agriculture. Tobacco was an important early crop during the colonial era, but was eventually overtaken by sugarcane production as the region's staple crop. Sugar was produced from sugarcane for export to Europe. Cuba and Barbados were historically the largest producers of sugar. The tropical plantation system thus came to dominate Caribbean settlement. Other islands were found to have terrain unsuited for agriculture, for example Dominica, which remains heavily forested. The islands in the southern Lesser Antilles, Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao, are extremely arid, making them unsuitable for agriculture. However, they have salt pans that were exploited by the Dutch. Sea water was pumped into shallow ponds, producing coarse salt when the water evaporated.[49]
The natural environmental diversity of the Caribbean islands has led to recent growth in eco-tourism. This type of tourism is growing on islands lacking sandy beaches and dense human populations.[50]
Plants and animals
[edit]-
Epiphytes (bromeliads, climbing palms) in the rainforest of Dominica
-
A green and black poison frog, Dendrobates auratus
-
Costus speciosus, a marsh plant, Guadeloupe
-
An Atlantic ghost crab (Ocypode quadrata) in Martinique
-
Crescentia cujete, or calabash fruit, Martinique
-
Thalassoma bifasciatum (bluehead wrasse fish), over Bispira brunnea (social feather duster worms)
-
Two Stenopus hispidus (banded cleaner shrimp) on a Xestospongia muta (giant barrel sponge)
-
A pair of Cyphoma signatum (fingerprint cowry), off coastal Haiti
-
The Martinique amazon (Amazona martinicana), an extinct species of parrot in the family Psittacidae
-
Anastrepha suspensa, a Caribbean fruit fly
-
Hemidactylus mabouia, a tropical gecko in Dominica
Politics
[edit]Regionalism
[edit]
Caribbean societies are very different from other Western societies in terms of size, culture, and degree of mobility of their citizens.[51] The current economic and political problems the states face individually are common to all Caribbean states.[citation needed] Regional development has contributed to attempts to subdue current problems and avoid projected problems. From a political and economic perspective, regionalism serves to make Caribbean states active participants in current international affairs through collective coalitions. In 1973, the first political regionalism in the Caribbean Basin was created by advances of the English-speaking Caribbean nations through the institution known as the Caribbean Common Market and Community (CARICOM)[52] which is located in Guyana.
Certain scholars have argued both for and against generalizing the political structures of the Caribbean. On the one hand the Caribbean states are politically diverse, ranging from socialist systems towards more capitalist Westminster-style parliamentary systems. Other scholars argue that these differences are superficial, and that they tend to undermine commonalities in the various Caribbean states. Contemporary Caribbean systems seem to reflect a "blending of traditional and modern patterns, yielding hybrid systems that exhibit significant structural variations and divergent constitutional traditions yet ultimately appear to function in similar ways".[53] The political systems of the Caribbean states share similar practices.
The influence of regionalism in the Caribbean is often marginalized.[citation needed] Some scholars believe that regionalism cannot exist in the Caribbean because each small state is unique. On the other hand, scholars also suggest that there are commonalities amongst the Caribbean nations that suggest regionalism exists. "Proximity as well as historical ties among the Caribbean nations has led to cooperation as well as a desire for collective action".[54] These attempts at regionalization reflect the nations' desires to compete in the international economic system.[54]
Furthermore, a lack of interest from other major states promoted regionalism in the region. In recent years, the Caribbean has suffered from a lack of U.S. interest. "With the end of the Cold War, U.S. security and economic interests have been focused on other areas. As a result there has been a significant reduction in U.S. aid and investment to the Caribbean."[55] The lack of international support for these small, relatively poor states, helped regionalism prosper.
Following the Cold War another issue of importance in the Caribbean has been the reduced economic growth of some Caribbean States due to the United States and European Union's allegations of special treatment toward the region by each other. [clarification needed]
United States–European Union trade dispute
[edit]The Lomé Convention, which allowed banana exports from the former colonies of the Group of African, Caribbean and Pacific states (ACP) to enter Europe cheaply, came into effect in 1976.[56] In 1999, the United States under President Bill Clinton launched a challenge in the World Trade Organization against the European Union over Europe's preferential program, known as The World Trade Organization sided in the United States' favour and the beneficial elements of the convention to African, Caribbean and Pacific states have been partially dismantled and replaced by the Cotonou Agreement.[57]
During the US/EU dispute, the United States threatened to impose large tariffs on European Union goods (up to 100%) to pressure Europe to change the agreement with the Caribbean nations in favour of the Cotonou Agreement.[58]
Farmers in the Caribbean have complained of falling profits and rising costs as the Lomé Convention weakens.[59] Some farmers have faced increased pressure to turn towards the cultivation of illegal drugs, which has a higher profit margin and fills the sizable demand for these illegal drugs in North America and Europe.[60][61]
African Union relations
[edit]Many Caribbean nations have sought to deepen ties with the continent of Africa. The African Union-bloc has referred to the Caribbean as the potential "Sixth Region" of the African Union.[62] Some Caribbean states have already moved to join Africa institutions including Barbados, Grenada, Guyana, and the Bahamas which have all become members of the African Export Import Bank.[63] And the Caribbean Development Bank signing a cooperation strategic partnership agreement with the African Development Bank (AfDB)[64] At present Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Jamaica, Guyana, and Suriname are at various stages of establishing direct air flights with Africa to boost person-to-person links and boost trade between both regions.
