Eritoran
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 4 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 4 min
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | E 5564 |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous injection |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
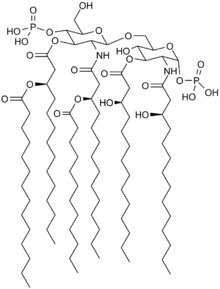
| Formula | C66H126N2O19P2 |
| Molar mass | 1313.677 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Eritoran is a synthetic lipid that inhibits the receptor TLR4. It was developed as a potential treatment for severe sepsis, an excessive inflammatory response to an infection. It failed a five year Phase III clinical trial, the results of which were published in 2013,[1][2] and as of 2014 was no longer being developed.[3]
It was being developed by the Japanese pharmaceutical company Eisai Co. and was administered intravenously as the sodium salt eritoran tetrasodium.[4]
TLR4 is part of the innate immune system and plays an important role in triggering defense against pathogens. Eritoran is similar in structure to the lipopolysaccharide lipid A - a part of bacteria that binds to TLR4 and activates TLR4, triggering a defense. Eritoran binds to TLR4 but blocks its activation.[1][4]
 |
 |
Too much signalling by TLR4 may be part of what causes cytokine storms and sepsis, but as of 2021 no drug that inhibits TLR4 has been shown to prevent or treat sepsis or cytokine storms in humans.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Chen F, Zou L, Williams B, Chao W (November 2021). "Targeting Toll-Like Receptors in Sepsis: From Bench to Clinical Trials". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 35 (15): 1324–1339. doi:10.1089/ars.2021.0005. PMC 8817700. PMID 33588628.
- ^ Opal SM, Laterre PF, Francois B, LaRosa SP, Angus DC, Mira JP, et al. (March 2013). "Effect of eritoran, an antagonist of MD2-TLR4, on mortality in patients with severe sepsis: the ACCESS randomized trial". JAMA. 309 (11): 1154–1162. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.2194. hdl:1854/LU-4222072. PMID 23512062.
- ^ Fink MP, Warren HS (October 2014). "Strategies to improve drug development for sepsis". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 13 (10): 741–758. doi:10.1038/nrd4368. PMID 25190187. S2CID 20904332.

- ^ a b c d Barochia A, Solomon S, Cui X, Natanson C, Eichacker PQ (April 2011). "Eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) treatment for sepsis: review of preclinical and clinical studies". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 7 (4): 479–494. doi:10.1517/17425255.2011.558190. PMC 3065179. PMID 21323610.
Further reading
[edit]- Tidswell M, Tillis W, Larosa SP, Lynn M, Wittek AE, Kao R, et al. (January 2010). "Phase 2 trial of eritoran tetrasodium (E5564), a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, in patients with severe sepsis". Critical Care Medicine. 38 (1): 72–83. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b07b78. PMID 19661804. S2CID 19160973.
- Shirey KA, Lai W, Scott AJ, Lipsky M, Mistry P, Pletneva LM, et al. (May 2013). "The TLR4 antagonist Eritoran protects mice from lethal influenza infection". Nature. 497 (7450): 498–502. Bibcode:2013Natur.497..498S. doi:10.1038/nature12118. PMC 3725830. PMID 23636320.
 KSF
KSF