Chabad
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 51 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 51 min
חב״ד | |
 Group picture of Chabad Shluchim (emissaries) in Crown Heights, Brooklyn | |
| Formation | 1775 |
|---|---|
| Founder | Shneur Zalman of Liadi |
| Founded at | Liozno, Russian Empire |
| Type | |
| Headquarters | 770 Eastern Parkway, Brooklyn, New York City, U.S. |
Region served | Worldwide |
| Membership | 90,000–95,000[1] (2018) |
Key people | Menachem Mendel Schneerson |
| Secessions | Strashelye, Kopust, Liadi, Niezhin, Avrutch, Malachim |
| Affiliations | Hasidic Judaism |
| Website | |
 |
| Part of a series on |
| Chabad |
|---|
| Rebbes |
|
| Places and landmarks |
| Holidays |
| Organizations |
| Schools |
| Texts |
| Practices and concepts |
| Chabad offshoots |
Chabad, also known as Lubavitch, Habad and Chabad-Lubavitch[2] (US: /xəˈbɑːd luˈbɑːvɪtʃ/; Hebrew: חב״ד לובביץּ׳; Yiddish: חב״ד ליובאוויטש), is a dynasty in Hasidic Judaism. Belonging to the Haredi (ultra-Orthodox) branch of Orthodox Judaism, it is one of the world's best-known Hasidic movements,[3] as well as one of the largest Jewish religious organizations. Unlike most Haredi groups, which are self-segregating, Chabad mainly operates in the wider world and caters to nonobservant Jews.
Founded in 1775[4] by Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi (1745–1812) in the city of Liozno in the Russian Empire, the name "Chabad" (חב״ד) is an acronym formed from the three Hebrew words—Chokmah, Binah, Da'at— for the first three sefirot of the kabbalistic Tree of Life after Keter: חכמה, בינה, דעת, "Wisdom, Understanding, and Knowledge"—which represent the intellectual and kabbalistic underpinnings of the movement.[5][6] The name Lubavitch derives from the town in which the now-dominant line of leaders resided from 1813 to 1915.[7][8] Other, non-Lubavitch scions of Chabad either disappeared or merged into the Lubavitch line. In the 1930s, the sixth Rebbe of Chabad, Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak Schneersohn, moved the center of the Chabad movement from Russia to Poland. After the outbreak of World War II, he moved the center of the movement to Brooklyn, New York, in the United States, where the Rebbe lived at 770 Eastern Parkway until the end of his life.
Between 1951 and 1994, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson transformed the movement into one of the most widespread Jewish movements in the world. Under his leadership, Chabad established a large network of institutions that seek to satisfy the religious, social and humanitarian needs of Jews across the world.[9] Chabad institutions provide outreach to unaffiliated Jews and humanitarian aid, as well as religious, cultural and educational activities. During his life and after his death, Schneerson has been believed by some of his followers to be the Messiah, with his own position on the matter debated among scholars. Messianic ideology in Chabad sparked controversy in various Jewish communities and it is still an unresolved matter. Following his death, no successor was appointed as a new central leader. The Rebbe was also known to have never visited Israel, for reasons which remain disputed among the Chabad community.
The global population of Chabad has been estimated to be 90,000–95,000 adherents as of 2018, accounting for 13% of the global Hasidic population.[1] However, up to one million Jews are estimated to attend Chabad services at least once a year.[10][11] In a 2020 study, the Pew Research Center found that 16% of American Jews participated in Chabad services or activities at least semi-regularly.[12]
History
[edit]The Chabad movement was established after the First Partition of Poland in the town of Liozno, Pskov Governorate, Russian Empire (now Liozna, Belarus), in 1775, by Shneur Zalman,[4] a student of Dov Ber of Mezeritch, the successor to Hasidism's founder, Rabbi Israel Baal Shem Tov. Rabbi Dovber Shneuri, the Second Rebbe, moved the movement to Lyubavichi (Yiddish: ליובאַװיטש, Lyubavitsh), in current-day Russia, in 1813.[7]
The movement was centered in Lyubavichi for a century until the fifth Rebbe, Rabbi Shalom Dovber left the village in 1915[8] and moved to the city of Rostov-on-Don. During the interwar period, following Bolshevik persecution, the Chabad-Lubavitch movement, under the Sixth Rebbe, Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak, was centered in Riga and then in Warsaw. The outbreak of World War II led the Sixth Rebbe to move to the United States. Since 1940,[4] the movement's center has been in the Crown Heights neighborhood of Brooklyn.[13][14]


While the movement spawned a number of offshoot groups throughout its history, the Chabad-Lubavitch branch is the only one still active, making it the movement's main surviving line.[15] Historian Jonathan Sarna has characterized Chabad as having enjoyed the fastest rate of growth of any Jewish religious movement in the period 1946–2015.[16]
In the early 1900s, Chabad-Lubavitch legally incorporated itself under Agudas Chasidei Chabad ("Association of Chabad Hasidim").[citation needed]
In the 1980s, tensions arose between Chabad and Satmar Chasidim as a result of several assaults on Chabad Hasidim by Satmar Hasidim.[17][18][19]
Oppression and resurgence in Russia
[edit]The Chabad movement was subjected to governmental oppression in Russia. The Russian government, first under the Czar, later under the Bolsheviks, imprisoned all but one of the Chabad rebbes.[20][21] The Bolsheviks also imprisoned, exiled and executed a number of Chabad Hasidim.[22][23][24] During the Second World War, many Chabad Hasidim evacuated to the Uzbek cities of Samarkand and Tashkent where they established small centers of Hasidic life, while at the same time seeking ways to emigrate from Soviet Russia due to the government's suppression of religious life.[25] The reach of Chabad in Central Asia also included earlier efforts that took place in the 1920s.[26] Following the war, and well after the center of the Chabad movement moved to the United States, the movement remained active in Soviet Russia, aiding the local Jews known as Refuseniks who sought to learn more about Judaism.[27] And throughout the Soviet era, the Chabad movement maintained a secret network across the USSR.[28] Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, state persecution of Chabad ceased. The Chief Rabbi of Russia, Berel Lazar, a Chabad emissary, maintains warm relations with Russian President Vladimir Putin.[29] Lazar also received the Order of Friendship and Order "For Merit to the Fatherland" medals from him.[30]
Leadership
[edit]
| Part of a series on |
| Chabad (Rebbes and Chasidim) |
|---|
 |
|
|
The Chabad movement has been led by a succession of Hasidic rebbes. The main branch of the movement, Chabad-Lubavitch, has had seven rebbes:
- Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi (1745–1812), founded the Chabad movement in the town of Liozna. The Chabad movement began as a separate school of thought within the Hasidic movement, focusing of the spread of Hasidic mystical teachings using logical reasoning (creating a kind of Jewish "rational-mysticism").[31] Shneur Zalman's main work is the Tanya (or Sefer Shel Beinonim, "Book of the Average Man"). The Tanya is the central book of Chabad thought and is studied daily by followers of the Chabad movement. Shneur Zalman's other works include a collection of writings on Hasidic thought, and the Shulchan Aruch HaRav, a revised version of the code of Halakha, both of which are studied regularly by followers of Chabad. Shneur Zalman's successors went by last names such as "Schneuri" and "Schneersohn" (later "Schneerson"), signifying their descent from the movement's founder. He is commonly referred to as the "Old Rebbe" (Yiddish: אַלטער רבי, romanized: Alter Rebbe or Hebrew: אדמו״ר הזקן, romanized: Admur Hazoken).[32][33]
- Rabbi Dovber Schneuri (1773–1827), son of Rabbi Shneur Zalman, led the Chabad movement in the town of Lyubavichi (Lubavitch). His leadership was initially disputed by Rabbi Aaron Halevi of Stroselye, however, Rabbi Dovber was generally recognized as his father's rightful successor, and the movement's leader. Rabbi Dovber published a number of his writings on Hasidic thought, greatly expanding his father's work. He also published some of his father's writings. Many of Rabbi Dovber's works have been subsequently republished by the Chabad movement. He is commonly referred to as the Mitteler Rebbe (Yiddish: מיטעלער רבי 'Middle Rabbi', Hebrew: אדמו״ר האמצעי, romanized: Admur Ha'emtzoei).[34][35]
- Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneersohn (1789–1866), a grandson of Rabbi Shneur Zalman and son-in-law of Rabbi Dovber. Following his attempt to persuade the Chabad movement to accept his brother-in-law or uncle as rebbe, Rabbi Menachem Mendel assumed the title of rebbe of Chabad, also leading the movement from the town of Lyubavichi (Lubavitch). He published a number of his works on both Hasidic thought and Jewish law. Rabbi Menachem Mendel also published some of the works of his grandfather, Rabbi Shneur Zalman. He is commonly referred to as the Tzemach Tzedek after the title of his responsa.[36]
- Rabbi Shmuel Schneersohn (1834–1882), was the seventh and youngest son of Rabbi Menachem Mendel. He assumed the title of rebbe in town of Lyubavichi (Lubavitch), while several of his brothers assumed the title of rebbe in other towns, forming Chabad groups of their own which existed for several decades. Years after his death, his teachings were published by the Chabad movement. He is commonly referred to as the Maharash, an acronym for Moreinu HaRav Shmuel ('our teacher, Rabbi Shmuel').[37][38]
- Rabbi Shalom Dovber Schneersohn (1860–1920), Shmuel's second son, succeeded his father as rebbe. Rabbi Shalom Dovber waited some time before officially accepting the title of rebbe, as not to offend his elder brother, Zalman Aaron. He established a yeshiva called Tomchei Temimim. During World War I, he moved to Rostov-on-Don. Many of his writings were published after his death, and are studied regularly in Chabad yeshivas. He is commonly referred to as the Rashab, an acronym for Rabbi Shalom Ber.[39]
- Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak Schneersohn (1880–1950), the only son of Sholom Dovber, succeeded his father as rebbe of Chabad. Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak was exiled from Russia, following an attempt by the Bolshevik government to have him executed.[40] He led the movement from Warsaw, Poland, until the start of World War II. After fleeing the Nazis, Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak lived in Brooklyn, New York until his death. He established much of Chabad's current organizational structure, founding several of its central organizations as well as other Chabad institutions, both local and international. He published a number of his writings, as well as the works of his predecessors. He is commonly referred to as the Rayatz or the Frierdiker Rebbe ('Previous Rebbe').
- Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson (1902–1994),[a] son-in-law of Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak, and a great-grandson of the third Rebbe of Lubavitch, assumed the title of rebbe one year after his father-in-law's death. Rabbi Menachem Mendel greatly expanded Chabad's global network, establishing hundreds of new Chabad centers across the globe. He published many of his own works as well as the works of his predecessors. His teachings are studied regularly by followers of Chabad. He is commonly referred to as "the Lubavitcher Rebbe", or simply "the Rebbe". Even after his death, many continue to revere him as the leader of the Chabad movement.[34]
Influence
[edit]Chabad's influence among world Jewry has been far-reaching since World War II. Chabad pioneered the post-World War II Jewish outreach movement, which spread Judaism to many assimilated Jews worldwide, leading to a substantial number of baalei teshuva ("returnees" to Judaism). The very first Yeshiva/Rabbinical College for such baalei teshuva, Hadar Hatorah, was established by the Lubavitcher rebbe. It is reported that up to a million Jews attend Chabad services at least once a year.[11][41]
According to journalist Steven I. Weiss, Chabad's ideology has dramatically influenced non-Hasidic Jews' outreach practices.[42] Because of its outreach to all Jews, including those Jews who are quite alienated from religious Jewish traditions, Chabad has been described as the one Orthodox group which evokes great affection from large segments of American Jewry.[43]
Philosophy
[edit]Chabad Hasidic philosophy focuses on religious and spiritual concepts such as God, the soul, and the meaning of the Jewish commandments. Classical Judaic writings and Jewish mysticism, especially the Zohar and the Kabbalah of Rabbi Isaac Luria, are frequently cited in Chabad works. These texts are used both as sources of Chabad teachings and as material requiring interpretation by Chabad authors. Many of these teachings discuss what is commonly referred to as bringing "heaven down to earth", i.e. making the Earth a dwelling place for God. Chabad philosophy is rooted in the teachings of Rabbis Yisroel ben Eliezer, (the Baal Shem Tov, founder of Hasidism) and Dovber ben Avraham, the "Maggid of Mezritch" (Rabbi Yisroel's successor).[citation needed]
Rabbi Shneur Zalman's teachings, particularly in the Tanya, formed the basis of Chabad philosophy, as expanded by succeeding generations. Many Chabad activities today are understood as applications of Shneur Zalman's teachings.[citation needed]
Tanya
[edit]The Tanya (תניא) is a book by Rabbi Shneur Zalman first published in 1797. It is the first schematic treatment of Hasidic moral philosophy and its metaphysical foundations.[32]
According to the Tanya, the intellect consists of three interconnected processes: Chochma (wisdom), Bina (understanding), and Da'at (knowledge). While other branches of Hasidism primarily focused on the idea that "God desires the heart," Shneur Zalman argued that God also desires the mind, and he also argued that the mind is the "gateway" to the heart. With the Chabad philosophy, he elevated the mind above the heart, arguing that "understanding is the mother of fear and love for God".[44]
The Tanya has five sections. The original name of the first section is Sefer Shel Beinonim, the "Book of the Intermediates". It is also known as Likutei Amarim ("Collected Sayings"). Sefer Shel Beinonim analyzes the inner struggle of the individual and the path to resolution. Citing the biblical verse "the matter is very near to you, in your mouth, your heart, to do",[45] the philosophy is based on the notion that the human is not inherently evil; rather, every individual has an inner conflict that is characterized by two different inclinations, the good and the bad.[46]
Chabad often contrasted itself with what is termed the Chagat schools of Hasidism.[b] While all schools of Hasidism put a central focus on the emotions, Chagat saw emotions as a reaction to physical stimuli, such as dancing, singing, or beauty. Shneur Zalman, on the other hand, taught that the emotions must be led by the mind, and thus the focus of Chabad thought was to be Torah study and prayer rather than esotericism and song.[32] As a Talmudist, Shneur Zalman endeavored to place Kabbalah and Hasidism on a rational basis. In Tanya, he defines his approach as moach shalit al halev (Hebrew: מוח שליט על הלב, "the brain ruling the heart").[47]
Community
[edit]
An adherent of Chabad is called a Chabad Chasid (or Hasid) (Hebrew: חסיד חב"ד), a Lubavitcher (Yiddish: ליובאַוויטשער), a Chabadnik (Hebrew: חבדניק), or a Chabadsker (Yiddish: חבדסקער).[48] Chabad's adherents include both Hasidic followers, as well as non-Hasidim, who have joined Chabad synagogues and other Chabad-run institutions.[49]
Although the Chabad movement was founded and originally based in Eastern Europe, various Chabad communities span the globe, including Crown Heights, Brooklyn, and Kfar Chabad, Israel.[50][51] The movement has attracted a significant number of Sephardic adherents in the past several decades,[52] and some Chabad communities include both Ashkenazi and Sephardic Jews. For example, in Montreal, close to 25% of Chabad households include a Sephardi parent.[53][54]
According to sociologists studying contemporary Jewry, the Chabad movement fits into neither the standard category of Haredi nor that of modern Orthodox among Orthodox Jews. This is due in part to the existence of the number of Chabad supporters and affiliates who are not Orthodox (dubbed by some scholars as "non-Orthodox Hasidim"), the general lack of official recognition of political and religious distinctions within Judaism, and the open relationship with non-Orthodox Jews represented by the activism of Chabad emissaries.[49][55]
Population
[edit]In 2018, Marcin Wodziński conducted the first global estimate of worldwide Hasidism in the Historical Atlas of Hasidism. Using Chabad community directories, Wodziński estimated that Chabad included 16,000–17,000 households, or 90,000–95,000 individuals, representing 13% of the total Hasidic population and ranking Chabad as the second-largest Hasidic community behind the Satmar community.[1]
United States
[edit]
Estimates for Chabad and other Hasidic groups are often based on extrapolation from the limited information available in US census data for some of the areas where Hasidim live. A 2006 estimate was drawn from a study on the Montreal Chabad community (determining average household size), in conjunction with language and other select indicators from US census data, it is estimated that Chabad in the United States includes approximately 4,000 households, which contains between 22,000 and 25,000 people. In terms of Chabad's relation to other Hasidic groups, within the New York metropolitan area, Chabad in the New York area accounts for around 15% of the total New York Hasidic population. Chabad is estimated to have an annual growth of 3.6%:[56]
- Crown Heights – The Crown Heights Chabad community's estimated size is 12,000 to 16,000.[57] It was estimated that between 25% and 35% of Chabad Hasidim in Crown Heights speak Yiddish. This figure is significantly lower than other Hasidic groups and may be attributed to the addition of previously non-Hasidic Jews to the community. It was also estimated that over 20% of Chabad Hasidim in Crown Heights speak Hebrew or Russian.[56] The Crown Heights Chabad community has its own Beis Din (rabbinical court) and Crown Heights Jewish Community Council (CHJCC).
- Chabad hipsters – Beginning from the late 2000s through the 2010s, a minor trend of cross acculturation of Chabad Hasidim and contemporary hipster subculture appeared within the New York City Jewish community. According to The Jewish Daily Forward, a small number of members of the Chabad Hasidic community, mostly residing in Crown Heights, Brooklyn, appear to now have adopted various cultural affinities of the local hipster subculture. These members are referred to as Chabad hipsters or Hipster Hasidim.[58][59]
Israel
[edit]- Kfar Chabad – Kfar Chabad's population was placed at 6,489 in 2024; all of the residents of the town are believed to be Chabad adherents, with this number being based on figures published by the Israeli Census Bureau.[60] Other estimates place the community population at around 7,000.[57]
- Safed – The Chabad community in Safad (Tzfat) originated during the wave of Eastern European immigration to Palestine from 1777–1840. The Chabad community established synagogues and institutions in Safad. The early settlement declined by the 20th century but it was renewed following an initiative by the seventh rebbe in the early 1970s, which reestablished the Chabad community in the city.[61] Rabbi Yeshaya HaLevi Horowitz (1883–1978), a Safad-born direct descendant of Rabbi Yeshaya Horowitz, author of the Shnei Luchot HaBrit, served as the rabbi of the Chabad community in Safad from 1908 until his immigration to the U.S. during World War I.[62] Members of the Chabad community run a number of outreach efforts during the Jewish holidays. Activities include blowing the shofar for the elderly on Rosh Hashana, reading the Megilla for hospital patients on Purim and setting up a Sukka on the town's main street during the Sukkot holiday.[61]
- Nachlat Har Chabad in Kiryat Malakhi is home to 2800 residents, with institutions including a yeshiva and a girls' school.
France
[edit]The Chabad community in France is estimated to be between 10,000 and 15,000. The majority of the Chabad community in France are the descendants of immigrants from North Africa (specifically Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia) during the 1960s.[57][63]
Canada
[edit]- Montreal – The estimated size of the Chabad community of Greater Montreal is 1,590. The estimate is taken from a 2003 community study.[64][65] The Chabad community in Montreal originated sometime before 1931. While early works on Canadian Jewry make little or no mention of early Hasidic life in Canada, later researchers have documented Chabad's accounts in Canada starting from the 1900s and 1910s. Steven Lapidus notes that there is mention of two Chabad congregations in a 1915 article in the Canadian Jewish Chronicle listing the delegates of the first Canadian Jewish Conference. One congregation is listed as Chabad of Toronto, and the other is simply listed as "Libavitzer Congregation". The sociologist William Shaffir has noted that some Chabad Hasidim and sympathizers did reside in Montreal before 1941 but does not elaborate further. Steven Lapidus notes that in a 1931 obituary published in Keneder Odler, a Canadian Yiddish newspaper, the deceased Rabbi Menashe Lavut is credited as the founder of Anshei Chabad in Montreal and the Nusach Ari synagogue. Thus the Chabad presence in Montreal predates 1931.[66]
United Arab Emirates
[edit]- Dubai – The Jewish Community Center of UAE has a synagogue and a Talmud Torah. 1,000 kosher chickens per week are provided to the community by local kosher shechita. The community is headed by Rabbi Levi Duchman.[67][68][69]

Customs and holidays
[edit]Customs
[edit]Chabad adherents follow Chabad traditions and prayer services based on Lurianic Kabbalah.[70] General Chabad customs, called minhagim (or minhagei Chabad), distinguish the movement from other Hasidic groups. Some of the main Chabad customs are minor practices performed on traditional Jewish holidays:
- Passover – It is customary in Chabad communities, on Passover, to limit contact of matzah (an unleavened bread eaten on Passover) with water. This custom is called gebrokts (Yiddish: געבראָכטס, lit. 'broken'). However, on the last day of Passover, it is customary to intentionally have matzah come in contact with water.[71]
- Chanukah – It is the custom of Chabad Hasidim to place the Chanukah menorah against the room's doorpost (and not on the windowsill).[72][73][74]
- Prayer – The founder of Chabad wrote a very specific liturgy for the daily and festival prayers based on the teachings of the Kabbalists, primarily the Arizal.