The first inter-regional Africa-Caribbean Community (CARICOM) Summit took place in September 2021. In August 2023 the African Union's African Export–Import Bank officially opened its first Caribbean Community office in Barbados beginning the process of integrating willing Caribbean states as the 6th region of the African Union.[1][2]
Caribbean Financial Action Task Force and Association of Caribbean States
[edit]Caribbean nations have also started to more closely cooperate in the Caribbean Financial Action Task Force and other instruments to add oversight of the offshore industry. One of the most important associations that deal with regionalism amongst the nations of the Caribbean Basin has been the Association of Caribbean States (ACS). Proposed by CARICOM in 1992, the ACS soon won the support of the other countries of the region. It was founded in July 1994. The ACS maintains regionalism within the Caribbean on issues unique to the Caribbean Basin. Through coalition building, like the ACS and CARICOM, regionalism has become an undeniable part of the politics and economics of the Caribbean. The successes of region-building initiatives are still debated by scholars, yet regionalism remains prevalent throughout the Caribbean.
Bolivarian Alliance
[edit]The President of Venezuela, Hugo Chavez launched an economic group called the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA), which several eastern Caribbean islands joined.
List of countries and territories
[edit]Demographics
[edit]Life expectancy
[edit]Life expectancy in some countries of the Caribbean in 2023, according to estimation of the World Bank Group:[73][74][75]
| Countries and territories |
2023 | Historical data | recovery from COVID-19: 2019→2023 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Male | Female | Sex gap | 2014 | 2014 →2019 |
2019 | 2019 →2020 |
2020 | 2020 →2021 |
2021 | 2021 →2022 |
2022 | 2022 →2023 |
2023 | ||
| 81.69 | 78.03 | 85.24 | 7.21 | 80.04 | 1.40 | 81.44 | −1.43 | 80.01 | −0.24 | 79.77 | −0.34 | 79.43 | 2.26 | 81.69 | 0.25 | |
| 80.52 | 77.30 | 83.90 | 6.60 | 78.87 | 0.80 | 79.67 | 0.15 | 79.82 | 0.25 | 80.07 | 0.25 | 80.32 | 0.20 | 80.52 | 0.85 | |
| 80.36 | 77.98 | 82.87 | 4.89 | 77.86 | 1.19 | 79.05 | 0.18 | 79.23 | 0.07 | 79.30 | 0.68 | 79.98 | 0.37 | 80.36 | 1.31 | |
| 80.22 | 76.77 | 83.84 | 7.07 | 79.73 | 0.35 | 80.08 | 0.01 | 80.08 | 0.12 | 80.21 | 0.03 | 80.24 | −0.01 | 80.22 | 0.15 | |
| 78.08 | 75.67 | 80.52 | 4.85 | 77.83 | −0.41 | 77.41 | −0.01 | 77.41 | −4.21 | 73.20 | 4.43 | 77.63 | 0.46 | 78.08 | 0.67 | |
| 78.01 | 75.83 | 80.30 | 4.47 | 77.21 | 0.48 | 77.69 | −0.19 | 77.50 | −0.27 | 77.23 | 0.68 | 77.92 | 0.09 | 78.01 | 0.32 | |
| 77.60 | 74.55 | 80.29 | 5.74 | 76.91 | 0.26 | 77.17 | −0.01 | 77.16 | 0.04 | 77.20 | 0.29 | 77.48 | 0.11 | 77.60 | 0.43 | |
| 77.28 | 74.53 | 80.05 | 5.52 | 76.53 | 0.32 | 76.84 | 0.05 | 76.89 | −1.60 | 75.30 | 1.88 | 77.18 | 0.10 | 77.28 | 0.43 | |
| 76.80 | 72.46 | 80.82 | 8.37 | 76.38 | 0.11 | 76.49 | 0.01 | 76.50 | −0.81 | 75.69 | 1.04 | 76.73 | 0.07 | 76.80 | 0.31 | |
| 76.37 | 73.70 | 79.53 | 5.83 | 75.73 | −0.05 | 75.68 | −0.68 | 75.00 | −0.50 | 74.50 | 1.68 | 76.18 | 0.19 | 76.37 | 0.69 | |
| 76.35 | 73.70 | 78.78 | 5.08 | 75.26 | 0.76 | 76.02 | −0.61 | 75.41 | −1.75 | 73.66 | 2.57 | 76.23 | 0.13 | 76.35 | 0.33 | |
| 76.18 | 73.63 | 78.61 | 4.98 | 75.93 | 0.57 | 76.50 | 0.15 | 76.65 | −0.07 | 76.58 | −0.90 | 75.68 | 0.50 | 76.18 | −0.32 | |
| 75.20 | 72.36 | 78.36 | 5.99 | 75.05 | −0.07 | 74.97 | 0.05 | 75.02 | −0.50 | 74.52 | 0.63 | 75.15 | 0.05 | 75.20 | 0.23 | |
