Diu district
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 10 min
Diu district
Distrito de Dio[1] | |
|---|---|
 Map of Diu district, the exclave of Simbor is not shown | |
| Coordinates: 20°43′N 70°59′E / 20.71°N 70.98°E | |
| Country | |
| Union Territory | |
| Founded by | Francisco de Almeida |
| Headquarter | Diu town |
| Area | |
• Total | 40 km2 (20 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 30 m (100 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
• Total | 52,074 |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,400/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Diucar/ Diuese[2][3] |
| Languages[4] | |
| • Official | Hindi, English |
| • Other | Gujarati, Portuguese[5][6][7] |
| Website | http://diu.gov.in/ |
Diu district /ˈdiːuː/ is one of the three districts of the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu of India.[8] The district is made up of Diu Island and two small enclaves of Simbor and Gogola, at the border with the state of Gujarat. The district headquarters are at Diu Town. It is the ninth least populous district in the country (out of 640).[9]
History
[edit]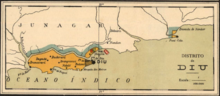

The district was historically part of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat. Mirroring the system of administrative division in Portugal, Diu district (Distrito de Diu) was established as an administrative division of the Portuguese State of India (Estado da Índia) in the first half of the 19th century. It was headed by a district governor, subordinate to the governor-general of Portuguese India in Goa. The district included the single municipality of Diu, which was further subdivided into civil parishes.[10]
It remained an overseas territory of Portugal until it was annexed by Indian forces on 19 December 1961. From 1961 to 1987, it was a part of the union territory of Goa, Daman and Diu. In 1987, it became a part of the newly formed union territory of Daman and Diu. In January 2020, the district became part of the new union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.[10]
Geography
[edit]Diu district occupies an area of 40 square kilometres (15 sq mi),[11]
It consists of Diu Island and a part on the mainland (the Ghogolá peninsula). 20 km East of Diu Island, is the small territory of Simbor.
Sub-districts
[edit]Diu Island
[edit]The town of Diu and most of the district's villages and settlements are on Diu Island. Many of these places have been renamed since the Invasion of 1961.
| Settlement type | Portuguese name | Indian name |
|---|---|---|
| Town | Diu | Diu |
| Village | Podamo | Fudam |
| Village | Bunxivará | Bucharwada |
| Settlement | Dangarvadi | Dangarwadi |
| Village | Brancavará | Vanakbara |
| Uninhabited | Fortim do Mar | Pani Kota |
| Uninhabited | Castilo de Diu | Diu Fortress |
Ghogholá
[edit]The area on the mainland borders Gir Somnath district of Gujarat. It contains the village of Ghogholá. The village lies on the mainland opposite the eastern end of the island .
Simbor
[edit]The tiny territory of Simbor, located about 25 km east of the town of Diu, is also part of the district. It has no permanent population.
Demographics
[edit]According to the 2011 census Diu district has a population of 52,074,[9] roughly equal to the nation of Saint Kitts and Nevis.[12] This gives it a ranking of 631st in India (out of a total of 640).[9] The district has a population density of 1,301 inhabitants per square kilometre (3,370/sq mi) .[9] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 17.73%.[9] Diu has a sex ratio of 1030 females for every 1000 males,[9] and a literacy rate of 83.36%.[9]
Sister cities
[edit]Diu Island is twinned with the city of Loures, in Portugal.[13]
Landmarks
[edit]Diu is home to a few surviving buildings and monuments with Portuguese architecture. The best preserved are the churches and fortifications.
The nearest railway junction is Veraval, which is 90 km from Diu. Major cities like Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Pune, Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh), Dwarka and Thiruvananthapuram are directly connected to Veraval Railway Station. Delwada is 8 km from Diu.