- The founder of Chabad also instituted various other halachic rulings, including the use of stainless steel knives for the slaughter of animals before human consumption, which are now universally accepted in all sects of Judaism.
Holidays
[edit]There are a number of days marked by the Chabad movement as special days. Major holidays include the dates of the release of the leaders of the movement, the rebbes of Chabad, from prison, others corresponded to the leaders' birthdays, anniversaries of death, and other life events.
The days marking the leaders' release, are celebrated by the Chabad movement as "Days of Liberation" (Hebrew: יום גאולה (Yom Geulah)). The most noted day is Yud Tes Kislev—the liberation of Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi, the founder of the Chabad movement. The day is also called the "New Year of Hasidism".[72]
The birthdays of several of the movement's leaders are celebrated each year including Chai Elul, the birthday of Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi, the founder of the Chabad movement,[75][76] and Yud Aleph Nissan, the birthday of Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson, the seventh rebbe of Chabad.[77]
The anniversaries of death, or yartzeit, of several of the movement's leaders are celebrated each year, include Yud Shvat, the yartzeit of Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak Schneersohn, the sixth rebbe of Chabad,[78] Gimmel Tammuz, the yartzeit of Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson, the seventh rebbe of Chabad,[78][79] and Chof Beis Shvat, the yartzeit of Chaya Mushka Schneerson, the wife of Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson.[80]
Organizations
[edit]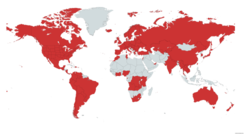
Chabad's central organization representing the movement at large, Agudas Chasidei Chabad, is headed by Rabbi Abraham Shemtov. The educational, outreach and social services arms, Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch and Machneh Israel are headed by Rabbi Yehuda Krinsky, as well as the Chabad-Lubavitch publishing house, Kehot Publication Society.
Local Chabad centers and institutions are usually incorporated as separate legal entities.[81]
Institutions
[edit]As of 2020 there were over 3,500 Chabad centers in 100 countries.[82][83] The Chabad movement's online directory lists around 1,350 Chabad institutions. This number includes schools and other Chabad-affiliated establishments. The number of Chabad centers vary per country; the majority are in the United States and Israel. There are over 100 countries with a Chabad presence.
In total, according to its directory, Chabad maintains a presence in 950 cities around the world: 178 in Europe, 14 in Africa, 200 in Israel, 400 in North America, 38 in South America, and about 70 in Asia (excluding Israel, including Russia).[84]
By geographic region
[edit]Chabad presence varies from region to region. The continent with the highest concentration of Chabad centers is North America. The continent with the fewest centers is Africa.[85][86]

| Geographic location | Chabad institutions |
|---|---|
| North America | 2,894 |
| Europe | 1,133 |
| Asia | 615 |
| South America | 208 |
| Oceania | 67 |
| Africa | 55 |
| Total | 4,972 |
Chabad house
[edit]A Chabad house is a form of Jewish community center, primarily serving both educational and observance purposes.[87][failed verification] Often, until the community can support its own center, the Chabad house is located in the shaliach's home, with the living room being used as the "synagogue". Effort is made to provide an atmosphere in which the nonobservant will not feel intimidated by any perceived contrast between their lack of knowledge of Jewish practice and the advanced knowledge of some of the people they meet there.[88] The term "Chabad House" originated with the creation of the first such outreach center on the campus of UCLA by Rabbi Shlomo Cunin.[89] A key to the Chabad house was given to the Rebbe and he asked if that meant that the new house was his home. He was told yes and he replied, "My hand will be on the door of this house to keep it open twenty-four hours a day for young and old, men and women alike."[90]
Followers of Chabad can be seen attending to tefillin booths at the Western Wall and Ben Gurion International Airport as well as other public places and distributing Shabbat candles on Fridays. Chabad rabbis and their families are sent to various major cities around the globe, to teach college students, build day schools, and create youth camps. Many of these efforts are geared towards secular or less religious Jews. Additionally, unmarried rabbinical students spend weeks during the summer in locations that do not yet have a permanent Chabad presence, making housecalls, putting up mezuzot and teaching about Judaism. This is known as Merkos Shlichus.
Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson also initiated a Jewish children's movement, called Tzivos Hashem (lit. "Army [of] God"), for under bar/bat mitzvah-age children, to inspire them to increase in study of Torah and observance of mitzvot.
Rabbi Schneerson also encouraged the use of modern technology in outreach efforts such as Mitzva tanks, which are mobile homes that travel a city or country.[91] The Chabad website, chabad.org, a pioneer of Jewish religious outreach on the Internet, was started by Rabbi Yosef Y. Kazen and developed by Rabbi D. Zirkind. In 2023, it was reportedly the largest faith-based website, with 52 million unique visitors and 102,129 content pages covering all facets of Judaism.[92]
In June 1994, Rabbi Schneerson died with no successor. Since then, over two thousand couples have taken up communal leadership roles in outreach, bringing the estimated total number of "Shluchim" to over five thousand worldwide.[93][94]
In the 2008 Mumbai attacks, the local Chabad house was targeted.[95][96] The local Chabad emissaries, Rabbi Gavriel Holtzberg and his wife Rivka, and four other Jews were tortured and murdered by Islamic terrorists.[97] Chabad received condolences from around the world.[98][99]
Fundraising
[edit]Funds for activities of a Chabad center rely entirely on the local community. Chabad centers do not receive funding from Lubavitch headquarters. For the day-to-day operations, local emissaries do all the fundraising by themselves.
Chabad emissaries often solicit the support of local Jews.[100] Funds are used toward purchasing or renovating Chabad centers, synagogues and mikvahs.[101]
Activities
[edit]The Chabad movement has been involved in numerous activities in contemporary Jewish life. These activities include providing Jewish education to different age groups, outreach to non-affiliated Jews, publishing Jewish literature, and summer camps for children, among other activities.
Education
[edit]Chabad runs a number of educational institutions. Most are Jewish day schools; others offer secondary and adult education:
- The Chabad operates more than 1,000 schools, preschools and other educational institutions around the globe.[92]
- Day schools – In the United States, there are close to 300 day schools and supplementary schools run by Chabad.[102][103] The report findings of studies on Jewish day schools and supplementary Jewish education in the United States show that the student body currently enrolled in some 295 Chabad schools exceeds 20,750, although this figure includes Chabad Hasidic children as well as non-Chabad children.[103][104]
- Secondary schools – Chabad runs multiple secondary education institutions, most notable are Tomchei Tmimim for young men, and Bais Rivka for young women.
- Adult education – Chabad runs adult education programs including those organized by the Rohr Jewish Learning Institute[105][106] and the Jewish Learning Network.
Outreach activities
[edit]
Many of the movement's activities emphasize outreach activities. This is due to Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson encouraging his followers to reach out to other Jews.[107] Chabad outreach includes activities promoting the practice of Jewish commandments (Mitzvah campaigns), as well as other forms of Jewish outreach. Much of Chabad's outreach is performed by Chabad emissaries (see Shaliach (Chabad)). Most of the communities that Chabad emissaries reach out to are other Jewish communities, such as Reform Jews.[108]
Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn, 6th leader of the Chabad-Lubavitch branch of Hasidic Judaism, and then his successor, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson were responsible for focusing Chabad's activities on outreach. Rabbi Schneerson was a pioneer in the field of Orthodox Judaism outreach (Kiruv).
Each sent out large numbers of rabbinic emissaries, known as "Shluchim", to settle in places across the world for outreach purposes. The centers that these Shluchim established were termed "Chabad houses".
Chabad has been active in reaching out to Jews through its synagogues, and various forms of more direct outreach efforts. The organization has been recognized as one of the leaders in using free holiday services to reach out across denominations.[109]
Rabbi Yosef Yitzchok Schneersohn, had a core of dedicated Hasidim who maintained underground yeshivos and mikvehs, and provided shechitah and ritual circumcision services in the Soviet Union.
Mitzvah campaigns
[edit]The Rebbes of Chabad have issued the call to all Jews to attract non-observant Jews to adopt Orthodox Jewish observance, teaching that this activity is part of the process of bringing the Messiah. Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson issued a call to every Jew: "Even if you are not fully committed to a Torah life, do something. Begin with a mitzvah—any mitzvah—its value will not be diminished by the fact that there are others that you are not prepared to do".[110]
Schneerson also suggested ten specific mitzvot that he believed were ideally suited for the emissaries to introduce to non-observant Jews. These were called mivtzoim—meaning "campaigns" or "endeavors". These were lighting candles before Shabbat and the Jewish holidays by Jewish women, putting on tefillin, affixing a mezuzah, regular Torah study, giving tzedakah, purchasing Jewish books, observing kashrut (kosher), kindness to others, Jewish religious education, and observing the family purity laws.[citation needed]
In addition, Schneerson emphasized spreading awareness of preparing for and the coming of the moshiach, consistent with his philosophy. He wrote on the responsibility to reach out to teach every fellow Jew with love, and implored that all Jews believe in the imminent coming of the moshiach as explained by Maimonides. He argued that redemption was predicated on Jews doing good deeds, and that gentiles should be educated about the Noahide Laws.
Schneerson was emphatic about the need to encourage and provide strong education for every child, Jew and non-Jew alike. In honor of Schneerson's efforts in education the United States Congress has made Education and Sharing Day on the Rebbe's Hebrew birthday (11 Nissan).