| 74.55 | 70.91 | 78.19 | 7.28 | 74.03 | −2.62 | 71.41 | 1.59 | 72.99 | −2.24 | 70.75 | 3.74 | 74.49 | 0.06 | 74.55 | 3.14 | |
| 73.72 | 70.53 | 76.97 | 6.44 | 73.14 | −0.03 | 73.11 | −0.48 | 72.64 | −0.88 | 71.76 | 2.45 | 74.21 | −0.49 | 73.72 | 0.61 | |
| 73.49 | 70.38 | 76.68 | 6.31 | 72.90 | −0.06 | 72.84 | −0.19 | 72.64 | −1.53 | 71.11 | 2.22 | 73.33 | 0.16 | 73.49 | 0.65 | |
| World | 73.33 | 70.95 | 75.84 | 4.89 | 71.78 | 1.09 | 72.87 | −0.68 | 72.18 | −0.97 | 71.22 | 1.75 | 72.97 | 0.36 | 73.33 | 0.46 |
| Caribbean small states | 73.03 | 69.82 | 76.36 | 6.54 | 71.26 | 0.56 | 71.82 | −0.19 | 71.63 | −2.23 | 69.40 | 3.21 | 72.61 | 0.42 | 73.03 | 1.22 |
| 72.70 | 69.31 | 76.30 | 6.99 | 72.68 | −0.43 | 72.25 | 0.06 | 72.31 | −3.19 | 69.12 | 3.55 | 72.67 | 0.03 | 72.70 | 0.45 | |
| 72.14 | 68.57 | 76.02 | 7.45 | 71.23 | 0.31 | 71.54 | −0.36 | 71.18 | −1.91 | 69.27 | 1.04 | 70.31 | 1.83 | 72.14 | 0.60 | |
| 71.48 | 68.97 | 73.99 | 5.02 | 72.36 | −0.83 | 71.53 | −0.08 | 71.45 | −2.37 | 69.08 | 2.40 | 71.48 | 0.00 | 71.48 | −0.05 | |
| 71.23 | 68.66 | 74.31 | 5.65 | 70.36 | 0.64 | 70.99 | −1.39 | 69.61 | −0.47 | 69.13 | 2.06 | 71.19 | 0.04 | 71.23 | 0.24 | |
| 71.13 | 68.21 | 74.55 | 6.33 | 71.19 | 0.12 | 71.31 | −0.04 | 71.27 | −1.44 | 69.83 | 1.25 | 71.08 | 0.05 | 71.13 | −0.17 | |
| 64.94 | 61.73 | 68.30 | 6.57 | 62.97 | 1.36 | 64.33 | −0.55 | 63.77 | −1.16 | 62.61 | 1.34 | 63.95 | 0.99 | 64.94 | 0.61 | |
Indigenous groups
[edit]



At the time of European contact, the dominant ethnic groups in the Caribbean included the Taíno of the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles, the Island Caribs of the southern Lesser Antilles, and smaller distinct groups such as the Guanajatabey of western Cuba and the Ciguayo of eastern Hispaniola. The population of the Caribbean is estimated to have been around 750,000 immediately before European contact, although lower and higher figures are given. After contact, social disruption and epidemic diseases such as smallpox and measles (to which they had no natural immunity)[76] led to a decline in the Amerindian population.[77][78] such as the Kongo, Igbo, Akan, Fon and Yoruba as well as military prisoners from Ireland, who were deported during the Cromwellian reign in England.[citation needed] Immigrants from Britain, Italy, France, Spain, the Netherlands, Portugal and Denmark also arrived, although the mortality rate was high for both groups.[79]
The population is estimated to have reached 2.2 million by 1800.[80] Immigrants from India, China, Indonesia, and other countries arrived in the mid-19th century as indentured servants.[81] After the ending of the Atlantic slave trade, the population increased naturally.[82] The total regional population was estimated at 37.5 million by 2000.[83]
In Haiti and most of the French, Anglophone and Dutch Caribbean, the population is predominantly of African origin; on many of the islands/nations there are also significant populations of mixed racial origin (including Mulatto-Creole, Dougla, Mestizo, Quadroon, Cholo, Castizo, Criollo, Zambo, Pardo, Asian Latin Americans, Chindian, Cocoa panyols, and Eurasian). On the Cayman Islands, Aruba and Belize mixed-race people form the majority of the population. There are also populations of European ancestry; English, French, Dutch, Italian, Portuguese and Spanish ancestry. Asians, especially those of Chinese, Indian descent, and Javanese Indonesians, form a significant minority in parts of the region. Indians form a plurality of the population in Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, and Suriname. Most of their ancestors arrived in the 19th century as indentured laborers.