Churches and chapels
[edit]
1. Churches of St. Paul and St. Thomas (Diu)
2. Church of St. Francis of Assisi (Diu)
3. Church of Our Lady of Remedes (Fudam)
4. Church of Our Lady of Mercy (Vanakbara)
There has been a steady exodus of Christians from Diu[14] ever since the Invasion of 1961. This has led to many of their historic and historic and religious sites being victims of abandonment, disrepair, conversion to secular use or demolishment.
| Type[15][16] | Portuguese Name | English Translation | Location | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cathedral | Catedral de São Paulo (Sé) | Church of St. Paul | Diu Town | Active (demoted to church) |
| Church | Igreja de São Tomás | Church of St. Thomas | Diu Town | Secularized (Museum) |
| Church | Igreja de São Francisco de Assis | Church of St. Francis of Assisi | Diu Town | Secularized (Hospital) |
| Church | Igreja de São João de Deus | Church of St. John of God | Diu Town | Inactive (Ruins) |
| Church | Igreja de Nossa Senhora da Esperança | Church of Our Lady of Hope | Diu town | Inactive (Ruins) |
| Church | Igreja da Misericórdia | Church of Mercy (informally 'Fort Church') | Diu Fort | Inactive (Ruins) |
| Church | Igreja de Nossa Senhora dos Remédios | Church of Our Lady of Remedies | Podamo | Active |
| Church | Igreja de Nossa Senhora da Misericórdia | Church of Our Lady of Mercy | Brancavará | Inactive (Intact) |
| Convent | Convento dos Dominicanos | Dominican Convent | Diu town | Demolished (1961) |
| Convent | Convento de Santa Ana | Convent of St. Anne | Diu Town | Active (School) |
| Chapel | Capela de São Tiago | Chapel of St. James | Diu Fort | Inactive (Ruins) |
| Chapel | Capela de São Martinho | Chapel of Saint Martin | Diu Fort | Demolished (2023) |
| Chapel | Capela de Nossa Senhora da Vitória | Chapel of Our Lady of Victory | Fortim do Mar | Inactive (Ruins) |
Fortresses
[edit]Due to constant invasions from neighboring kingdoms as well as distant powers, the Portuguese built several fortifications all over the district. Most survived to this day, although some have little to no physical traces of their existence.
| Portuguese Name | English Translation | Location | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cidadela de Diu | Diu Fortress | Diu Town | |
| Fortim do Mar | Panikota | Diu Town | Ruin |
| Forte Santo Antonio | Fort St. Anthony of Simbor | Simbor | Ruin |
| Forte de Nagoá | - | Nagoá near Podamo | Ruins lost |
| Forte de Barra | - | Brancavará | Ruins lost |
Beaches
[edit]- Nagoá Beach, most visited beach in on Diu.
- Ghogolá Beach, largest beach off the island of Diu.
- Chakratirth Beach
- Barra Beach
- Nadia Caves
Gallery
[edit]-
Diu Fort Fixed Cannons
-
St. Thomas Church, Diu
-
Diu fort
-
Nadia Caves of Diu
-
St. Paul's Church, Diu
-
Church in Nani Daman Fort
-
Se Cathedral
-
View of Water Fort Prison from Diu Fort with watchtower of Diu Fort
-
Portuguese Fort
-
Diu shores in Monsoon
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Almeida, José C. (1965). "Alguns aspectos demograficos de Goa, Damao e Dio: Some demographic aspects of Goa, Daman & Diu".
- ^ "Survey chapter: Diu Indo-Portuguese".
- ^ "Diu Indo-Portuguese at present".
- ^ "52nd Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India" (PDF). 29 March 2016. p. 87. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ "District at a Glance".
- ^ "Survey chapter: Diu Indo-Portuguese".
- ^ "Firangiwada Heritage Walk".
- ^ "Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu UTs merge for 'better admin efficiency, service': MoS Home". Indus Dictum. 4 December 2019. Archived from the original on 11 November 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- ^ a b "Diu History". Diu Tourism Department. U.T. Administration of Dadra & Nagar Haveli And Daman & Diu. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- ^ Srivastava, Dayawanti et al. (ed.) (2010). "States and Union Territories: Daman and Diu: Government". India 2010: A Reference Annual (54th ed.). New Delhi, India: Additional Director General, Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Government of India. p. 1216. ISBN 978-81-230-1617-7.
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison: Population". Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2011.
Saint Kitts and Nevis 50,314 July 2011 est.
- ^ "Município – Cooperação externa – Diu". cm-loures.pt (in Portuguese). Loures, Portugal: Câmara Municipal de Loures. 2014. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- ^ "Census: Population: by Religion: Christian: Daman and Diu".
- ^ "Schools in the territory of Diu during the Portuguese India".
- ^ "Diu".
 KSF
KSF