Shluchim (Emissaries)
[edit]In 1950, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson urged Chabad to begin shlichus ("serving as an emissary [performing outreach]"). Since then, Chabad shluchim ("emissaries", sing. shliach) have moved all over the world to encourage non-observant Jews to adopt Jewish observance. They assist Jews with all their religious needs, as well as with physical assistance and spiritual guidance and teaching. The stated goal is to encourage Jews to learn more about their Jewish heritage and to practice Judaism.[111]
Thousands of rabbis, educators, ritual slaughterers, and ritual circumcisers have been trained and ordained to serve as shluchim. Typically, a young Lubavitch rabbi and his wife, in their early twenties, with one or two children, will move to a new location, and as they settle in will raise a large family who, as a family unit, will aim to fulfill their mandate of bringing Jewish people closer to Orthodox Judaism and encouraging gentiles to adhere to the Seven Laws of Noah.[111]
Shluchim operate Chabad Houses, Jewish day schools, and Jewish summer camps. As of 2021, there are over 6,500 Chabad shluchim families worldwide, operating over 3,500 institutions in over 110 countries.[112][113] Chabad runs the largest network of synagogues of any Jewish movement as of 2023.[114]
Mitzvah tank
[edit]
A mitzvah tank is a vehicle which is used as a portable "educational and outreach center" and a "mini-synagogue" (or a "minagogue") by Chabad members who are involved in outreach. Mitzvah tanks are commonly used for advancing the mitzvah campaigns. Mitzvah tanks have been commonplace on the streets of New York City since 1974.[115] Today, they are used all over the globe in countries where Chabad is active.
Campus outreach
[edit]In recent years, Chabad has greatly expanded its outreach on university and college campuses. The Chabad on Campus is active on dozens of campuses outside of the United States, some of which include Canada, Israel, UK, Austria, Germany, France, Holland, Hungary, Italy, Russia, Argentina, China and Australia.[92] Chabad Student Centers are active on over 950 campuses.[116][failed verification] Professor Alan Dershowitz has said "Chabad's presence on college campuses today is absolutely crucial," and "we cannot rest until Chabad is on every major college campus in the world."[117]
CTeen
[edit]The Chabad Teen Network (CTeen) is an international organization dedicated to educating Jewish youth about their heritage. It is the teen-focused arm of the Chabad movement operated by Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch. There are over 100,000 members worldwide[118] with 630 chapters across 44 countries.[119] CTeen is open to all Jewish teens, regardless of affiliation, and has been called "the fastest growing and most diverse Jewish youth organization in the world."[120]
The organization was launched in 2010,[121] and operates worldwide in cities such as Paris, Rio de Janeiro, Leeds, Munich, Buenos Aires and New York.[122] Its director is Rabbi Shimon Rivkin, and Rabbi Moshe Kotlarsky serves as chairman.[123] Individual chapters and programs are managed by local directors.

CTeen runs a number of ongoing and annual programs, some of which include:
- CTeen International Shabbaton, an annual inspirational weekend that brings together thousands of teens from around the world. The program includes a traditional Shabbat experience in the heart of Hasidic Crown Heights, a Torah completion ceremony in Times Square, and the CTeen Choice Awards at Brooklyn's Pier 12. The weekend includes a Saturday night concert in Times Square with guest performances by singers such as Gad Elbaz, Yakov Shwekey and American Hasidic rapper Nissim Black.[120][124]
- CTeen XTREME, a summer travel camp where campers challenge themselves both physically and spiritually by partaking in extreme sports, observing a completely tech-free Shabbat, and keeping kosher on the road.[125]
- CTeen U, a college-accredited program where teens learn about Jewish philosophy, ethics and history. The program was launched in 2019 through a partnership with Yeshiva University.[126]
- Heritage Quest, educational travel programs that aim to deepen the connection of Jewish teens to their heritage through trips to Poland and Israel, offering teens the chance to explore their roots at the source.[127][128]
- Kosher Food Club, a co-curricular high school club operating in over fifty high schools throughout the United States that serves as a humanitarian initiative to promote healthy lifestyles, feed the homeless, and provide educational and hands-on experiences making traditional Jewish foods.[129][130]
- National Campus Office, coordinator of Chabad on Campus, a network of Jewish Student Centers on more than 230 university campuses worldwide (as of April 2016), as well as regional Chabad-Lubavitch centers at an additional 150 universities worldwide[131]
- Suicide Alert, workshops that equip teens to assist peers dealing with anxiety and depression resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic. The workshops have been organized by CTeen chapters in Florida, New Hampshire and New Jersey, among others, in partnership with the Gelt Charitable Foundation.[132][133]
Publishing
[edit]Chabad publishes and distributes Jewish religious literature. Under Kehot Publication Society, Chabad's main publishing house, Jewish literature has been translated into 12 different languages. Kehot regularly provides books at discounted prices, and hosts book-a-thons. Kehot commonly distributes books written or transcribed from the rebbes of Chabad, prominent chassidim and other authors who have written Jewish materials.[citation needed] Kehot is a division of Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch, the movement's educational arm.[134]
More than any other Jewish movement, Chabad has used media as part of its religious, social, and political experience. Their latest leader, Menachem Mendel Schneerson, was the most video-documented Jewish leader in history.[135][page needed] The Chabad movement publishes a wealth of Jewish material on the internet. Chabad's main website Chabad.org, is one of the first Jewish websites[136] and the first and largest virtual congregation.[137][138] It serves not just its own members, but Jewish people worldwide in general.[139] Other popular Chabad community websites include asktherav.com, anash.org, CrownHeights.info, and the Hebrew site, COL.org.il.[140][141]
Social media influencers
[edit]Chabad-affiliated social media influencers include Miriam Ezagui and Yossi Farro. Farro wrapped tefillin for Lil Dicky, James Franco, and other public figures, at first by chance, then by seeking out well-known Jews and asking if they would meet with him to wrap tefillin.[142] Chabad influencers Daniel and Raizel Namdar started a "family-oriented channel aimed at breaking stereotypes about Jewish life".[143]
Summer camps
[edit]Chabad has set up an extensive network of camps around the world, most using the name Gan Israel, a name chosen by Schneerson although the first overnight camp was the girls division called Camp Emunah. There are 1,200 sites serving 210,000 children, most of whom do not come from Orthodox homes. Of these, 500 camps are in the United States.[144][145]
Political activities
[edit]Rabbi Schneerson involved himself in matters relating to the resolution of the Israeli-Arab conflict.[146] He maintained that as a matter of Jewish law,[147] any territorial concession on Israel's part would endanger the lives of all Jews in the Land of Israel and is therefore forbidden. He also insisted that even discussing the possibility of such concessions showed weakness, would encourage Arab attacks, and therefore endanger Jewish lives.[148]
In US domestic politics, Schneerson supported government involvement in education and welcomed the establishment of the United States Department of Education in 1980 yet insisted that part of a school's educational mission was to incorporate the values espoused in the Seven Laws of Noah. He called for the introduction of a moment of silence at the beginning of the school day, and for students to be encouraged to use this time for such improving thoughts or prayers as their parents might suggest.[149]
In 1981, Schneerson publicly called for the use of solar energy. Schneerson believed that the US could achieve energy independence by developing solar energy technologies. He argued that the dependence on foreign oil may lead to the country compromising on its principles.[150][151]
Library dispute with Russia
[edit]In 2013, US federal judge Royce Lamberth ruled in favor of Chabad lawyers who sought contempt sanctions on three Russian organizations to return the Schneersohn Library, 12,000 books belonging to Rabbi Yosef Schneersohn seized and nationalized by the Bolsheviks in 1917–18, to the Brooklyn Chabad Library.[30][152] Chabad Rabbi Berel Lazar, Russia's Chief Rabbi, reluctantly accepted Putin's request in moving the Schneerson Library to Moscow's Jewish Museum and Tolerance Center as a form of compromise, which was criticized by the Chabad Library.[30]
Controversies
[edit]Chabad's 200-year history has seen several movement-wide controversies. Two major leadership succession controversies occurred in the 19th century; one took place in the 1810s following the death of the movement's founder, the other occurred in the 1860s following the death of the third Rebbe. Two other minor offshoot groups were formed later in the movement's history. The movement's other major controversy is Chabad messianism, which began in the 1990s.
Succession disputes and offshoot groups
[edit]A number of groups have split from the Chabad movement, forming their own Hasidic groups, and at times positioning themselves as possible successors of previous Chabad rebbes. Following the deaths of the first and third rebbes of Chabad, disputes arose over their succession.
Following the death of Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi, the first Chabad rebbe, a dispute over his succession led to a break within the movement. While the recognized successor was his oldest son, Rabbi Dovber Schneuri, a student of Rabbi Schneur Zalman, Rabbi Aaron HaLevi assumed the title of rebbe and led a number of followers from the town of Strashelye (forming the Strashelye dynasty). The new group had two rebbes, Rabbi Aaron and his son Rabbi Haim Rephael. The new group eventually disbanded following Rabbi Haim Rephael's death.[15][153] One of the main points the two rabbis disagreed on was the place of spiritual ecstasy in prayer. R' Aaron supported the idea while Rabbi Dovber emphasized genuine ecstasy can only be a result of meditative contemplation (hisbonenus). Rabbi Dovber published his arguments on the subject in a compilation titled Kuntres Hispa'alus ("Tract on Ecstasy").[154]
Following the death of the third Chabad rebbe, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneersohn (the Tzemach Tzedek), a dispute over his succession led to the formation of several Chabad groups. While Rabbi Shmuel Schneersohn was recognized as the heir to the Chabad-Lubavitch line, several of his brothers formed groups of their own in the towns of Kopys (forming the Kapust dynasty), Nezhin (forming the Niezhin dynasty), Lyady (forming the Liadi dynasty), and Ovruch (forming the Avrutch dynasty). The lifespan of these groups varied; Niezhin and Avrutch had one rebbe each, Liadi had three rebbes, and Kapust had four. Following the deaths of their last rebbes, these groups eventually disbanded.[155][156][157][158][159]
Two other minor offshoot groups were formed by Chabad Hasidim. The Malachim were formed as a quasi-Hasidic group. The group claims to recognize the teachings of the first four rebbes of Chabad, thus rivaling the later Chabad rebbes. The Malachim's first and only rebbe, Rabbi Chaim Avraham Dov Ber Levine haCohen (1859/1860–1938), also known as "The Malach" (lit. "the angel"), was a follower of the fourth and fifth rebbes of Chabad.[160][161][162] While Levine's son chose not to succeed him, the Malachim group continues to maintain a yeshiva and minyan in Williamsburg, Brooklyn.