The Spanish-speaking Caribbean populations are primarily of European, African, or racially mixed origins. Cuba has a European majority, along with a significant population of African ancestry. Puerto Rico has a mixed race majority with a mixture of European-African-Native American (tri-racial), and a large White and West African (black) minority. The Dominican Republic has the largest mixed-race population, primarily descended from Europeans, West Africans, and Amerindians.

The majority of Jamaica is of West African origin, in addition to a significant population of mixed racial background, and has minorities of Chinese, Europeans, Indians, Latinos, Jews, and Arabs. This is a result of years of importation of slaves and indentured laborers, and migration. Most multi-racial Jamaicans refer to themselves as either mixed race or brown. Similar populations can be found in the Caricom states of Belize, Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago. Trinidad and Tobago has a multi-racial cosmopolitan society due to the arrivals of Africans, Indians, Chinese, Arabs, Jews, Latinos, and Europeans along with the native indigenous Amerindians population. This multi-racial mix of the Caribbean has created sub-ethnicities that often straddle the boundaries of major ethnicities and include Mulatto-Creole, Mestizo, Pardo, Zambo, Dougla, Chindian, Afro-Asians, Eurasian, Cocoa panyols, and Asian Latinos.
Language
[edit]Spanish (64%), French (25%), English (14%), Dutch, Haitian Creole, and Papiamento are the predominant official languages of various countries in the region. However, virtually every Caribbean country has a distinct creole language or dialect that often serves as its vernacular language. Most of these do not enjoy official status, with the aforementioned Haitian Creole and Papiamento being notable exceptions. Other languages such as Caribbean Hindustani, Chinese, Javanese, Arabic, Hmong, Amerindian languages, other African languages, other European languages, and other Indian languages can also be found.
Religion
[edit]





Christianity is the predominant religion in the Caribbean (84.7%).[84] Other religions in the region are Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, Rastafari, Buddhism, Chinese folk religion (incl. Taoism and Confucianism), Baháʼí, Jainism, Sikhism, Kebatinan, Traditional African religions, Yoruba (incl. Trinidad Orisha), Afro-American religions, (incl. Santería, Palo, Umbanda, Brujería, Hoodoo, Candomblé, Quimbanda, Orisha, Xangô de Recife, Xangô do Nordeste, Comfa, Espiritismo, Santo Daime, Obeah, Candomblé, Abakuá, Kumina, Winti, Sanse, Cuban Vodú, Dominican Vudú, Louisiana Voodoo, Haitian Vodou, and Vodun).
Culture
[edit]Cuisine
[edit]Favourite or national dishes
[edit]

- Anguilla – rice, peas and fish
- Antigua and Barbuda – fungee and pepperpot
- Bahamas – Guava duff, Conch Salad, Peas n' Rice, and conch fritters
- Barbados – Cou-cou and flying fish
- Belize – rice and beans, stew chicken with potato salad; white rice, stew beans and fry fish with cole slaw
- British Virgin Islands – fish and fungee
- Cayman Islands – turtle stew, turtle steak, grouper, conch stew, Cayman-style beef with rice and beans, cassava cake
- Colombian Caribbean – rice with coconut milk, arroz con pollo, sancocho, Arab cuisine (due to the large Arab population)
- Cuba – platillo Moros y Cristianos, ropa vieja, lechon, maduros, ajiaco
- Dominica – mountain chicken, rice and peas, dumplings, saltfish, dashin, bakes (fried dumplings), coconut confiture, curry goat, cassava farine, oxtail
- Dominican Republic – arroz con pollo with stewed red kidney beans, pan fried or braised beef, salad/ ensalada de coditos, empanadas, mangú, sancocho
- Grenada – oil down, Roti and rice & chicken
- Guyana – roti and curry, pepperpot, cook-up rice, metemgee, pholourie
- Haiti – griot (fried pork) served with du riz a pois or diri ak pwa (rice and beans)
- Jamaica – ackee and saltfish, callaloo, jerk chicken, curry chicken
- Montserrat – Goat water
- Puerto Rico – yellow rice with green pigeon peas, saltfish stew, roasted pork shoulder, Puerto Rican style pasteles (root vegetable meat patties), chicken fricassée, pasteles, mofongo, tripe soup, tostones, alcapurria, codfish fritters, coconut custard, rice pudding, guava turnovers, Mallorca bread
- Saint Kitts and Nevis – goat water, coconut dumplings, spicy plantain, saltfish, breadfruit
- Saint Lucia – callaloo, dal roti, dried and salted cod, green bananas, rice and beans
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines – roasted breadfruit and fried jackfish
- Suriname – brown beans and rice, roti and curry, peanut soup, battered fried plantain with peanut sauce, nasi goreng, moksi-alesi, bara, pom
- Trinidad and Tobago – doubles, curry with roti or dal bhat, aloo pie, phulourie, callaloo, bake and shark, curry crab and dumpling
- United States Virgin Islands – stewed goat, oxtail or beef, seafood, callaloo, fungee
- Venezuela Caribbean – fried fish with salad and rise, tostones, sancocho, patacon, pabellon
Sport
[edit]
Cricket is a very popular sport in the countries and dependencies that formed the British West Indies. The West Indies cricket team competes in Test matches, One Day Internationals and Twenty20 Internationals. The West Indies' major domestic competitions are the Regional Four Day Competition (first-class) and the Regional Super50 (List A one-day) and more recently the Caribbean Premier League (Twenty20).
