Firefly luciferin
 From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min
From Wikipedia - Reading time: 5 min
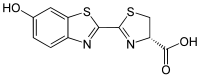
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4S)-2-(6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydrothiazole-4-carboxylic acid
| |
| Other names
D-(−)-Luciferin, beetle luciferin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.166 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H8N2O3S2 | |
| Molar mass | 280.32 g·mol−1 |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 330 nm (neutral and somewhat acidic aqueous solutions) [1] |
| Absorbance | ε330 = 18.2 mM−1 cm−1 [1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Firefly luciferin (also known as beetle luciferin) is the luciferin, or light-emitting compound, used for the firefly (Lampyridae), railroad worm (Phengodidae), starworm (Rhagophthalmidae), and click-beetle (Pyrophorini) bioluminescent systems. It is the substrate of luciferase (EC 1.13.12.7), which is responsible for the characteristic yellow light emission from many firefly species.
As with all other luciferins, oxygen is required to elicit light; however, it has also been found adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and magnesium are required for light emission.[2][3]
History
[edit]Much of the early work on the chemistry of the firefly luminescence was done in the lab of William D. McElroy at Johns Hopkins University. The luciferin was first isolated and purified in 1949, though it would be several years until a procedure was developed to crystallize the compound in high yield. This, along with the synthesis and structure elucidation, was accomplished by Dr. Emil H. White at the Johns Hopkins University, Department of Chemistry.[4] The procedure was an acid-base extraction, given the carboxylic acid group on the luciferin. The luciferin could be effectively extracted using ethyl acetate at low pH from powder of approximately 15,000 firefly lanterns.[5] The structure was later confirmed by combined use of infrared spectroscopy, UV–vis spectroscopy and synthetic methods to degrade the compound into identifiable fragments.[6]
Properties
[edit]Crystal luciferin was found to be fluorescent, absorbing ultraviolet light with a peak at 327 nm and emitting light with a peak at 530 nm. Visible emission occurs upon relaxation of the oxyluciferin from a singlet excited state down to its ground state.[7] Alkaline solutions caused a redshift of the absorption likely due to deprotonation of the hydroxyl group on the benzothiazole, but did not affect the fluorescence emission. It was found that the luciferyl adenylate (the AMP ester of luciferin) spontaneously emits light in solution.[8] Different species of fireflies all use the same luciferin, however the color of the light emitted can differ greatly. The light from Photuris pennsylvanica was measured to be 552 nm (green-yellow) while Pyrophorus plagiophthalamus was measured to emit light at 582 nm (orange) in the ventral organ. Such differences are likely due to pH changes or differences in primary structure of the luciferase.[9] Modification of the firefly luciferin substrate has led to "red-shifted" emissions (up to emission wavelength of 675 nm).[10]
Biological activity
[edit]The in vivo synthesis of firefly luciferin is not completely understood. Only the final step of the enzymatic pathway has been studied, which is the condensation reaction of D-cysteine with 2-cyano-6-hydroxybenzothiazole, and is the same reaction used to produce the compound synthetically.[11] This was confirmed by radiolabeling of atoms in the two compounds and by identification of a luciferin-regenerating enzyme.[12]
In firefly, oxidation of luciferins, which is catalyzed by luciferases, yields a peroxy compound 1,2-dioxetane. The dioxetane is unstable and decays spontaneously to carbon dioxide and excited ketones, which release excess energy by emitting light (bioluminescence).[13]
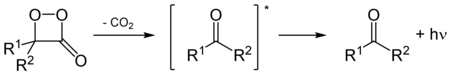
Firefly luciferin and modified substrates are fatty acid mimics and have been used to localize fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in vivo.[14] Firefly luciferin is a substrate of the ABCG2 transporter and has been used as part of a bioluminescence imaging high throughput assay to screen for inhibitors of the transporter.[15]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "D-luciferin product information" (PDF). Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ McElroy WD (1947). "The Energy Source for Bioluminescence in an Isolated System". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 33 (11): 342–345. Bibcode:1947PNAS...33..342M. doi:10.1073/pnas.33.11.342. PMC 1079070. PMID 16588763.
- ^ Green A, McElroy WD (1956). "Function of adenosine triphosphate in the activation of luciferin". Arch Biochem Biophys. 64 (2): 257–271. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(56)90268-5. PMID 13363432.
- ^ Strehler BL, McElroy WD (1949). "Purification of firefly luciferin". J Cell Physiol. 34 (3): 457–466. doi:10.1002/jcp.1030340310. PMID 15406363.
- ^ Bitler B, McElroy WD (1957). "The Preparation and Properties of Crystalline Firely Luciferin". Arch Biochem Biophys. 72 (2): 358–368. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(57)90212-6. PMID 13479120.
- ^ White EH, McCapra F, Field GF, McElroy WD (1961). "The Structure and Synthesis of Firefly Luciferin". J Am Chem Soc. 83 (10): 2402–2403. doi:10.1021/ja01471a051.
- ^ Marques SM, Joaquim (2009). "Firefly Bioluminescence: A Mechanistic Approach of Luciferase Catalyzed Reactions". IUBMB Life. 61 (1): 6–17. doi:10.1002/iub.134. PMID 18949818. S2CID 21583225.
- ^ Rhodes WC, McElroy WD (1958). "The synthesis and function of luciferyl-adenylate and oxyluciferyl-adenylate". J Biol Chem. 233 (6): 1528–1537. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)49367-2. PMID 13610868.
- ^ Seliger HH, Buck JB, Fastie WG, McElroy WD (1964). "The Spectral Distribution of Firefly Light". J Gen Physiol. 48 (1): 95–104. doi:10.1085/jgp.48.1.95. PMC 2195396. PMID 14212153.
- ^ Kiyama M, Saito R, Iwano S, Obata R, Niwa H, Maki SA (2016). "Multicolor Bioluminescence Obtained Using Firefly Luciferin". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (24): 2648–2655. doi:10.2174/1568026616666160413135055. PMID 27072707.
- ^ White EH, Worther H, Field GF, McElroy WD (1965). "Analogs of Firefly Luciferin". J. Org. Chem. 30 (7): 2344–2348. doi:10.1021/jo01018a054.
- ^ Gomi K, Kajiyama N (2001). "Oxyluciferin, a Luminescence Product of Firefly Luciferase, Is Enzymatically Regenerated into Luciferin". J Biol Chem. 276 (39): 36508–36513. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105528200. PMID 11457857.
- ^ Aldo Roda Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence: Past, Present and Future, p. 57, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2010, ISBN 1-84755-812-7
- ^ Mofford DM, Adams ST, Kumar Reddy GS, Randheer Reddy G, Miller SC (2015). "Luciferin Amides Enable in Vivo Bioluminescence Detection of Endogenous Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Activity". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 (27): 8684–8687. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b04357. PMC 4507478. PMID 26120870.
- ^ "Identification of Inhibitors of ABCG2 by a Bioluminescence Imaging-Based High-Throughput Assay". Cancer Res. 69.
External links
[edit]- Bioluminescence Page showing major luciferin types
 KSF
KSF