Diver certification
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 24 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 24 min

A Diving certification or C-card is a document (usually a wallet sized plastic card) recognizing that an individual or organization authorized to do so, "certifies" that the bearer has completed a course of training as required by the agency issuing the card. This is assumed to represent a defined level of skill and knowledge in underwater diving. Divers carry a qualification record or certification card which may be required to prove their qualifications when booking a dive trip, hiring scuba equipment, having diving cylinders filled, or in the case of professional divers, seeking employment.
Although recreational certifications are issued by numerous different diver training agencies, the entry-level grade is not always equivalent. Different agencies will have different entry-level requirements as well as different higher-level grades, but all are claimed to allow a diver to develop their skills and knowledge in achievable steps.[1][2]
In contradistinction, a diver's logbook, or the electronic equivalent, is primarily evidence of range of diving experience.
Origins
[edit]The Diving Certification model originated at Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) in 1952 after two divers died whilst using university-owned equipment.[3] The then President of the University of California, Robert Gordon Sproul, restricted diving to those who had been trained through the program at SIO and thus "certification" was born. A year later Los Angeles county sent Bev Morgan, Al Tillman, and Ramsey Parks to SIO for diver training.[4] Upon their return, these three then developed the Los Angeles Underwater Instructors Program, the oldest such instructor training program in the U.S., and they used the SIO Diver Certification concept.[5]
Description
[edit]C-card is the generic term for any certification card issued by a diver certification organization. While sometimes taken to mean the minimum level training required to dive safely, it also applies to advanced and specialization certifications.
A typical card will list:
- Name and logo of the certifying organization
- Name and photograph of the person certified
- Certification reference or serial number
- Type of certification (basic, open water, advanced, nitrox, probationary, special skill, etc.)
- Date of certification
- Name of instructor
- Instructor's registration number
Dive shops, charter boats and resorts worldwide may demand to see a C-card before filling cylinders, renting equipment, or allowing a person to participate in a dive. This is mainly done to minimize the potential legal liability of the vendor, but may also sometimes prevent untrained people from exposing themselves to hazards of which they are not aware.
Diver certification equivalences
[edit]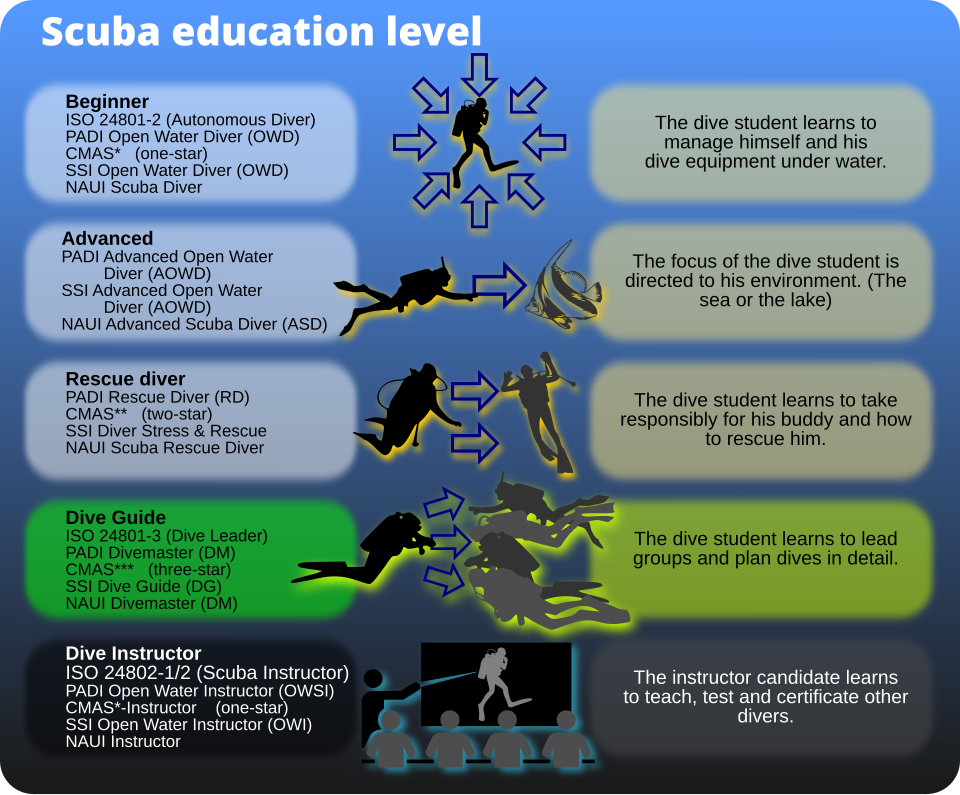
Recreational certification equivalences
[edit]European and ISO standards
[edit]There are two European standards with corresponding International standards specifying competence for recreational divers and recreational diving instructors.