The regional football governing body is the Caribbean Football Union. National teams have competed in the CFU Championship from 1978 to 1988 and the Caribbean Cup since 1989. The top 4 teams in the tournament qualify for the CONCACAF Gold Cup. Cuba qualified to the FIFA World Cup in 1938, Haiti in 1974, Jamaica in 1998 and Trinidad and Tobago in 2006.
The CFU Club Championship is the regional tournament for football clubs. The winner qualified for the CONCACAF Champions' Cup from 1997 until 2008. Since 2008–09, the top 3 clubs qualify for a preliminary round of the CONCACAF Champions League.
However, the most popular sport in Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Aruba and Curaçao is baseball. The Caribbean Series, held since 1949, features the national champions from the top Caribbean leagues. The Cuba national team has claimed the Baseball World Cup 25 times, whereas the Dominican Republic won the 2013 World Baseball Classic. In the Pan American Games, Cuba has won 12 editions and Dominican Republic once, whereas Puerto Rico earned the silver medal twice. In the Central American and Caribbean Games, Cuba has won 15 gold medals, whereas Dominican Republic has won three and Puerto Rico two. Several Caribbean players have joined the Major League Baseball: in the 2014 there were 82 Dominicans, 19 Cubans and 11 Puerto Ricans. Notable Caribbean players are Juan Marichal, Pedro Martínez, Roberto Clemente, Orlando Cepeda and Roberto Alomar.Regional institutions
[edit]Here are some of the bodies that several islands share in collaboration:
- African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
- Association of Caribbean States (ACS), Trinidad and Tobago
- Caribbean Association of Industry and Commerce (CAIC), Trinidad and Tobago
- Caribbean Association of National Telecommunication Organizations (CANTO), Trinidad and Tobago[87]
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Guyana
- Caribbean Development Bank (CDB), Barbados
- Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency (CDERA), Barbados
- Caribbean Educators Network[88]
- Caribbean Electric Utility Services Corporation (CARILEC), Saint Lucia[89]
- Caribbean Environment Programme (CEP), UN Environment Programme–administered Regional Seas Programme, secretariat located in Kingston, Jamaica[90]
- Caribbean Examinations Council (CXC), Barbados and Jamaica
- Caribbean Financial Action Task Force (CFATF), Trinidad and Tobago
- Caribbean Food Crops Society, Puerto Rico
- Caribbean Football Union (CFU), Jamaica
- Caribbean Hotel & Tourism Association (CHTA), Florida and Puerto Rico[91]
- Caribbean Initiative (Initiative of the IUCN)
- Caribbean Programme for Economic Competitiveness (CPEC), Saint Lucia
- Caribbean Regional Environmental Programme (CREP), Barbados[92]
- Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism (CRFM), Belize[93]
- Caribbean Regional Negotiating Machinery (CRNM), Barbados and Dominican Republic[94]
- Caribbean Telecommunications Union (CTU), Trinidad and Tobago
- Caribbean Tourism Organization (CTO), Barbados
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
- Foundation for the Development of Caribbean Children, Barbados
- Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre (LACNIC), Brazil and Uruguay
- Latin American and the Caribbean Economic System, Venezuela
- Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS), Saint Lucia
- United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC), Chile and Trinidad and Tobago
- University of the West Indies, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, and Antigua & Barbuda.[95] In addition, the fourth campus, the Open Campus was formed in June 2008 as a result of an amalgamation of the Board for Non-Campus Countries and Distance Education, Schools of Continuing Studies, the UWI Distance Education Centres and Tertiary Level Units. The Open Campus has 42 physical sites in 16 Anglophone Caribbean countries.
- West Indies Cricket Board, Antigua and Barbuda[96]
See also
[edit]- African diaspora
- Anchor coinage
- British African-Caribbean people
- Caribbean people
- Climate change in the Caribbean
- CONCACAF
- Council on Hemispheric Affairs
- Economy of the Caribbean
- South Asian diaspora
- List of Caribbean music genres
- List of sovereign states and dependent territories in the Caribbean
- Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin
- Piracy in the Caribbean
- Politics of the Caribbean
- Democracy in the Caribbean
- Tourism in the Caribbean
Geography:
Notes
[edit]- ^ Pronounced /ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ih-BEE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/ KARR-ih-bee-an;[4] Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben.
- ^ The Lucayan Archipelago is excluded from some definitions of "Caribbean" and instead classified as Atlantic; this is primarily a geological rather than cultural or environmental distinction.
- ^ Bermuda is an associate member of the Caribbean Community.