Following the death of the seventh Chabad Rebbe, Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson, an attempt by Shaul Shimon Deutsch to form a breakaway Chabad movement, with Deutsch as "Liozna Rebbe", failed to gain popular support.[163][164][165][166]
Chabad messianism
[edit]A few years prior to Schneerson's death, some members of the Chabad movement expressed their belief that Menachem Mendel Schneerson was the Messiah. Those subscribing to the beliefs have been termed meshichists (messianists). A typical statement of belief for Chabad messianists is the song and chant known as yechi adoneinu ("long live our master", Hebrew: יחי אדונינו).[167]
Since 1994, most Chabad followers continue to believe in Schneerson as the Jewish messiah.[168] Chabad messianists either believe Schneerson will be resurrected from the dead to be revealed as the messiah or profess the belief that Schneerson never died in the first place. The Chabad messianic phenomenon has been met mostly with public concerns or opposition by non-Chabad Jewish leaders[citation needed].
Israeli Officials
[edit]Itamar Ben Gvir and Yoav Gallant have been invited to Chabad's headquarters. According to Rabbi Motti Seligson, a spokesperson for Chabad, "Ben-Gvir was invited by some members of the community, but that the event was not officially sanctioned or organized by the synagogue’s leadership".[169] Anti-Israel protestors demonstrated outside the building, clashing with attendees, leading to six arrests.[170] A Brooklyn resident was reportedly "chased, kicked, spit at and pelted with objects" after a mob of Orthodox men mistook the mask-wearing woman for a protester against Ben Gvir's visit.[171] Ben-Gvir was also scheduled to attend an event at the Jewish Children's Museum in Brooklyn, an official Chabad institution, to foundraise for Chabad of Hebron, although the event was cancelled.[172][173] Chabad of Hebron serves "on a weekly basis, thousands of IDF Soldiers".[174][175] Ben Gvir's visit followed a visit by Gallant who has an arrest warrrant from the International Criminal Court.[176]
In the arts
[edit]Art
[edit]Chabad Hasidic artists Hendel Lieberman and Zalman Kleinman have painted a number of scenes depicting Chabad Hasidic culture, including religious ceremonies, study and prayer. Chabad artist Michoel Muchnik has painted scenes of the Mitzvah Campaigns.[135]: 156
Artist and shaliach Yitzchok Moully has adapted silkscreen techniques, bright colours and Jewish and Hasidic images to create a form of "Chasidic Pop Art".[177]
Music
[edit]Vocalists Avraham Fried and Benny Friedman have included recordings of traditional Chabad songs on their albums of contemporary Orthodox Jewish music. Bluegrass artist Andy Statman has also recorded Chabad spiritual melodies (niggunim).
Reggae artist Matisyahu has included portions of Chabad niggunim and lyrics with Chabad philosophical themes in some of his songs.
In 2022, an Israeli theatrical company produced a Chabad-themed musical HaChabadnikim which follows two young men from Kfar Chabad who go to live in Tel Aviv. The musical runs for 140 minutes.[178]
Literature
[edit]In the late 1930s, Dr Fishl Schneersohn, a psychiatrist, pedagogical theorist, and descendant of the founder of Chabad authored a Yiddish novel titled Chaim Gravitzer: The Tale of the Downfallen One from the World of Chabad. The novel explores the spiritual struggle of a Chabad Hasid who doubts his faith and finally finds peace in doing charitable work.[179]
Novelist Chaim Potok authored a work My Name is Asher Lev in which a Hasidic teen struggles between his artistic passions and the norms of the community. The "Ladover" community is a thinly veiled reference to the Lubavitcher community in Crown Heights.[180][181]
Chabad poet Zvi Yair has written poems on Chabad philosophical topics including Ratzo V'Shov (spiritual yearning).
The American Jewish writer and publisher, Clifford Meth, wrote a short science fiction story depicting the future followers of the "70th Rebbe" of Chabad and their outreach efforts on an alien planet called Tau Ceti IV. The story is told through the eyes of a young extraterrestrial yeshiva student.[182][183]
The American Jewish writer and publisher, Richard Horowitz, wrote a memoir, The Boys Yeshiva, describing his time teaching at a Chabad yeshiva in Los Angeles.[184]
Film and television
[edit]The Chabad-Lubavitch community has been the subject of a number of documentary films. These films include:
- Chassidism - the Joyful path to G-d : A 1966 documentary of Chabad Chassidim in Kfar Chabad, Israel. This film was directed and narrated by Koby Jaeger.
- The Spark – a 28-minute film, produced in 1974, providing an overview of the Lubavitch and Satmar of New York.[185] The film was directed by Mel Epstein.[186]
- The Return: A Hasidic Experience – a 1979 documentary film on Jews who joined the Chabad movement, directed by Yisrael Lifshutz and Barry Ralbag.[187][188][189][186]
- What Is a Jew? – a 1989 documentary on Chabad produced by the BBC for the series Everyman.
- King of Crown Heights – a 60-minute, 1993 film on Lubavitcher Hasidim by Columbia University student Roggerio Gabbai[185]
- Fires in the Mirror: Crown Heights, Brooklyn and Other Identities – a 1993 TV adaptation of the one-person play by Anna Deavere Smith. It explores the Black and Hasidic viewpoints of people connected directly and indirectly to the Crown Heights riots.[190] The adaptation was produced by PBS as part of its American Playhouse series.[191]
- The Return of Sarah's Daughters – a 1997 documentary film contrasting three Jewish women, one of whom joins Chabad.[192]
- Blacks and Jews – A 1997 documentary written and directed by Deborah Kaufman and Alan Snitow on the Crown Heights riot and other incidents involving intergroup conflict.[193]
- Welcome to the Waks Family – a 2003 documentary of a Chabad family in Australia.[194]
- Leaving the Fold – a 2008 documentary on young men and women who left the Hasidic Jewish community. The film was directed by Eric R. Scott and the stories featured include former Hasidic Jews living in the United States, Israel and Canada.[195][196] Featured in the film are two young men from a Chabad family in Montreal as well as a French Lubavitch rabbi.
- Gut Shabbes Vietnam – a 2008 documentary on a Chabad family in Vietnam. Written and directed by Ido and Yael Zand.[197]
- Shekinah Rising – a 70 min, 2013 documentary exploring the perspectives of the female students of a Chabad school in Montreal[198][199][200]
- Kathmandu – a 2012 television series aired on Israeli television based on the lives of the Chabad emissaries in Kathmandu, Nepal.[201]
- Project 2x1 – a 30 min, 2013 documentary on the Chabad Hasidim and West Indian residents of Crown Heights, using Google Glass in place of conventional camera techniques[202][203][204][205]
- The Rabbi Goes West – a 2019 documentary on a Chabad rabbi who moves to Montana.[206]
- Guns and Moses – a 2024 film produced by Salvador Litvak and Nina Litvak. The film portrays Rabbi Mo (Mark Feuerstein), a Chabad emissary, and his wife, Rebbetzin Hindy (Alona Tal), whose community is targeted by a white supremacist who shoots and kills a congregant. Rabbi Mo later trains in the use of firearms and seeks to find the killer. The film was released to Jewish film festivals in 2024.[207] The film's original title was Man in the Long Black Coat.[208]
Other television
[edit]- Religious America: Lubavitch – a 28-minute, 1974 PBS documentary series episode focusing on a day in the life of a Lubavitcher man.[185]
- Outback Rabbis – (2018) 50 min television segment by Australian TV network, SBS, covering the regional and rural Australia (RARA) program of Chabad. Directed by Danny Ben-Moshe. Featured on the SBS "Untold Australia" series.
Notable people
[edit]A
[edit]B
[edit]- Yaacov Behrman
- Yisroel Bernath
- Moshe Yehuda Blau
- Shmuley Boteach
- Yosef Yeshaya Braun
- Menachem Brod
- Shmuel Butman
C
[edit]E
[edit]F
[edit]G
[edit]- Gershon Mendel Garelik
- Yitzchak Ginsburgh
- Leib Groner
- Yitzchok Dovid Groner
- Shemaryahu Gurary
- Aharon Gurevich
- Chaim Gutnick
- Mordechai Gutnick
- Moshe Gutnick
H
[edit]- Abraham Hecht
- Hanoch Hecht
- Jacob J. Hecht
- Moshe Hecht
- Shea Hecht
- Yosef Heller
- Hirschy Zarchi
- Chaim Mordechai Aizik Hodakov
- Gavriel Holtzberg
J
[edit]K
[edit]L
[edit]M
[edit]- Jonathan Markovitch
- David Masinter
- Shmarya Yehuda Leib Medalia
- Shmuel Leib Medalia
- Meir Shlomo Yanovsky
- Nissan Mindel
- Zalman Moishe HaYitzchaki
O
[edit]P
[edit]R
[edit]S
[edit]- Mordechai Scheiner
- Isaac Schneersohn
- Schneour Zalman Schneersohn
- Levi Yitzchak Schneerson
- Ezra Schochet
- Jacob Immanuel Schochet
- Yitzchak Schochet
- Yaakov Schwei
- Zelig Sharfstein
- Abraham Shemtov
- Levi Shemtov
- Sholom Shuchat
- Eliyahu Simpson
- Adin Steinsaltz
T
[edit]W
[edit]Y
[edit]Z
[edit]See also
[edit]- Death of Zvi Kogan
- Satmar (Hasidic dynasty)
- Ger (Hasidic dynasty)
- Bobov (Hasidic dynasty)
- Breslov (Hasidic dynasty)
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Marcin Wodziński, Historical Atlas of Hasidism, Princeton University Press, 2018. pp. 192–196.
- ^ Additional spellings include Lubawitz, and Jabad (in Spanish speaking countries)
- ^ "Hasidism". jewishvirtuallibrary.org.
- ^ a b c "AGUDAS CHASIDEI CHABAD OF | 650 F.Supp. 1463 (1987) | Leagle.com". Leagle. Archived from the original on June 9, 2015.
- ^ Dara Horn, June 13, 2014 "Rebbe of Rebbe's" Archived October 26, 2014, at the Wayback Machine The Wall Street Journal
- ^ "About Chabad-Lubavitch on". Chabad.org. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ a b "Swastikas daubed on Russian Chabad center in cradle of Lubavitch Hasidic movement". August 21, 2018.
- ^ a b Green, David B. (March 21, 2013). "This Day in Jewish History, 1920 Lubavitcher Rabbi Who Met with Freud Dies". Haaretz.