The European Standard EN 14153/International Standard ISO 24801 contains minimum standards for recreational divers at three levels and defines the scope of diving for these certifications:
- EN 14153-1/ISO 24801-1 Recreational diving services - Safety related minimum competence requirements for the training of recreational scuba divers - Part 1: The level 1 "Supervised diver" has sufficient knowledge, skill and experience to dive, in open water, to a recommended maximum depth of 12 m, which do not require in-water decompression stops, under the direct supervision of a dive leader, in groups of up to four level 1 scuba divers per dive leader provided the dive leader is capable of establishing physical contact with all level 1 scuba divers at any point during the dive, only when appropriate support is available at the surface, and under conditions that are equal or better than the conditions where they were trained.[6]
- EN 14153-2/ ISO 24801-2 Recreational diving services - Safety related minimum competence requirements for the training of recreational scuba divers - Part 2: The level 2 "Autonomous diver" has sufficient knowledge, skill and experience to make dives, in open water, which do not require in-water decompression stops, to a recommended maximum depth of 20 m with other scuba divers of the same level, only when appropriate support is available at the surface, and under conditions that are equal or better than the conditions where they were trained without supervision of a scuba instructor, unless they have additional training or are accompanied by a dive leader.[7] and
- EN 14153-3/ ISO 24801-3 Recreational diving services - Safety related minimum competence requirements for the training of recreational scuba divers - Part 3: The level 3 "Dive leader" has sufficient knowledge, skill and experience to plan, organize and conduct their dives and lead other recreational scuba divers in open water. They are also competent to conduct any specialized recreational scuba diving activities for which they have received appropriate training, and to plan and execute emergency procedures appropriate for those diving environments and activities. If diving and environmental conditions are significantly different from those previously experienced, a level 3 "Dive Leader" requires an appropriate orientation with regard to local environmental conditions, and may require appropriate specialized training and experience to lead dives which have more demanding operational parameters.[8]
The European Standard EN 14413/International Standard ISO 24802 contains standards for recreational diving instructors:
- EN 14413-1/ ISO 24802-1 Recreational Diving Services - Safety related minimum requirements for the training of scuba instructors - Part 1: A level 1 scuba instructor is competent to teach and assess scuba students up to level 1 on their theoretical knowledge and skills in confined water. If supervised and authorized by a level 2 instructor, also to gain experience in teaching and assessing the theoretical knowledge of scuba diver levels 2 to 3, teach any level of scuba diver in confined water, and gain experience in teaching and assessing open water surface skills, and if directly observed and supervised by a level 2 instructor, to gain experience in teaching and evaluating any skills in confined and open water.
- EN 14413-2/ ISO 24802-2 Recreational Diving Services - Safety related minimum requirements for the training of scuba instructors - Part 2: A level 2 scuba instructor is competent to plan, organize and conduct dives and lead other recreational scuba divers of all levels in open water, including rescue activities, teach and assess students up to scuba diver level 1, 2 and 3, to supervise level 1 scuba instructors, and to plan, organize and conduct scuba diver training courses. With suitable additional training or experience the level 2 instructor is competent to plan, organize and conduct speciality training and diving operational activities.
The International Standard ISO 11107 Recreational diving services specifies the level of competence required of a scuba diver to be awarded an enriched air nitrox (EAN) diver certification by a training organization. These divers are competent to plan, conduct and log EAN open-water, single mixture, open-circuit no-decompression recreational dives, when accompanied by another scuba diver of at least level 2 "Autonomous Diver", and to procure EAN mixes, equipment and other services for recreational EAN diving without supervision.