- ^ 2019 estimate
References
[edit]- ^ a b "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ a b "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950–2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ Johnson, Todd M.; Crossing, Peter F. (14 October 2022). "Religions by Continent". Journal of Religion and Demography. 9 (1–2): 91–110. doi:10.1163/2589742x-bja10013.
- ^ a b Allsopp, Richard; Allsopp, Jeannette (2003). Dictionary of Caribbean English Usage. University of the West Indies Press. p. 136–. ISBN 978-976-640-145-0.
- ^ Engerman, Stanley L. (2000). "A Population History of the Caribbean". In Haines, Michael R.; Steckel, Richard Hall (eds.). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. pp. 483–528. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7. OCLC 41118518.
- ^ Hillman, Richard S.; D'Agostino, Thomas J., eds. (2003). Understanding the contemporary Caribbean. London, UK: Lynne Rienner. ISBN 978-1588266637. OCLC 300280211.
- ^ a b Rogoziński, Jan (1999). A Brief History of the Caribbean (Revised ed.). New York: Facts on File, Inc. pp. 3–4. ISBN 0-8160-3811-2. Retrieved 15 July 2024 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ a b "Bermuda Government after General Election of October 1 2020". bermuda-online.org. Retrieved 2024-10-17.
- ^ a b Jacobs, Stevenson (2003-07-03). "Premier signs Caricom deal". royalgazette.com. Retrieved 2024-10-17.
- ^ Higman, B. W. (2011). A Concise History of the Caribbean. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. xi. ISBN 978-0521043489.
- ^ "North America" Archived 3 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia; "associated with the continent is Greenland, the largest island in the world, and such offshore groups as the Arctic Archipelago, the Bahamas, the Greater and Lesser Antilles, the Queen Charlotte Islands, and the Aleutian Islands", but also "North America is bounded ... on the south by the Caribbean Sea", and "according to some authorities, North America begins not at the Isthmus of Panama but at the narrows of Tehuantepec".
- ^ The World: Geographic Overview, The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency; "North America is commonly understood to include the island of Greenland, the isles of the Caribbean, and to extend south all the way to the Isthmus of Panama"
- ^ "UNESCO LAC | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization". UNESCO. 2022-04-09. Archived from the original on 2022-04-09. Retrieved 2024-11-09.
- ^ The Netherlands Antilles: The joy of six, The Economist, 29 April 2010
- ^ "Carib". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 30 April 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2008.
inhabited the Lesser Antilles and parts of the neighbouring South American coast at the time of the Spanish conquest.
- ^ Elster, Charles Harrington. "Caribbean", from The Big Book of Beastly Mispronunciations Archived 17 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine. p.78. (2d ed. 2005)
- ^ In the early 20th century, only the pronunciation with the primary stress on the third syllable was considered correct, according to Frank Horace Vizetelly, A Desk-Book of Twenty-five Thousand Words Frequently Mispronounced (Funk and Wagnalls, 1917), p. 233.
- ^ Ladefoged, Peter; Johnson, Keith (2011). A Course in Phonetics. Cengage Learning. pp. 86–. ISBN 978-1-4282-3126-9.
- ^ Random House Dictionary
- ^ American Heritage Dictionary
- ^ Merriam Webster
- ^ See, e.g., Elster, supra.
- ^ a b Oxford Online Dictionaries
- ^ Lawler, Andrew (23 December 2020). "Invaders nearly wiped out Caribbean's first people long before Spanish came, DNA reveals". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- ^ Beazley, C. Raymond; Olson, Julius E.; Bourne, Edward Gaylord (April 1907). "The Northmen, Columbus and Cabot, 985-1503". The American Historical Review. 12 (3): 654. doi:10.2307/1832434. hdl:2027/loc.ark:/13960/t7mp5d39r. ISSN 0002-8762. JSTOR 1832434.
- ^ Livi-Bacci, Massimo (June 2006). "The Depopulation of Hispanic America after the Conquest". Population and Development Review. 32 (2): 199–232. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2006.00116.x. ISSN 0098-7921.
- ^ "End of Slavery in Cuba". historyofcuba.com. Archived from the original on 19 December 2022. Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- ^ Dosal, Paul. "THE CARIBBEAN WAR. The United States in the Caribbean, 1898–1998" (PDF). University of South Florida. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2004. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ^ "Caribbean Bathymetry 200m GEBCO contour 2020". caribbeanscienceatlas.tnc.org. Retrieved 2025-01-17.
- ^ "GEBCO Gazetteer". ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2025-01-17.
- ^ ten Brink, Uri. "Puerto Rico Trench 2003: Cruise Summary Results". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 24 July 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- ^ "Summary Climatological Normals 1981–2010" (PDF). Departamento Meteorologico Aruba. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 September 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ^ "Climate Data Aruba". Departamento Meteorologico Aruba. Archived from the original on 9 December 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2012.