- ^ "Uganda is 100th outpost for Chabad-Lubavitch". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 2017-11-20.
- ^ Heilman, Samuel (December 15, 2005). "The Chabad Lubavitch Movement: Filling the Jewish Vacuum Worldwide". Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ a b Slater, Elinor and Robert, Great Jewish Men, Jonathan David Publishers 1996 (ISBN 08246 03818). p. 279.
- ^ "Jewish Americans in 2020" (PDF). Pew Research Center.
- ^ "Sholom DovBer Schneersohn (1860–1920)". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Altein, R, Zaklikofsky, E, Jacobson, I: Out of the Inferno: The Efforts That Led to the Rescue of Rabbi Yosef Yitzchak Schneersohn of Lubavitch from War Torn Europe in 1939–40, p. 270. Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch, 2002 ISBN 0-8266-0683-0
- ^ a b Beck, Atara (16 August 2012). "Is Chabad Lubavitch". The Jerusalem Post.
- ^ Jonathan D. Sarna (October 14, 2015). "The Jewish Future: What will be the condition of the Jewish community 50 years from now?". Commentary Magazine. Commentary.
- ^ Jew cleared in beard-cutting case, Philadelphia Daily News, May 25, 1984
- ^ Goldman, Ari L. (22 June 1983). "ATTACK ON RABBI BRINGS ANGUISH TO BOROUGH PARK". The New York Times.
- ^ Letters to the Editor, Time, August 1, 1983
- ^ Skolnik, Fred; Berenbaum, Michael, eds. (2007). Encyclopaedia Judaica: Blu-Cof. Granite Hill Publishers.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Maya Balakirsky Katz (October 11, 2010). The Visual Culture of Chabad. Cambridge University Press. p. 40. ISBN 9780521191630.
- ^ "Mrs. Sima Itkin OBM". The Joseph and Rebecca Peltz Center for Jewish Life.
- ^ "The Former Soviet Union". Chabad.org.
The communists persecuted, chased and harassed the Rebbe and his operatives. [...] Through the years of communism, hundreds of Chassidic activists were executed. Thousands more were arrested and sent to Siberia for years of hard labor.
- ^ Rabbi Yehuda Ceitlin (November 30, 2012). "Chabadniks proud of 'criminal' past".
- ^ Estraikh, G. (2018). Escape through Poland: Soviet Jewish Emigration in the 1950s. Jewish History, 31(3-4), 291-317.
- ^ Levin, Z. (2015). 1 "The Wastelands": The Jews of Central Asia. In Collectivization and Social Engineering: Soviet Administration and the Jews of Uzbekistan, 1917–1939 (pp. 7–26). Brill.
- ^ Beizer, M. (2007). The Jews of struggle: the Jewish national movement in the USSR, 1967–1989.
- ^ Gitelman, Z. (2007). Do Jewish Schools Make a Difference in the Former Soviet Union?. East European Jewish Affairs, 37(3), 377–398.
- ^ Ben Sales (10 April 2017). "Politico says Chabad is Trump's partner in – something. Not so fast". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- ^ a b c Cnaan Lipshiz (5 June 2015). "Why Russian Chief Rabbi stands by Vladimir Putin". The Forward. Retrieved June 4, 2017.
- ^ Mindel, Nissan (1985). "Intro". The Philosophy of Chabad. Vol. 2. Brooklyn: Kehot Publication Society. ISBN 978-0826604170.
- ^ a b c The Encyclopedia of Hasidism, "Habad", Jonathan Sacks, pp. 161–164
- ^ Hasidism: The movement and its masters, Harry M. Rabinowicz, 1988, pp. 83–92, Jason Aronson, London ISBN 0-87668-998-5
- ^ a b Leadership in the Chabad movement, Avrum Erlich, Jason Aronson, 2000 ISBN 0-7657-6055-X
- ^ Hayom Yom, p. A10
- ^ Chanoch Glitzenshtein, Sefer Hatoldos Tzemach Tzedek
- ^ Hayom Yom, p. A14
- ^ "Sefer HaToldos Admur Maharash". Archived from the original on April 22, 2008. Retrieved March 8, 2008.
- ^ Hayom Yom, pp. 15–16
- ^ Encyclopedia of Hasidism, "Schneersohn, Joseph Isaac". Naftali Lowenthal. Aronson, London 1996. ISBN 1-56821-123-6
- ^ Sharon Chisvin (5 August 2007). "Chabad Lubavitch centre set for River Heights area". Winnipeg Free Press. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007.
- ^ Weiss, Steven I (January 20, 2006). "Orthodox Rethinking Campus Outreach". The Jewish Daily Forward. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Jewish Literacy, Telushkin, William Morrow 2001, p. 471
- ^ Tanya, Shneur Zalman of Liadi, Chapter 13.
- ^ Deuteronomy 30:14
- ^ The Encyclopedia of Hasidism, "Tanya", Jonathan Sacks, pp. 475–477 (15682–11236)
- ^ Tanya, ch. 12
- ^ Cohen, J. Simcha (December 28, 1999). How Does Jewish Law Work?. Jason Aronson. p. 329. ISBN 978-0-7657-6090-6. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- ^ a b Liebman, Charles S. "Orthodoxy in American Jewish Life." The American Jewish Year Book (1965): 21–97.
- ^ Goldschmidt, Henry (2006). Race and Religion Among the Chosen People of Crown Heights. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813538839. JSTOR j.ctt5hj1p2. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- ^ JTA (11 February 2016). "In all-Chabad Israeli village, Brooklyn meets country living". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- ^ Shokeid, Moshe (1988). Children of Circumstances: Israeli Emigrants in New York. Anthropology of Contemporary Issues. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. pp. 139–160. ISBN 978-0801420788.
- ^ "Did You Know 25% of Chabad in Montreal are Sefardi?". The Chabad Sociologist. July 9, 2013.
- ^ Shahar, Charles. "A Comprehensive Study of the Ultra Orthodox Community of Greater Montreal (2003)". Federation CJA (Montreal). 2003.
- ^ Ferziger, Adam S. "Church/sect theory and American orthodoxy reconsidered."Ambivalent Jew—Charles S. Liebman in memoriam, ed. Stuart Cohen and Bernard Susser (2007): 107–124.
- ^ a b Comenetz, Joshua. "Census-based estimation of the Hasidic Jewish population." Contemporary Jewry 26, no. 1 (2006): 35.
- ^ a b c Shaffir, William. "The renaissance of Hassidism." Archived 2016-11-06 at the Wayback Machine Jewish Journal of Sociology 48, no. 2 (2006).
- ^ Greenfield, Nicole. ."Birth of Hipster Hasidism?" Archived 2021-07-16 at the Wayback Machine Religion Dispatches. University of Southern Carolina. February 2, 2012
- ^ Nussbaum-Cohen, Debra. "Of Hasids, Hipsters, and Hipster Hasids." The Jewish Daily Forward. January 26, 2012.
- ^ "Regional Statistics". Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2025-02-09.
- ^ a b "The Chabad Hassidic Community in Tzfat". Safed.co.il. Retrieved September 14, 2014.
- ^ "Sefer HaZohar – Including Glosses by Rabbi Yeshaya Horowitz of Safad and His Son Rabbi Shmuel Horowitz Author of 'Yemei Shmuel.'" Judaica Auction no. 27- Books and Manuscripts Archived October 6, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. Kedem Auction House. Retrieved September 14, 2014. Retrieved 24 April 2016
- ^ Gutwirth, Jacques. 2005. Hassidim in France today. Jewish Journal of Sociology 47(1–2). pp.5–21.
- ^ "Chabad of Montreal: Here's the stats!!!". The Chabad Sociologist. October 13, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Shahar, Charles. "Main Report: A Comprehensive Study of the Ultra Orthodox Community of Greater Montreal (2003)". Federation CJA (Montreal). (2003): pp. 7–33.
- ^ Lapidus, Steven (2004). "The Forgotten Hasidim: Rabbis and Rebbes in Prewar Canada". Canadian Jewish Studies. 12. Retrieved January 13, 2014.
- ^ Salami, Daniel (2020-06-11). "A robust Jewish life exists in the U.A.E." ynetnews. Retrieved 2020-06-18.
- ^ "Baltimore Jewish Life | A New Talmud Torah Opens in Dubai". baltimorejewishlife.com. Retrieved 2020-06-18.
- ^ "Kiddush, Torah learning, and gefilte fish in Dubai – Jewish World". Arutz Sheva. 11 June 2020. Retrieved 2020-06-18.
- ^ Nissan Mindel. "Rabbi Isaac Luria – The Ari Hakodosh". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Gebrokts: Wetted Matzah". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ a b "Shabbat Candle-Lighting Times". chabad.org.
- ^ Schneersohn, Shalom Dovber. Tanu Rabbanan: Ner Chanukah Sichos In English, N.Y., 1990.
- ^ "Laws and Customs: Chanukah". CrownHeights.info. November 24, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Dalfin, Chaim (September 6, 2012). "Chabad Elul Customs". Shmais.com. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Menachem Mendel Schneerson. "Chai Elul: Breathing New Life Into Our Divine Service". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Dade Jews throw birthday party for New York Rabbi", David Hancock, The Miami Herald, April 14, 1992
- ^ a b "Yahrtzeit Observances". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "A Brief Biography". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Chof Beis Shvat. Chabad.info". Archived from the original on December 16, 2013.
- ^ Burstein, Paul (2011). "Jewish Nonprofit Organizations in the U.S.: A Preliminary Survey". Contemporary Jewry. 31 (2): 129–148. doi:10.1007/s12397-010-9028-5. S2CID 144478093.
- ^ Drake, Carolyn (February 2006). "A Faith Grows in Brooklyn". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 2006-02-03. Retrieved 2006-01-23.
- ^ "Facts and Statistics - Chabad.org".
- ^ "Chabad-Lubavitch Directory". Chabad. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Lubavitch, Chabad. "Chabad Lubavitch Brooklyn New York NY World Headquarters". lubavitch.com. Archived from the original on 2013-09-01. Retrieved 2013-11-06.
- ^ Lubavitch, Chabad. "Chabad Lubavitch Brooklyn New York NY World Headquarters". lubavitch.com. Archived from the original on 2015-10-16. Retrieved 2013-11-04.
