Enneagram (geometry)
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 7 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 7 min
| Enneagram | |
|---|---|
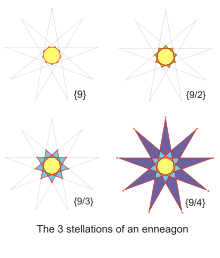 Enneagrams shown as sequential stellations | |
| Edges and vertices | 9 |
| Symmetry group | Dihedral (D9) |
| Internal angle (degrees) | 100° {9/2} 20° {9/4} |
| Star polygons |
|---|
|
|
In geometry, an enneagram (🟙 U+1F7D9) is a nine-pointed plane figure. It is sometimes called a nonagram, nonangle, or enneagon.[1]
The word 'enneagram' combines the numeral prefix ennea- with the Greek suffix -gram. The gram suffix derives from γραμμῆ (grammē) meaning a line.[2]
Regular enneagram
[edit]A regular enneagram is a 9-sided star polygon. It is constructed using the same points as the regular enneagon, but the points are connected in fixed steps. Two forms of regular enneagram exist:
- One form connects every second point and is represented by the Schläfli symbol {9/2}.
- The other form connects every fourth point and is represented by the Schläfli symbol {9/4}.
There is also a star figure, {9/3} or 3{3}, made from the regular enneagon points but connected as a compound of three equilateral triangles.[3][4] (If the triangles are alternately interlaced, this results in a Brunnian link.) This star figure is sometimes known as the star of Goliath, after {6/2} or 2{3}, the star of David.[5]
| Compound | Regular star | Regular compound |
Regular star |
|---|---|---|---|
 Complete graph K9 |
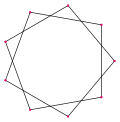 {9/2} |
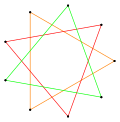 {9/3} or 3{3} |
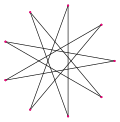 {9/4} |
Other enneagram figures
[edit] The final stellation of the icosahedron has 2-isogonal enneagram faces. It is a 9/4 wound star polyhedron, but the vertices are not equally spaced. |
 The Fourth Way teachings and the Enneagram of Personality use an irregular enneagram consisting of an equilateral triangle and an irregular hexagram based on 142857. |
 The Bahá'í nine-pointed star |
 A 9/3 enneagram |
The nine-pointed star or enneagram can also symbolize the nine gifts or fruits of the Holy Spirit.[6]
In popular culture
[edit]- The heavy metal band Slipknot previously used the {9/3} star figure enneagram[7] and currently uses the {9/4} polygon as a symbol. The prior figure can be seen on the cover of All Hope Is Gone.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Between a square rock and a hard pentagon: Fractional polygons". 28 September 2017.
- ^ γραμμή, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus.
- ^ Grünbaum, B. and G. C. Shephard; Tilings and patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman & Co., (1987), ISBN 0-7167-1193-1.
- ^ Grünbaum, B.; Polyhedra with Hollow Faces, Proc of NATO-ASI Conference on Polytopes ... etc. (Toronto 1993), ed T. Bisztriczky et al., Kluwer Academic (1994) pp. 43-70.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Nonagram". mathworld.wolfram.com.
- ^ Our Christian Symbols by Friedrich Rest (1954), ISBN 0-8298-0099-9, page 13.
- ^ "slipknot". eBay.
Bibliography
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 26. pp. 404: Regular star-polytopes Dimension 2)
External links
[edit] Media related to Enneagram at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Enneagram at Wikimedia Commons- Nonagram -- from Wolfram MathWorld
 KSF
KSF