- ^ "Average Weather for Mayaguez, PR – Temperature and Precipitation". Weather.com. Archived from the original on 6 February 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service – Havana". Cuban Institute of Meteorology. June 2011. Archived from the original on 9 December 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- ^ "Casa Blanca, Habana, Cuba: Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight Charts and Data". Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
- ^ Spalding, Mark; Ravilious, Corinna; Green, Edmund Peter (10 September 2001). World Atlas of Coral Reefs. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23255-6. Retrieved 25 June 2012.
- ^ Littler, D. and Littler, M. (2000) Caribbean Reef Plants. OffShore Graphics, Inc., ISBN 0967890101.
- ^ Minter, D.W., Rodríguez Hernández, M. and Mena Portales, J. (2001) Fungi of the Caribbean. An annotated checklist. PDMS Publishing, ISBN 0-9540169-0-4.
- ^ Kirk, P. M.; Ainsworth, Geoffrey Clough (2008). Ainsworth & Bisby's Dictionary of the Fungi. CABI. ISBN 978-0-85199-826-8.
- ^ "Fungi of Cuba – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ "Fungi of Puerto Rico – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ "Fungi of the Dominican Republic – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ "Fungi of Trinidad & Tobago – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ "North American Extinctions v. World". The Great Story. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ "Caribbean Coral Reefs". coral-reef-info.com. 9 November 2020. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 29 October 2010.
- ^ Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P. J.; Hooten, A. J.; Steneck, R. S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C. D.; Sale, P. F.; et al. (2007). "Coral Reefs Under Rapid Climate Change and Ocean Acidification". Science. 318 (5857): 1737–42. Bibcode:2007Sci...318.1737H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.702.1733. doi:10.1126/science.1152509. PMID 18079392. S2CID 12607336.
- ^ "Caribbean coral reefs may disappear within 20 years: Report". IANS. news.biharprabha.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2014. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ Rogoziński, Jan (2000). A Brief History of the Caribbean. Penguin. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-452-28193-6.
- ^ Rogoziński, Jan (2000). A Brief History of the Caribbean. Penguin. p. 356. ISBN 978-0-452-28193-6.
- ^ Gowricharn, Ruben. Caribbean Transnationalism: Migration, Pluralization, and Social Cohesion, Lanham: Lexington Books, 2006. p. 5 ISBN 0-7391-1167-1
- ^ Hillman, p. 150
- ^ Hillman, p. 165
- ^ a b Serbin, Andres (1994). "Towards an Association of Caribbean States: Raising Some Awkward Questions". Journal of Interamerican Studies and World Affairs. 36 (4): 61–90. doi:10.2307/166319. JSTOR 166319. S2CID 158660832.
- ^ Hillman, p. 123
- ^ "The U.S.-EU Banana Agreement". USTR. 2001. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008. See also: Sanders, Ronald (16 May 2008). "Dominica: Poverty and Potential". BBC. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "WTO rules against EU banana import practices". eubusiness.com. 29 November 2007. Archived from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ "No truce in banana war". BBC News. 8 March 1999. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ Clinton In Caribbean: No Bananas Today, 11 May 1997, The New York Times.
- ^ "World: Americas St Vincent hit by banana war". BBC News. 13 March 1999. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ "Concern for Caribbean farmers". Bbc.co.uk. 7 January 2005. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ African Union 6th Region Diaspora Headquarters to be established in Accompong, Jamaica Archived 11 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine, 24 January 2018.
- ^ "Barbados inks MOU with African Export-Import Bank". Archived from the original on 17 July 2022. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ AfDB, CDB move to deepen Africa, Caribbean cooperation, sign MoU Archived 25 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine, 18 June 2022
- ^ "SPP Background". CommerceConnect.gov. Security and Prosperity Partnership of North America. Archived from the original on 18 June 2008. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ "Ecoregions of North America". United States Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
- ^ "What's the difference between North, Latin, Central, Middle, South, Spanish and Anglo America?". About.com. Archived from the original on 10 April 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ Unless otherwise noted, land area figures are taken from "Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density" (PDF). Demographic Yearbook. United Nations Statistics Division. 2008. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 14 October 2010.
- ^ Since the Lucayan Archipelago is located in the Atlantic Ocean rather than Caribbean Sea, the Bahamas are part of the West Indies but are not technically part of the Caribbean, although the United Nations groups them with the Caribbean.
- ^ a b c Population estimates are taken from the Central Bureau of Statistics Netherlands Antilles. "Statistical information: Population". Government of the Netherlands Antilles. Archived from the original on 1 May 2010. Retrieved 14 October 2010.
- ^ Because of ongoing activity of the Soufriere Hills volcano beginning in July 1995, much of Plymouth was destroyed and government offices were relocated to Brades. Plymouth remains the de jure capital.
- ^ Since the Lucayan Archipelago is located in the Atlantic Ocean rather than Caribbean Sea, the Turks and Caicos Islands are part of the West Indies but are not technically part of the Caribbean, although the United Nations groups them with the Caribbean.