CMAS standards
[edit]
The Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques (CMAS) (World Underwater Federation) oversees an international system of recreational snorkel and scuba diver training and recognition. CMAS publishes minimum training standards which provide an international equivalence system for diver certification issued by its member federations.[9]
WRSTC standards
[edit]The World Recreational Scuba Training Council (WRSTC) publishes a series of nine course standards for recreational diver training.[10] The US national council (RSTC) is the accredited standards developer for the "Diving Instructional Standards and Safety" (Z375) committee of the American National Standards Institute.[11]
Commercial certification equivalences
[edit]
The International Diving Schools Association publishes a list of commercial diver certification equivalences, based on the minimum requirements of the association for 4 levels of commercial diver certification:[12]
| Country | IDSA Level 1 Commercial scuba (30m) |
IDSA Level 2 Surface Supplied Inshore Air Diver (30m) |
IDSA Level 3 Surface Supplied Offshore Air Diver (50m) |
IDSA Level 4 Closed Bell Diver (100m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Part 1 | Part 3 | Part 4 | |
| Belgium | OOW-SYNTRA or OTS-CFPME |
|||
| Canada | Unrestricted SCUBA | Unrestricted SCUBA plus Restricted Surface Supplied Diver | Surface Supplied Mixed Gas Diver to 70m, or Unrestricted Surface Supplied Diver to 50m + Unrestricted SCUBA |
Bell diver |
| Denmark | National SCUBA Diver | Surface supplied diver to 50m | ||
| Finland | National SCUBA Diver | National Surface Supply Diver - 50m | ||
| France | Class 1 Mention A or B | Class 1 Mention A | Class 2 Mention A | Class 3 Mention A |
| The Netherlands | Certificate A | Certificate B | ||
| Italy (Sicily) | Sommozzatore/Inshore diver | Sommozzatore/Inshore diver | Sommozzatore Top up/Offshore air diver | Altofondalista/Offshore sat diver |
| New Zealand | Part 1 | Part 2 | ||
| Norway | NPD Surface Diver | NPD Bell diver | ||
| South Africa | Class 4 | Class 3 | Class 2 | Class 1 |
| Sweden | Diver Certificate A | Diver Certificate B | Diver Certificate C Wet Bell 60m | |
| UK | HSE Part 4 or HSE SCUBA |
HSE Part 3 + Task Training Module or HSE SCUBA + HSE Surface Supply + Tools Training Module |
HSE Part 1 or HSE SCUBA + HSE Surface Supply + Tools Training Module + Surface Supplied Top Up |
HSE Part 2 or HSE Closed Bell |
| USA | American National Standard for Divers - ANSI/ACDE012009 |
See also
[edit]- Diver training – Processes to develop the skills and knowledge to dive safely underwater
- CMAS* SCUBA Diver – Entry level recreational diving certification from CMAS
- Open Water Diver – Entry-level autonomous diver certification for recreational scuba diving
- Advanced Open Water Diver – Recreational scuba diving certification slightly above minimum entry level
- Rescue Diver – Recreational scuba certification emphasising emergency response and diver rescue
- Master Scuba Diver – Scuba diver certification
- Divemaster – Recreational dive leader certification and role
- Diving instructor – Person who trains and assesses underwater divers
- Master Instructor – Grade of recreational dive instructor with some experience
- Commercial diver registration in South Africa – Registration of commercial divers by the South African Department of Employment and Labour
- U.S. Navy Diving Manual – Training and operations handbook
References
[edit]- ^ "Open Water Diver". PADI. 2008. Archived from the original on 2018-10-01. Retrieved 2009-08-27.
- ^ "Diving Course Syllabus". BSAC. 2009. Retrieved 2009-08-27.
- ^ Manual for Diving Safety (PDF) (11th ed.). San Diego: Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California. 2005. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-20.
- ^ Hanauer, Eric; "Diving Pioneers: An Oral History of Diving in America" ISBN 0-922769-43-5
- ^ "Scripps Institution of Oceanography Diver Certification". SIO. 2011. Archived from the original on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-13.
- ^ "EN 14153-1 / ISO 24801-1". EUF Certification International. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ "EN 14153-2 / ISO 24801-2". EUF Certification International. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ "EN 14153-3 / ISO 24801-3". EUF Certification International. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ "(CMAS International Diver Training Certification System) General requirements". Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques. Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ^ "Dive Standards & Medical Statement". WRSTC. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ "ANSI Accredited Standards Developers listing" (PDF). American National Standards Institute. p. 150. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2014. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ Staff (October 2009). "Appendix 1". International Diver Training Certification: Diver Training Standards (PDF) (Revision 4 ed.). 47 Faubourg de la Madeleine 56140 Malestroit Brittany, France: International Diving Schools Association. p. 52. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2013-10-08.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)
 KSF
KSF