- ^ Marcelle S. Fischler (December 16, 2005). "Is It a Home or a House of Worship?". The New York Times. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Passover seders, around the world". Kentucky New Era. Associated Press. March 23, 2007. p. 28. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Challenge
- ^ Chumash Devarim. New York: Kehot Publication Society. 2011. pp. vii. ISBN 978-0-8266-0194-0.
- ^ "N.Y. / Region: 'Are You Jewish?'", The New York Times, 27 April 2011, archived from the original on 2021-12-12, retrieved 2019-12-05
- ^ a b c "Facts and Statistics". Chabad.
- ^ "Banquet/Partner". Kinus Hashluchim. Retrieved 2019-12-05.
- ^ "Shluchim Roll Call - International Conference of Chabad Emissaries (2019)". Chabad.org. Retrieved 2019-12-05.
- ^ Ralph Blumenthal (November 29, 2008). "Jewish Center Is Stormed, and 6 Hostages Die". The New York Times. p. A13. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Joshua Runyan (November 30, 2008). "Funeral Preparations for Chabad House Victims Under Way". Chabad. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ Damien McElroy (December 1, 2008). "Mumbai attacks: Jews tortured before being executed during hostage crisis". Archived from the original on 2022-01-12. Retrieved February 8, 2017.
- ^ "Obama sends condolences to Chabad". Jewish Telegraph Agency (JTA). December 4, 2008. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Israeli Chabad couple to be expelled from India 'for spying' | The Times of Israel". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 2021-06-10.
- ^ Mark Avrum Ehrlich (2004). The Messiah of Brooklyn: Understanding Lubavitch Hasidim Past and Present. Jersey City, N.J.: KTAV. p. 134. ISBN 978-0881258363.
- ^ Fishkoff, Sue, The Rebbe's Army: Inside the World of Chabad-Lubavitch, Schocken Books 2003 (ISBN 08052 11381) pages 160–161.
- ^ "Comparing Full Time and Part Time Numbers at Chabad Schools". The Chabad Sociologist. August 6, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ a b Schick, Marvin (October 2009). "A Census of Jewish Day Schools in the United States 2008–2009" (PDF). Avi Chai Foundation. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Wertheimer, Jack (August 2008). "A Census of Jewish Supplementary Schools in the United States: 2006–2007" (PDF). Avi Chai Foundation. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Wertheimer, Jack (June 16, 2014). "Why the Lubavitch Movement Thrives in the Absence of a Living Rebbe". JA Mag in Jewish World. Orthodox Union. Retrieved 30 September 2014.
Among the latter is the Jewish Learning Institute, the largest educational program for Jewish adults in the world (with the possible exception of the Daf Yomi enterprise), which currently enrolls over 66,000 teens and adults at some 850 sites around the world, each following a prescribed course of study according to a set timetable.
- ^ Dashefsky, Arnold; Sheskin, Ira, eds. (2014). "National Jewish Organizations". American Jewish Year Book. Vol. 113 (Volume 113 ed.). Springer International Publishing. pp. 447–597. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-01658-0_10. ISBN 978-3-319-01657-3. S2CID 154745222.
... is currently the largest provider of adult Jewish learning. JLI's mission is to inspire Jewish learning worldwide and to transform Jewish life and the greater community through Torah study. Its goal is to create a global network of informed students connected by bonds of shared Jewish experience. JLI's holistic approach to Jewish study considers the impact of Jewish values on personal and interpersonal growth. (The authors of the book are Professor Ira Sheskin of Department of Geography and Regional Studies, The Jewish Demography Project, The Sue and Leonard Miller Center for Contemporary Judaic Studies, University of Miami, and Professor Arnold Dashefsky, Department of Sociology, The Center for Judaic Studies and Contemporary Jewish Life, University of Connecticut.)
- ^ Hayom Yom, p. A38
- ^ Heilman, Samuel C. (2017-06-06), "ChaBaD Lubavitch", Who Will Lead Us?, University of California Press, doi:10.1525/california/9780520277236.003.0006, ISBN 9780520277236, retrieved 2022-04-26
- ^ Fishkoff, Sue. "‘Praying without paying’ becoming a more popular option among shuls"[permanent dead link], Texas Jewish Post. Accessed September 22, 2007. "Many people credit Chabad-Lubavitch with spearheading the movement for free holiday services across the denominational spectrum."
- ^ "The Rebbe's 10-Point Mitzvah Campaign". Chabad. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ a b Fishkoff, Sue, The Rebbe's Army, Schocken books 2003 (ISBN 08052 11381)[page needed]
- ^ "International Roll Call, Conference of Chabad Emissaries (2021)". Chabad.org. Chabad-Lubavitch. Retrieved 10 March 2023.
- ^ "Facts and Statistics". Chabad.org. Chabad-Lubavitch. Retrieved 10 March 2023.
- ^ Yellin, Deena (2022-11-18). "Dinner for 6,500: NJ to host record gathering for growing Chabad Jewish movement". NorthJersey.com. Retrieved 10 March 2023.
- ^ "1974: The Mitzvah Tank on". Chabad. Retrieved 2011-04-13.
- ^ "Directory of Chabad on Campus". Chabad. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ "Address by Professor Alan Dershowitz". Oxford Chabad Society. 2005-11-27. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Jewish school shooting survivors seek healing at New York meet-up". Times of Israel.
- ^ "Chabad Teen Network". CTeen.
- ^ a b CTeen International. "Orlando well represented at International CTeen Shabbaton". Heritage Florida Jewish News.
- ^ Levy, Faygie (28 May 2015). "In Just Five Years, CTeen Movement Attracts Tens of Thousands of Young Jews". eJewish Philanthropy. Archived from the original on 2015-06-01.
- ^ Smilk, Carin M. (July 21, 2017). "Teens and mentors from Bangkok to Brazil at Poconos Retreat". Israel National News. Retrieved 2021-09-14.
- ^ Bowling, Suzanna (2 March 2020). "Thousands of Jewish Teens Gather in Times Square For Havdalah – Times Square Chronicles". Times Square Chronicles. Archived from the original on 2020-05-24. Retrieved 2021-11-23.
- ^ "Local teens have time of their lives at NYC Shabbaton". Jewish Community Voice. 10 April 2019.
- ^ "Chabad of Hunterdon CTeen group makes impact in community". Nj. 26 February 2015.
- ^ "Chabad and Yeshiva University Offer Torah Class for High Schoolers". Jewish Journal. 14 October 2020. Archived from the original on 2020-10-14.
- ^ "CTeen Summer 'Quest' to Explore Roots in Poland and Israel - Another adventure in the roster of programs for Jewish youth - Chabad.org".
- ^ "Meet Hallandale's New CTeen Directors". 17 October 2019.
- ^ "CTeen | Leadership". CTeen.
- ^ "Jewish Teens in Skokie, Ill., Respond to Hate With Celebration - Windows smashed in nearby synagogue followed by outpouring of Jewish pride - Chabad.org".
- ^ "The National Campus Office". lubavitch.com. 2009. Archived from the original on 19 August 2010. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ^ "By us, for us". LivingWorks. Archived from the original on 2021-11-03. Retrieved 2021-11-03.
- ^ "Suicide Prevention Training Workshop". TAPinto.
- ^ "Publishing". 16 April 2025.
- ^ a b Maya Balakirsky Katz (2010). The Visual Culture of Chabad. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Zaleski, Jeffrey P. (June 1997). The Soul of Cyberspace: How New Technology Is Changing Our Spiritual Lives. Harpercollins. ISBN 978-0-06-251451-6. Retrieved April 7, 2007.
- ^ Our Founding Director Archived August 27, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, Chabad.org
- ^ Harmon, Ami (December 13, 1998). "Yosef Kazen, Hasidic Rabbi And Web Pioneer, Dies at 44". The New York Times. Retrieved January 1, 2010.
- ^ Steinfels, Peter (January 22, 2000). "Beliefs". The New York Times. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Golan, Oren (2012). "Frontiers of online religious communities: The case of Chabad Jews". In Heidi Campbell (ed.). Digital Religion: Understanding Religious Practice in New Media Worlds. Routledge. p. 160. ISBN 9780415676106. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ^ Shaer, Matthew (2011). Among Righteous Men: A Tale of Vigilantes and Vindication in Hasidic Crown Heights. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118095201. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 17, 2014.[page needed]
- ^ Tress, Luke (2024-12-24). "This Chabadnik is on a mission to wrap tefillin for US Jewish celebrities". The Times of Israel. Retrieved 2025-05-21.
- ^ Bouskila, Inbal Ann (2024-11-28). "Chabad couple speak out after murder of rabbi in Dubai: 'The answer to hate is to be stronger Jews'". ynetnews. Retrieved 2025-05-21.
- ^ Julie Wiener (September 1, 2000). "Chabad camps electrify many Jews, not just Lubavitch". J. The Jewish News of Northern California. Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
- ^ "Camp Gan Israel Directory". Chabad. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ "When Silence is a Sin". Sichos in English. Letter to Zalman Shazar Archived November 13, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Based on Shulchan Aruch Orach Chayim, 328
- ^ Essentially his argument sought merely the position that would prevent loss of life, rather than taking a stance in the nature of the Land of Israel and Zionism. Freeman, Tzvi. "Should I Pray for the Death of Terrorists?". Chabad. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ Hayom Yom, p. A29
- ^ "Website video link". chabad.org. April 15, 1981. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ "Chabad.org website video link". chabad.org. 1981-04-15. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ^ Avital Chizhik (September 30, 2013). "Putin refuses to let the Lubavitcher Rebbe's library leave Moscow". Tablet. Retrieved June 4, 2017.
- ^ Ehrlich, Avrum M.; Ehrlich, Mark Avrum (2000). "11: The Leadership of Dov Ber". Leadership in the HaBaD Movement: A critical evaluation of HaBaD leadership, history, and succession. Jason Aronson. ISBN 978-0765760555.[page needed]
- ^ Ehrlich, Leadership in the HaBaD Movement, pp. 160–192, esp. pp. 167–172.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Hasidism, entry: Schneersohn, Shmaryahu Noah. Naftali Lowenthal. Aronson, London 1996. ISBN 1-56821-123-6
- ^ Kaminetzky, Yosef Y. (2005). Days in Chabad. Brooklyn: Kehot Publication Society. p. 19. ISBN 978-0826604897.
- ^ "Rabbi Chaim Schneur Zalman of Liadi" (PDF). L'Maan Yishmeu (128). 2012.