- ^ a b "Life expectancy at birth, total". The World Bank Group. 15 April 2025. Retrieved 28 April 2025.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, male". The World Bank Group. 15 April 2025. Retrieved 28 April 2025.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, female". The World Bank Group. 15 April 2025. Retrieved 28 April 2025.
- ^ Byrne, Joseph Patrick (2008). Encyclopedia of Pestilence, Pandemics, and Plagues: A-M. ABC-CLIO. p. 413. ISBN 978-0-313-34102-1.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Engerman, p. 486
- ^ The Sugar Revolutions and Slavery Archived 22 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Library of Congress
- ^ Engerman, pp. 488–492
- ^ Engerman, Figure 11.1
- ^ Engerman, pp. 501–502
- ^ Engerman, pp. 504, 511
- ^ Table A.2, Database documentation, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) Population Database, version 3, International Center for Tropical Agriculture, 2005. Accessed on line 20 February 2008.
- ^ Christianity in its Global Context Archived 2013-08-15 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Federation Focus: Baseball is in Dominican Republic's DNA". World Baseball Softball Confederation. Retrieved 2024-07-27.
- ^ "DR1.com - Dominican Republic News & Travel Information Service". dr1.com. Retrieved 2024-07-27.
- ^ "CANTO Caribbean portal". Canto.org. Archived from the original on 20 November 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "Caribbean Educators Network". CEN. Archived from the original on 14 April 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "Carilec". Carilec.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "Who we are". The Caribbean Environment Programme and Cartagena Convention Secretariat. United Nations Environment Programme. Retrieved 8 July 2024.
- ^ "About Us". Caribbean Hotel & Tourism Association. Archived from the original on 2 April 2014. Retrieved 17 June 2014.
- ^ "Caribbean Regional Environmental Programme". Crepnet.net. Archived from the original on 11 June 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism". Caricom-fisheries.com. Archived from the original on 24 October 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "Official website of the RNM". Crnm.org. Archived from the original on 22 April 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "University of the West Indies". Uwi.edu. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
- ^ "West Indies Cricket Board WICB Official Website". Windiescricket.com. Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 6 December 2008.
Bibliography
[edit]- Engerman, Stanley L. "A Population History of the Caribbean", pp. 483–528 in A Population History of North America Michael R. Haines and Richard Hall Steckel (Eds.), Cambridge University Press, 2000, ISBN 0-521-49666-7.
- Hillman, Richard S., and Thomas J. D'agostino, eds. Understanding the Contemporary Caribbean, London: Lynne Rienner, 2003 ISBN 1-58826-663-X.
Further reading
[edit]- Develtere, Patrick R. 1994. "Co-operation and development: With special reference to the experience of the Commonwealth Caribbean" ACCO, ISBN 90-334-3181-5
- Gowricharn, Ruben, ed. Caribbean Transnationalism: Migration, Pluralization, and Social Cohesion. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books, 2006. ISBN 978-0-7391-1167-3
- Henke, Holger, and Fred Reno, eds. Modern Political Culture in the Caribbean. Kingston: University of West Indies Press, 2003. ISBN 976-640-135-7
- Heuman, Gad. Brief Histories: The Caribbean. London: Hodder Arnold, 2006. ISBN 9780340763636
- de Kadt, Emanuel, (editor). Patterns of foreign influence in the Caribbean, Oxford University Press, 1972. ISBN 0-19-214988-1
- Knight, Franklin W. and Colin A. Palmer, eds. The Modern Caribbean (The University of North Carolina Press, 1989). ISBN 0-8078-1825-9
- Kurlansky, Mark. 1992. A Continent of Islands: Searching for the Caribbean Destiny. Addison-Wesley Publishing. ISBN 0-201-52396-5
- Langley, Lester D. The United States and the Caribbean in the Twentieth Century. London: University of Georgia Press, 4th edition, 1989. ISBN 0-8203-1153-7
- Maingot, Anthony P. The United States and the Caribbean: Challenges of an Asymmetrical Relationship. Westview Press, 1994. ISBN 0-8133-2242-1
- Palmié, Stephan, and Francisco A. Scarano, eds. The Caribbean: A History of the Region and Its Peoples (University of Chicago Press; 2011); 660 pp.; writings on the region since the pre-Columbian era. ISBN 978-0-226-64506-3
- Ramnarine, Tina K. Beautiful Cosmos: Performance and Belonging in the Caribbean Diaspora. London: Pluto Press, 2007. ISBN 978-0-7453-1767-0
- Rowntree, Lester, Martin Lewis, Marie Price, William Wyckoff. Diversity Amid Globalization: World Regions, Environment, Development, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 4th edition, 2009. ISBN 978-0-13-600554-4
External links
[edit]- Digital Library of the Caribbean
- Latin American, Caribbean, Latinx, and Iberian Free Online Resources (LACLI)
- Manioc, open access digital Library, books, images, conferences, articles about the Caribbean
- Federal Research Division of the U.S. Library of Congress: Caribbean Islands (1987)
 Media related to Caribbean at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Caribbean at Wikimedia Commons
 KSF
KSF



