- ^ Zevin, Shelomoh Yosef; Kaploun, Uri (1980). A Treasury of Chassidic Tales on the Torah: A Collection of Inspirational Chassidic Stories Relevant to the Weekly Torah Readings. Vol. 1. Mesorah Publications. p. 115. ISBN 978-0899069005.
- ^ Dalfin, Chaim (1998). The Seven Chabad-Lubavitch Rebbes. Jason Aronson. ISBN 978-1461710134.
- ^ B. Sobel, The M'lochim
- ^ Ehrlich, M. Avrum (2000). Leadership in the HaBaD movement : a critical evaluation of HaBaD leadership, history, and succession. Northvale, N.J.: J. Aronson. pp. 269–271. ISBN 0-7657-6055-X. OCLC 39633846.
- ^ Mintz, Jerome R. (1992). Hasidic People: A Place in the New World. Harvard University Press. pp. 21–26. ISBN 978-0674041097.
- ^ "Dissidents Name 'Rebbe'," The Forward, December 6, 1996
- ^ Heinon, Herb, "Bigger than Death," The Jerusalem Post, August 15, 1997
- ^ Segall, Rebecca, "Holy Daze The problems of young Lubavitcher Hasidim in a world without the Rebbe," The Village Voice, September 30, 2000
- ^ Eisenberg, Charles. The Book of Daniel: A Well Kept Secret. Xulon Press. 2007. Page 103.
- ^ The full text is Yechi adoneinu moreinu v'rabbeinu melech ha-moshiach l'olam vo'ed ("Long live our master, our teacher, and our rabbi, King Messiah, for ever and ever).
- ^ Newfield, Joseph (Spring–Summer 2021). "After The Death Of Chabad's Messiah". Harvard Divinity Bulletin. Archived from the original on 2021-05-26.
- ^ "US visit by far-right Israeli minister draws tense protests and 'big fissures' in Jewish community". AP News. April 25, 2025.
- ^ OFFENHARTZ, JAKE (April 25, 2025). "Mob chased Brooklyn woman after mistaking her for protester at speech by Israeli security minister". AP News.
- ^ OFFENHARTZ, JAKE (April 28, 2025). "Mob chased Brooklyn woman after mistaking her for protester at speech by Israeli security minister". AP News.
- ^ Lapin, Andrew (April 18, 2025). "Brooklyn event with Itamar Ben-Gvir cancelled days before Israeli far-right minister's US trip". Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
- ^ Maltz, Judy (Apr 30, 2025). "What Chabad really thinks about Itamar Ben-Gvir and his far-right ideology". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 30 April 2025.
- ^ "About Us". Chabad of Hebron. Archived from the original on 9 Aug 2020.
- ^ "Chabad of Hebron - Chabad House - Hebron, Israel". www.chabad.org.
- ^ Keene, Louis (April 27, 2025). "Protesters clash in Crown Heights as Ben-Gvir visits Chabad headquarters". The Forward.
- ^ "'Under the Black Hat' Pop Art in Jerusalem Focuses on Chassidim – Rabbi Yitzchok Moully brings spiritual and emotional depth to a new exhibit". chabad.org.
- ^ "HaChabadnikim." www.cameri.co.il. Accessed 12 Nov. 2023.
- ^ "חיים גראַװיצער (די געשיכטע פֿון דעם געפֿאַלענעם): פֿון דער חבדישער װעלט | Chaim Gravitzer (The Tale of the Downfallen One): From the World of Chabad". In geveb.
- ^ "Hirsch Succeeds with Theatrical Production of 'My Name is Asher Lev'". 29 August 2012.
- ^ Cochrum, Alan Morris. "CHILDREN OF ISRAEL: JACOB FIGURES AND THEMES IN THE NOVELS OF CHAIM POTOK" (PDF). ResearchCommons. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Aardwolf (1994) comic books".
- ^ "Comics Bulletin - Clifford Meth: Meth Addict - A Funny Thing Happened on the Way to the Library".[permanent dead link]
- ^ Horowitz, Richard. "The Boys Yeshiva: A Memoir" – via Amazon.
- ^ a b c Documentary Films about Hasidism. PBS
- ^ a b "Movies: Theater Guide". New York. September 15, 1986. p. 176 – via Google Books.
- ^ "An Interview with the Slopeover Rebbe". thejewishreview.org.
- ^ "News Brief – Jewish Telegraphic Agency". 29 April 1981.
- ^ The Return: a Hassidic experience. June 18, 2020. OCLC 50902286.
- ^ Smith, Anna Deavere. Fires in the Mirror. New York City: Bantam Doubleday Dell Publishing Group, Inc., 1993.
- ^ O'Connor, John J. (April 28, 1993). "Review/Television; One-Woman Show on Black vs. Jew". The New York Times.
- ^ "A Life Apart: Hasidism In America – Filmography". PBS.
- ^ "Broadcast of Deborah Kaufman's "Blacks and Jews" | Jewish Women's Archive". jwa.org.
- ^ "Welcome to the Waks Family". NFSA Online Shop.
- ^ Unreich, Rachelle (June 23, 2008). "Leaving the fold". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ "Leaving The Fold" (PDF). SEVENTH ART RELEASING. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-09-07. Retrieved 2023-10-22.
- ^ "Search results from Film, Video, Vietnam, Vietnam, Hebrew". Library of Congress.
- ^ "Secrets and lives of Hasidic women". The Globe and Mail.
- ^ "New film Shekinah provides unprecedented access to the world of young Hasidic women". TheSuburban.com. October 11, 2013. Archived from the original on December 20, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Arnold, Janice (October 20, 2013). "Film presents chassidic women's attitudes to intimacy". The Canadian Jewish News. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Zany, Heartfelt 'Kathmandu' Evokes the Soul of Jewish Culture in Nepal". December 5, 2012.
- ^ Hampton, Matthew (November 26, 2013). "Crown Heights 'Google Glass' Doc Premieres Next Month". Prospect Heights Patch. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Piras, Lara (October 9, 2013). "Google Glass Filmed Documentary Goes Where Normal Camera Crews Can't". psfk.com. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Evans, Lauren (October 7, 2013). "Intrepid 20-Somethings Examine Crown Heights Through Google Glass". Gothamist. Archived from the original on December 25, 2014. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ Sharp, Sonja (October 7, 2013). "Crown Heights Documentary Claims to be First Ever Shot With Google Glass". DNAInfo. Archived from the original on November 4, 2014. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ "Rabbi Goes West, The". jfi.org.
- ^ "Guns and Moses: The Heroic Hasid". Jewish Journal. Accessed 22 June 2024.
- ^ Mark Feuerstein, Neal McDonough, Dermot Mulroney, Christopher Lloyd Starring in ‘Man in the Long Black Coat’ (EXCLUSIVE). Variety. Accessed 22 June 2024.
Sources
[edit]- Menachem Mendel Schneerson (1994). Hayom Yom. Kehot Publication Society. ISBN 978-0-8266-0669-3.
Further reading
[edit]- Schneerson, Menachem Mendel. On the Essence of Chasidus: A Chasidic Discourse by Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson of Chabad-Lubavitch. Merkos L'Inyonei Chinuch, 2003 (ISBN 0-8266-0466-8)
- Drake, Carolyn. "A Faith Grows in Brooklyn". National Geographic (February 2006).
- Ehrlich, Avrum M. Leadership in the Chabad Movement: A Critical Evaluation of Habad Leadership, History, and Succession, Jason Aronson, 2000. (ISBN 0-7657-6055-X)
- Feldman, Jan L. Lubavitchers as Citizens: A Paradox of Liberal Democracy, Cornell University Press, 2003 (ISBN 0-8014-4073-4)
- Fishkoff, Sue. The Rebbe's Army: Inside the World of Chabad-Lubavitch, Schocken, 2003 (ISBN 0-8052-4189-2)
- Heilman, Samuel and Menachem Friedman. The Rebbe: The Life and Afterlife of Menachem Mendel Schneerson (Princeton University Press; 2010) 400 pages
- Hoffman, Edward. Despite All Odds: The Story of Lubavitch. Simon & Schuster, 1991 (ISBN 0-671-67703-9)
- Jacobson, Simon. Toward a Meaningful Life: The Wisdom of the Rebbe, William Morrow, 2002 (ISBN 0-06-051190-7)
- Katz, Maya Balakirsky, "Trademarks of Faith: Chabad and Chanukah in America", Modern Judaism, 29,2 (2009), 239–267.
- Challenge: An Encounter with Lubavitch-Chabad, Lubavitch Foundation of Great Britain, 1973. ISBN 0-8266-0491-9.
- Miller, Chaim. Turning Judaism Outward: A Biography of Rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson the Seventh Lubavitcher Rebbe. Kol Menachem, 2014.
- Mindel, Nissan. The Philosophy of Chabad. Chabad Research Center, 1973 (ISBN 082660417X)
- Oberlander, Boruch and Elkanah Shmotkin. Early Years: The Formative Years of the Rebbe, Rabbi Menachem M. Schneerson, as Told by Documents and Archival Data, Kehot Publication Society. 2016. (ISBN 978-1-932349-04-7).
- Steinzaltz, Adin Even Israel. My Rebbe. Koren Publishers, 2014.
- Tannenbaum, Michal and Hagit Cohen. 2018. "Language Educational Policy in the Service of Group Identity: The Habad case". Language Policy Volume 17, Issue 3, pp 319–342.
- Telushkin, Joseph. Rebbe: The Life and Teachings of Menachem M. Shneerson, the Most Influential Rabbi in Modern History. Harperwave, 2014.
- Weiss, Steven I. (January 20, 2006). "Orthodox Rethinking Campus Outreach" Archived 2007-05-05 at the Wayback Machine. The Jewish Daily Forward.
Early community histories of Chabad produced by members or former members of the Chabad community include Toldot Amudei HaChabad (Konigsberg, 1876) by Michael Levi Rodkinson and Beit Rebbe (Berdichev, 1902) by Hayim Meir Heilman.
- Tworek, W. (2017). Lubavitch Hasidism. Oxford Bibliographies.
- Karlinsky, N. (2007). The Dawn of Hasidic—Haredi Historiography. Modern Judaism-A Journal of Jewish Ideas and Experience, 27(1), 20-46.
- Assaf, D. (2010). Untold Tales of the Hasidim: Crisis & Discontent in the History of Hasidism. UPNE.
 KSF
KSF